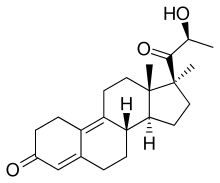
Trimegestone
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | G03FA16 (WHO) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms | RU-27987 |
| CAS Number | 74513-62-5 |
| PubChem (CID) | 68926 |
| ChemSpider | 62152 |
| KEGG | D06235 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H30O3 |
| Molar mass | 342.472 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
Trimegestone (INN) (brand name Ondeva), also known as 21-hydroxypromegestone, as well as 17β-((S)-2-hydroxypropanoyl)-17α-methylestra-4,9-dien-3-one, is a steroidal progestin of the 19-norprogesterone group related to promegestone which was introduced in France in 2001 and is used as a hormonal contraceptive and in hormonal replacement therapy for postmenopausal symptoms.[1][2][3][4] It is not available in the United States.[5]
Trimegestone has very high affinity for the progesterone receptor, only weak affinity for the mineralocorticoid receptor, and little or no affinity for other steroid hormone receptors.[2][3][5] In accordance, it is described as a very potent and pure progestogen,[2] in fact the most potent progestin of the 19-norprogesterone group (clinically effective in endometriosis at only 0.1 mg/day),[2][3][6] and possesses weak antimineralocorticoid activity and no androgenic, antiandrogenic, estrogenic, or glucocorticoid activity.[6][7] Due to its unique structure, unlike progesterone and some other progestins, trimegestone does not metabolize into neuroactive steroids, and hence does not influence GABAA receptor signaling.[7]
See also
References
- ↑ C.R. Ganellin; David J. Triggle (21 November 1996). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. CRC Press. pp. 2063–. ISBN 978-0-412-46630-4.
- 1 2 3 4 Eckhard Ottow; Hilmar Weinmann (8 September 2008). Nuclear Receptors as Drug Targets. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 208–. ISBN 978-3-527-62330-3.
- 1 2 3 Winnifred Cutler (30 March 2009). Hormones and Your Health: The Smart Woman's Guide to Hormonal and Alternative Therapies for Menopause. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 43–. ISBN 978-0-470-52553-1.
- ↑ Annual Reports in Medicinal Chemistry. Academic Press. 31 December 2012. pp. 273, 647. ISBN 978-0-12-397214-9.
- 1 2 Thomas L. Lemke; David A. Williams (24 January 2012). Foye's Principles of Medicinal Chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 1403–. ISBN 978-1-60913-345-0.
- 1 2 Kuhl, H (2009). "Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens: influence of different routes of administration" (PDF). Climacteric. 8 (sup1): 3–63. doi:10.1080/13697130500148875. ISSN 1369-7137.
- 1 2 Winneker RC, Bitran D, Zhang Z (2003). "The preclinical biology of a new potent and selective progestin: trimegestone". Steroids. 68 (10-13): 915–20. PMID 14667983.