Sunny Isles Beach, Florida
| City of Sunny Isles Beach Sunny Isles Beach | ||
|---|---|---|
| City | ||
|
Sunny Isles Beach skyline | ||
| ||
| Motto: The City of Sun and Sea | ||
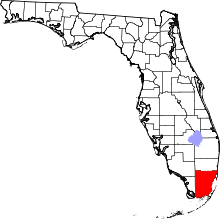
 Location in Miami-Dade County and the state of Florida | ||
 U.S. Census Bureau map showing city limits | ||
| Coordinates: 25°56′30″N 80°07′30″W / 25.94167°N 80.12500°WCoordinates: 25°56′30″N 80°07′30″W / 25.94167°N 80.12500°W | ||
| Country |
| |
| State |
| |
| County |
| |
| Incorporation | June 16, 1997 | |
| Government | ||
| • Type | Council-Manager | |
| • Mayor | George “Bud” Scholl | |
| • Vice Mayor | Jeanette Gatto | |
| • Councilmembers | Isaac Aelion, Jennifer Levin, and Dana Goldman | |
| • City Manager | Christopher J. Russo | |
| • City Clerk | Jane A. Hines | |
| Area | ||
| • City | 1.4 sq mi (3.6 km2) | |
| • Land | 1.0 sq mi (2.6 km2) | |
| • Water | 0.4 sq mi (1.0 km2) 28.37% | |
| Population (2010) | ||
| • City | 20,832 | |
| • Density | 20,518.9/sq mi (7,922.4/km2) | |
| • Metro | 5,564,635 | |
| Time zone | Eastern (EST) (UTC-5) | |
| • Summer (DST) | EDT (UTC-4) | |
| ZIP code | 33160 | |
| Area code(s) | 305, 786 | |
| FIPS code | 12-69550[1] | |
| Website | http://www.sibfl.net | |
Sunny Isles Beach (SIB, officially City of Sunny Isles Beach) is a city located on a barrier island in northeast Miami-Dade County, Florida, United States. The City is bounded by the Atlantic Ocean on the east and the Intracoastal Waterway on the west. As of 2010, the population is 20,832.
Sunny Isles Beach is an area of cultural diversity with stores lining Collins Avenue, the main thoroughfare through the city.
It is a growing[2][3] resort area and developers such as Michael Dezer have invested heavily in construction of high-rise hotels and condominiums while licensing the Donald Trump name for some of the buildings for promotional purposes.[3] Sunny Isles Beach has a central location, minutes from Bal Harbour to the south, and Aventura to the north and west.
Sunny Isles Beach was also the 2008 site of MTV's annual "Spring Break" celebration, with headquarters at the local Newport Beachside Resort.[4]
Media
Sunny Isles Beach has its own newspaper, "Sunny Isles Community News, which is published bi-weekly and is part of Miami Community Newspapers. Sunny Isles Beach is also served by the Miami-Ft.Lauderdale market for local radio and television.
History
In 1920, Harvey Baker Graves, a private investor, purchased a 2.26-square-mile (5.9 km2) tract of land for development as a tourist resort. He named it Sunny Isles -- The Venice of America.[5]
When the Haulover bridge was completed in 1925, the area became accessible from Miami Beach, attracting developers who widened streams, dug canals and inlets and created islands and peninsulas for building waterfront properties on Biscayne Bay.[5]
In the 1920s, Carl G. Fisher built an all-wooden racetrack with stands for 12,000 spectators, known as the Fulford-Miami Speedway. This event, held on February 22, 1926, dubbed "Carl G. Fisher Cup Race," was a forerunner to the auto races at Sebring and Daytona. In September 1926, after just one race, the track was destroyed by the 1926 Miami Hurricane.[6] This event was held in Fulford-By-the-Sea which is today's North Miami Beach. Sunny Isles Beach was known as North Miami Beach until 1931, then known as Sunny Isles until 1997.[7]
In 1936, Milwaukee malt magnate Kurtis Froedtert bought Sunny Isles.[8] The Sunny Isles Pier was built and soon became a popular destination. Sunny Isles developed slowly until the 1950s when the first single-family homes were built in the Golden Shores area. During the 1950s and 1960s more than 30 motels sprang up along Collins Avenue including the Ocean Palm, the first two-story motel in the U.S. Designed by Norman Giller in 1948 it was developed and owned by the Gingold family for the next 45 years and provided the springboard for Sunny Isles economic development. Tourists came from all over to vacation in themed motels of exotic design along "Motel Row".[5] One motel, The Fountainhead, was so named by its owner, Norman Giller, after the novel by Ayn Rand.[9] As of 2013, the Ocean Palm Motel is closed.
