Piscataway, Maryland
| Piscataway, Maryland | |
|---|---|
| Unincorporated community | |
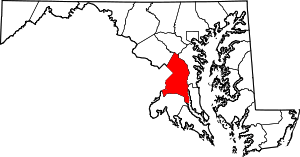
 Piscataway, Maryland  Piscataway, Maryland Location within the state of Maryland | |
| Coordinates: 38°42′2″N 76°58′20″W / 38.70056°N 76.97222°WCoordinates: 38°42′2″N 76°58′20″W / 38.70056°N 76.97222°W | |
| Country |
|
| State |
|
| County |
|
| Time zone | Eastern (EST) (UTC-5) |
| • Summer (DST) | EDT (UTC-4) |
| GNIS feature ID | 597903 |
Piscataway is an unincorporated community in Prince George's County, Maryland, United States. It is one of the oldest European-colonized communities in the state.[1] The Piscataway Creek provided sea transportation for export of tobacco. It is located near the prior Piscataway tribe village of Kittamaqundi.[2]
Piscataway was created in 1706 when the colonial Maryland Legislature authorized surveying and laying out the towns of Queen Anne Town, Nottingham, Mill Town, Piscataway, Aire (also known as Broad Creek) and Upper Marlboro (then known as Marlborough Town).[3][4][5]
In 1747, the legislature tried to improve the quality and the method of marketing tobacco, then the major crop of the area. It established a formal system of tobacco inspection and quality control. The town was home to one of seven state tobacco warehouses built in Prince George's County.[5] A "Committee of Correspondence" plotted local actions for the American Revolution in Piscataway. One famous resident was William Marbury, involved in a famous early Supreme Court case.[6][7][8]
During Prohibition in the 1920s, the area was known for the production and sale of moonshine. Some of the product was moved by boat to other areas along the Chesapeake Bay. The creek is now silted in and no longer navigable.
The St. Mary's Catholic Church, school, and cemetery are a prominent feature of the community. The complex includes the small 1904 church and a larger 1988 sanctuary. Its parish boundaries include portions of five separate postal towns/communities, giving it the largest territory of any parish in the Archdiocese of Washington.
A number of historic houses still survive in the middle of the little town, including a former hotel/tavern, although the last business (the John Wood store) closed in the 1970s. A large development called "The Preserve" is partially opened and is eventually planned to have 1,100 single-family homes. A short bypass road recently opened around the community. The central part of the historic village, centered on stretch of Floral Park Road, has been listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
The poem "The Sot-Weed Factor," by Ebenezer Cooke, mentions details of life in Piscataway during the early colonial period. The same subject was the subject of a novel by the same name by John Barth.[9]
See also
References
- ↑ U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Piscataway, Maryland
- ↑ Paul Joseph Travers (1990). The Patapsco: Baltimore's River of History. Maryland Historical Society Tidewater Publishers. p. 20.
- ↑ Baltz, Shirley Vlasak (1984). A Chronicle of Belair. Bowie, Maryland: Bowie Heritage Committee. pp. 4–7. LCCN 85165028.
- ↑ "African-American Sites Along the Patuxent River: Queen Anne Town". Maryland Department of Natural Resources. Retrieved 05/04/2007. Check date values in:
|access-date=(help) - 1 2 Virta, Alan (1984). Prince George's County: A Pictorial History. Norfolk, Virginia: The Donning Company. p. -40.
- ↑ "Marbury v. Madison". Retrieved 24 May 2011.
- ↑ "Judicial Review and the Supreme Court". Retrieved 24 May 2011.
- ↑ Barbara Frederick; Russel Stevenson & Emma K. Young (August 2010). "National Register of Historic Places Registration: Piscataway Village Historic District" (PDF). Maryland Historical Trust. Retrieved 2016-01-01.
- ↑
External links
- Piscataway Village Historic District, Prince George's County, Inventory No.: PG:84-23, including undated photo, at Maryland Historical Trust website
- Boundary Map of the Piscataway Village Historic District, Prince George's County, at Maryland Historical Trust
Further reading
- Along the Potomac Shore in Prince George's County (local history book)