KCNIP1
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
Kv channel-interacting protein 1 also known as KChIP1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNIP1 gene.[3][4]
Function
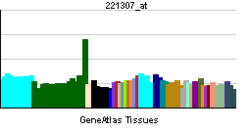
This gene encodes a member of the family of voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channel-interacting proteins (KCNIPs, also frequently called "KChIP"), which belong to the recoverin branch of the EF-hand superfamily.[5] Members of the KCNIP family are small calcium binding proteins. They all have EF-hand-like domains, and differ from each other in the N-terminus. They are integral subunit components of native Kv4 channel complexes. They may regulate A-type currents, and hence neuronal excitability, in response to changes in intracellular calcium. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variant encoding different isoforms.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ An WF, Bowlby MR, Betty M, Cao J, Ling HP, Mendoza G, Hinson JW, Mattsson KI, Strassle BW, Trimmer JS, Rhodes KJ (Feb 2000). "Modulation of A-type potassium channels by a family of calcium sensors". Nature. 403 (6769): 553–556. doi:10.1038/35000592. PMID 10676964.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: KCNIP1 Kv channel interacting protein 1".
- ↑ Burgoyne RD (2007). "Neuronal calcium sensor proteins: generating diversity in neuronal Ca2+ signalling". Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 8 (3): 182–193. doi:10.1038/nrn2093. PMC 1887812
 . PMID 17311005.
. PMID 17311005.
Further reading
- Bähring R, Dannenberg J, Peters HC, et al. (2001). "Conserved Kv4 N-terminal domain critical for effects of Kv channel-interacting protein 2.2 on channel expression and gating". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (26): 23888–23894. doi:10.1074/jbc.M101320200. PMID 11287421.
- Nakamura TY, Nandi S, Pountney DJ, et al. (2001). "Different effects of the Ca(2+)-binding protein, KChIP1, on two Kv4 subfamily members, Kv4.1 and Kv4.2". FEBS Lett. 499 (3): 205–209. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(01)02560-1. PMID 11423117.
- Kutsenko AS, Gizatullin RZ, Al-Amin AN, et al. (2002). "NotI flanking sequences: a tool for gene discovery and verification of the human genome". Nucleic Acids Res. 30 (14): 3163–3170. doi:10.1093/nar/gkf428. PMC 135748
 . PMID 12136098.
. PMID 12136098. - Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–16903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241
 . PMID 12477932.
. PMID 12477932. - Shibata R, Misonou H, Campomanes CR, et al. (2003). "A fundamental role for KChIPs in determining the molecular properties and trafficking of Kv4.2 potassium channels". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (38): 36445–36454. doi:10.1074/jbc.M306142200. PMID 12829703.
- Van Hoorick D, Raes A, Keysers W, et al. (2004). "Differential modulation of Kv4 kinetics by KCHIP1 splice variants". Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 24 (2): 357–366. doi:10.1016/S1044-7431(03)00174-X. PMID 14572458.
- Scannevin RH, Wang K, Jow F, et al. (2004). "Two N-terminal domains of Kv4 K(+) channels regulate binding to and modulation by KChIP1". Neuron. 41 (4): 587–598. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(04)00049-2. PMID 14980207.
- Lin YL, Lin SR, Wu TT, Chang LS (2004). "Evidence showing an intermolecular interaction between KChIP proteins and Taiwan cobra cardiotoxins". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 319 (3): 720–724. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.05.064. PMID 15184042.
- Lin YL, Chen CY, Cheng CP, Chang LS (2004). "Protein-protein interactions of KChIP proteins and Kv4.2". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 321 (3): 606–610. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.07.006. PMID 15358149.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–2127. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928
 . PMID 15489334.
. PMID 15489334. - Pruunsild P, Timmusk T (2005). "Structure, alternative splicing, and expression of the human and mouse KCNIP gene family". Genomics. 86 (5): 581–593. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2005.07.001. PMID 16112838.
- Pioletti M, Findeisen F, Hura GL, Minor DL (2007). "Three-dimensional structure of the KChIP1-Kv4.3 T1 complex reveals a cross-shaped octamer". Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 13 (11): 987–995. doi:10.1038/nsmb1164. PMC 3018330
 . PMID 17057713.
. PMID 17057713. - Hasdemir B, Fitzgerald DJ, Prior IA, Tepikin AV, Burgoyne RD (2005). "Traffic of Kv4 K+ channels mediated by KChIP1 is via a novel post-ER vesicular pathway". J. Cell Biol. 171 (3): 459–469. doi:10.1083/jcb.200506005. PMC 2171252
 . PMID 16260497.
. PMID 16260497. - Venn N, Haynes LP, Burgoyne RD (2008). "Specific effects of KChIP3/calsenilin/DREAM but not KChIPs1, 2 and 4 on calcium signalling and regulated secretion in PC12 cells". Biochem. J. 413 (1): 71–80. doi:10.1042/BJ20080441. PMC 2474559
 . PMID 18393943.
. PMID 18393943.
External links
- KCNIP1 protein, human at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.