In 1982 the half-mile-long Sunny Isles Pier was designated a historic site. In the early-mid 80s, it went through restoration and re-opened to the public in 1986.[10] The pier was severely damaged in October 2005 by Hurricane Wilma. After 8 years, it was remodeled and reopened as Newport Fishing Pier on June 15, 2013.[11]
In 1997, the citizens of the area voted to incorporate as a municipality. Sunny Isles was renamed Sunny Isles Beach.[12] Sunny Isles Beach began major redevelopment during the real estate boom of the early 2000s with mostly luxury high-rise condominiums and some hotels under construction along the beach side of Collins Avenue (A1A) replacing most of the historic one- and two-story motels along Motel Row. In 2011, construction began on two more high-rises, Regalia, located on the northern border of the city along A1A, and The Mansions at Acqualina,[13] located adjacent to the Acqualina Resort & Spa on the Beach.
Geography

Sunny Isles Beach is located at 25°56′30″N 80°7′30″W / 25.94167°N 80.12500°W (25.941270, -80.125111).[14] According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 3.7 km2 (1.4 sq mi) with 2.6 km2 (1.0 sq mi) of it as land and 1 km2 (0.4 sq mi) of it (28.37%) as water.
Surrounding areas
- Golden Beach
- Aventura
 Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean - Aventura, North Miami Beach, North Miami
 Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean - North Miami
 Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean - Unincorporated Miami-Dade County (Haulover Park)
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 2000 | 15,315 | — | |
| 2010 | 20,832 | 36.0% | |
| Est. 2015 | 22,123 | [15] | 6.2% |
| Sunny Isles Beach Demographics | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 Census | Sunny Isles Beach | Miami-Dade County | Florida |
| Total population | 20,832 | 2,496,435 | 18,801,310 |
| Population, percent change, 2000 to 2010 | +36.0% | +10.8% | +17.6% |
| Population density | 20,518.9/sq mi | 1,315.5/sq mi | 350.6/sq mi |
| White or Caucasian (including White Hispanic) | 90.6% | 73.8% | 75.0% |
| (Non-Hispanic White or Caucasian) | 50.2% | 15.4% | 57.9% |
| Black or African-American | 3.2% | 18.9% | 16.0% |
| Hispanic or Latino (of any race) | 44.4% | 65.0% | 22.5% |
| Asian | 1.4% | 1.5% | 2.4% |
| Native American or Native Alaskan | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.4% |
| Pacific Islander or Native Hawaiian | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.1% |
| Two or more races (Multiracial) | 2.2% | 2.4% | 2.5% |
| Some Other Race | 2.4% | 3.2% | 3.6% |
As of 2010, there were 18,984 households out of which 46.1% were vacant. In 2000, 12.6% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 37.8% were married couples living together, 8.0% had a female householder with no husband present, and 51.1% were non-families. 43.9% of all households were made up of individuals and 23.5% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 1.87 and the average family size was 2.55.
In 2000, the city's population was spread out with 11.3% under the age of 18, 5.4% from 18 to 24, 26.9% from 25 to 44, 24.3% from 45 to 64, and 32.2% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 50 years. For every 100 females there were 86.3 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 83.6 males.
In 2000, the median income for a household in the city was $31,627, and the median income for a family was $40,309. Males had a median income of $36,893 versus $28,207 for females. The per capita income for the city was $27,576. About 11.2% of families and 14.7% of the population were below the poverty line, including 18.9% of those under age 18 and 12.2% of those age 65 or over.
As of 2000, Spanish was the mother tongue for 40.08%, while English was spoken by 36.86% of all residents. Living up to its nickname of "Little Moscow," 7.37% of the population had Russian as their first language. Other languages included French (4.08%), Yiddish (2.63%), Hebrew (2.42%), Portuguese (2.01%), Polish (1.38%), Hungarian (0.93%), Italian (0.69%), Arabic (0.66%), German (0.55%), and French Creole (0.35%).[17]
As of 2000, Sunny Isles Beach had the 21st highest percentage of Brazilian residents in the US, with 1.50% of the US populace (tied with several other places in the US, including Key Biscayne.)[18] It had the fifteenth highest percentage of Colombian residents in the US, at 6.07% of the city's population,[19] and the forty-fifth highest percentage of Cuban residents in the US, at 9.75% of the city's population.[20] It also had the seventeenth most Israelis in the US, at 1.70% (tied with Ojus,)[21] while it had the twenty-ninth highest percentage of Peruvians, at 1.77% of all residents.[22] Sunny Isles Beach's Romanian community had the sixteenth highest percentage of residents, which was at 1.50% (tying with several other US places, such as Dover, Florida.)[23] It's also home to the sixth highest percentage of Venezuelan residents in the US, at 1.96% of the population.[24]
Also, as of 2010, the six main ancestries of the population (excluding Hispanic ancestry) were 9.4% Russian, 5.8% Italian, 5.0% Polish, 4.9% American, 2.9% Irish, and 2.7% German.[25]
Education
Sunny Isles Beach is within the Miami-Dade County Public Schools system. Some of the schools that serve Sunny Isles Beach are located in unincorporated Dade County.
