RTI-150
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | 752958-88-6 |
| PubChem (CID) | 9972881 |
| ChemSpider | 8148473 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1812740 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H27NO2 |
| Molar mass | 313.434 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
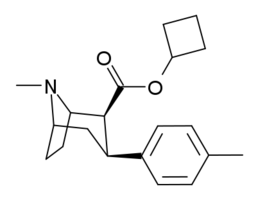
RTI(-4229)-150, ((−)-2β-Carbocyclobutoxy-3β-(4-methylphenyl)tropane) is a phenyltropane derivative which acts as a potent dopamine reuptake inhibitor and stimulant drug. It is around 5x more potent than cocaine, but is more selective for the dopamine transporter relative to the other monoamine transporters. RTI-150 has a fast onset of effects and short duration of action, and its abuse potential in animal studies is similar to that of cocaine itself; its main application in scientific research has been in studies investigating the influence of pharmacokinetics on the abuse potential of stimulant drugs, with the rapid entry of RTI-150 into the brain thought to be a key factor in producing its high propensity for development of dependence in animals.[1][2][3] RTI-150 is not explicitly illegal anywhere in the world, but its similar structure and pharmacological activity to cocaine makes it possible that it would be considered a controlled substance analogue in countries such as the USA, Canada, Australia and New Zealand which have controlled substance analogue legislation.
See also
References
- ↑ Kimmel HL, Carroll FI, Kuhar MJ. Locomotor stimulant effects of novel phenyltropanes in the mouse. Drug and Alcohol Dependence. 2001 Dec 1;65(1):25-36. doi:10.1016/S0376-8716(01)00144-2 PMID 11714587
- ↑ Kimmel HL, O'Connor JA, Carroll FI, Howell LL. Faster onset and dopamine transporter selectivity predict stimulant and reinforcing effects of cocaine analogs in squirrel monkeys. Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behaviour. 2007 Jan;86(1):45-54. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2006.12.006 PMID 17258302
- ↑ Kimmel HL, Negus SS, Wilcox KM, Ewing SB, Stehouwer J, Goodman MM, Votaw JR, Mello NK, Carroll FI, Howell LL. Relationship between rate of drug uptake in brain and behavioral pharmacology of monoamine transporter inhibitors in rhesus monkeys. Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behaviour. 2008 Sep;90(3):453-62. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2008.03.032 PMID 18468667