Elementary schools
Residents are zoned to an elementary school as follows:
- Ojus Elementary School for residents north of 172nd Street and south of 183rd Street
- Highland Oaks Elementary School for residents north of 183rd Street
- Norman S. Edelcup/Sunny Isles Beach K-8 for Sunny Isles Beach residents
K-8 center
The Norman S. Edelcup/Sunny Isles Beach K-8 is currently educating students from Kindergarten through 8th Grade from all of Sunny Isles, Eastern Shores, and Golden Beach. The school opened in 2008, reducing class sizes in Ruth K. Broad Bay Harbor Elementary, Ojus Elementary, and Highland Oaks. The school has or is currently participating in: VMath Live, Accelerated Reader, Mock Elections, Book Drives, Toy Drives, etc. The school has state of the art technology that includes Smart Boards and surround sound microphones for both teachers and students. The school has Intracostal and Ocean Views from almost every classroom in the 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th floor.
Middle schools and High schools
Residents are zoned to Highland Oaks Middle School and Alonzo and Tracy Mourning Senior High Biscayne Bay Campus. Dr. Michael M. Krop Senior High School also serves the area.[26] Prior to the opening of Mourning in 2009 Krop served Sunny Isles Beach.[27]
International relations
Twin towns – Sister cities
Sunny Isles Beach, Florida is twinned with:
References
- ↑ "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 2013-09-11. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ↑ "Dezer Properties Takes Relateds". Miami Herald. 26 February 2010.
- 1 2 "Sunny Isles- Boom or Bust: Miami". Bobmiami.com. Retrieved 2013-07-16.
- ↑ "Spring Break 2008". MTV. Retrieved 2013-07-17.
- 1 2 3 http://www.sibfl.net/wp-content/uploads/2013/05/Adopted_Budget_10-11.pdf
- ↑ "Our History - City of North Miami Beach, Florida". Citynmb.com. Retrieved 2013-07-20.
- ↑ "Our History - City of North Miami Beach, Florida". Citynmb.com. Retrieved 2013-07-20.
- ↑ "Buys Sunny Isles Development" Wall Street Journal Dec. 14, 1936
- ↑ Judy Cantor (1995-08-03). "Kitsch Highway - Page 1 - Arts - Miami". Miami New Times. Retrieved 2013-07-20.
- ↑ Nevins, Buddy (20 July 1986). "Restored Sunny Isles Pier Opens". Sun Sentinel. Retrieved 2013-07-16.
- ↑ Bock, Daniel (2013-06-21). "SIB celebrates reopening of Newport Fishing Pier - Aventura / Sunny Isles". MiamiHerald.com. Retrieved 2013-07-16.
- ↑ "Voters To Pick City's Name". Sun Sentinel. 3 September 1998. Retrieved 2013-07-16.
- ↑ "The Mansions at Acqualina Acqualina". Acqualinamiami.com. Retrieved 16 July 2013.
- ↑ "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. 2011-02-12. Retrieved 2011-04-23.
- ↑ "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Incorporated Places: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2015". Retrieved July 2, 2016.
- ↑ "Census of Population and Housing". Census.gov. Archived from the original on May 11, 2015. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
- ↑ "MLA's Data Center Results of Sunny Isles Beach, FL". Modern Language Association. Retrieved 2007-10-27.
- ↑ "Ancestry Map of Brazilian Communities". Epodunk.com. Retrieved 2007-10-27.
- ↑ "Ancestry Map of Colombian Communities". Epodunk.com. Retrieved 2007-10-27.
- ↑ "Ancestry Map of Cuban Communities". Epodunk.com. Retrieved 2007-10-27.
- ↑ "Ancestry Map of Israeli Communities". Epodunk.com. Retrieved 2007-10-27.
- ↑ "Ancestry Map of Peruvian Communities". Epodunk.com. Retrieved 2007-10-27.
- ↑ "Ancestry Map of Romanian Communities". Epodunk.com. Retrieved 2007-10-27.
- ↑ "Ancestry Map of Venezuelan Communities". Epodunk.com. Retrieved 2007-10-27.
- ↑ "Sunny Isles Beach, FL Detailed Map". city-data.com. Retrieved 2015-01-11.
- ↑ "Educational Facilities | City of Sunny Isles Beach". Sibfl.net. Retrieved 2013-07-17.
- ↑ "SS_QQQ1_1-24-09.pdf." Alonzo and Tracy Mourning Senior High Biscayne Bay Campus. Retrieved on May 6, 2012.
- ↑ "Netanya - Twin Cities". Netanya Municipality. Archived from the original on 2013-02-01. Retrieved 2013-08-01.
- ↑ "Taormina, Italy".
- ↑ "Hengchun, Taiwan".
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sunny Isles Beach, Florida. |
- City of Sunny Isles Beach official website