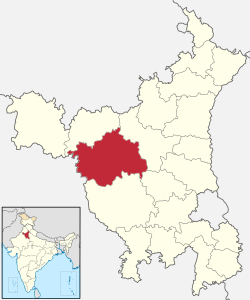
Hisar (city)
| Hisar हिसार ਹਿਸਾਰ | |
|---|---|
| City | |
|
From top going clockwise: District Administrative Complex, St. Thomas Church, Fort of Firoz Shah, Sheela Mata Temple and observatory at OP Jindal Gyan Kendra. | |
| Nickname(s): The city of Steel | |
 Hisar  Hisar | |
| Coordinates: 29°09′N 75°42′E / 29.150°N 75.700°ECoordinates: 29°09′N 75°42′E / 29.150°N 75.700°E | |
| Country | India |
| State | Haryana |
| District | Hisar[1] |
| Division | Hisar |
| Incorporated | 1832 |
| Government | |
| • Type | Municipal Corporation |
| • Body | Municipal Corporation of Hisar |
| • Mayor | Shakuntla Rajliwala |
| • Member of Parliament | Dushyant Chautala |
| Elevation | 215 m (705 ft) |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 301,249 |
| • Rank | 141[2] |
| • Density | 438/km2 (1,130/sq mi) |
| Languages | |
| • Official | Hindi, Punjabi |
| Time zone | IST (UTC+5:30) |
| PIN | 125 xxx |
| UNLOCODE | IN HSS |
| Telephone code | 91-1662 xxx xxx |
| Vehicle registration | HR-20, HR-39 |
| Nearest city | New Delhi |
| Sex ratio | 844[2] ♂/♀ |
| Literacy | 81.04[2]% |
| Lok Sabha constituency | Hisar |
| Vidhan Sabha constituency | Hisar |
| Planning agency | HUDA |
| Climate | Cw (Köppen) |
| Precipitation | 490.6 millimetres (19.31 in) |
| Avg. summer temperature | 32.5 °C (90.5 °F) |
| Avg. winter temperature | 17.6 °C (63.7 °F) |
| Website |
www |
Hisar ![]() pronunciation or Hissar, is the administrative headquarters of Hisar district of Hisar division in the state of Haryana in northwestern India. It is located 164 km (102 mi) to the west of New Delhi, India's capital, and has been identified as a counter-magnet city for the National Capital Region to develop as an alternative center of growth to Delhi.
pronunciation or Hissar, is the administrative headquarters of Hisar district of Hisar division in the state of Haryana in northwestern India. It is located 164 km (102 mi) to the west of New Delhi, India's capital, and has been identified as a counter-magnet city for the National Capital Region to develop as an alternative center of growth to Delhi.
The city was ruled by several major powers, including the Mauryans in the third century BC, the Tughlaqs in the 14th century, the Mughals in the 16th century, and the British in the 19th century. After India achieved independence, it was unified with the state of Punjab. When the Punjab was divided in 1966, Hisar became part of Haryana.
The current name was given in 1354 AD, as Hisar-e-Firoza by Firuz Shah Tughlaq, the Sultan of Delhi from 1351 to 1388. The Ghaggar and Drishadvati Rivers once flowed through the city, but they have now changed their course. Hisar has a continental climate, with very hot summers and relatively cool winters. The most commonly spoken languages are Hindi, Haryanvi, and Bagri.
History
Early history
Archeological excavations at nearby locations of Rakhigarhi, Siswal, and Lohari Ragho suggest the presence of human habitation from pre-Harappan period. Later, Aryan people settled around Drsadvati River. The Jain literature Uttaradhayana Sutra mentions a town Isukara in the Kuru country which is believed to be the earlier name of Hisar.[3] The kingdom of Hisar, with its capital at Agroha, possibly assisted Chandragupta Maurya in his war against the Greeks.[4] The kingdom was then included in the Mauryan Empire, as evidenced by the discovery of Ashokan pillars in the vicinity of the city. The city later came under the Kushan Empire and the Gupta Empire.[3] In the 12th century, the Chauhan king Prithviraj Chauhan made Hansi, located in the present day Hisar district, his capital and built a fort.[5] It remained a strategic place for Chauhan Empire until Prithviraj was defeated in the Second Battle of Tarain by the invading Ghurid ruler Muhammad Ghori.[3]
Tughlaq era

Hisar was founded in 1354 AD, as 'Hisar-e-Firoza' by Firoz Shah Tughlaq, who reigned over the Sultanate of Delhi from 1351 to 1388.[6][7] He built a walled fort with four gates, the Delhi Gate and Mori Gate to the east, the Nagori Gate to the south, and the Talaqi Gate to the west.[8] The construction of the fort started in 1354 AD and was completed in 1356 AD.[8] In the middle of the fort stood the Firoz Shah Palace. Apart from its several underground apartments, the complex had different buildings such as Baradari, Lat ki Masjid, Diwan-e-Aam, and Shahi Darwaza.[4] Near the palace was the Gujri Mahal built by the emperor for his wife Gujri.[8] The city was named as Hisar-e-Firoza, which means Fort of Firoz in Persian. Timur invaded the city in 1398 AD and his soldiers set fire to the fort.[4]
The city later come under the rule of Sayyid dynasty and Lodi dynasty before Babur defeated Ibrahim Lodi in the first battle of Panipat.[4]
Mughal era
When Babur invaded India in the 1524–1526, Hisar was part of Ibrahim Lodi's empire.[4] In the battle of Panipat in 1526, Babur sent prince Humayun, who succeeded in defeating the army of Ibrahim Lodi. Babur handed over the city of Hisar to Humayun as a reward for his success on his first military expedition.[4] In 1540, Hisar came under the control of Sher Shah Suri when he defeated Humayun but Humayun took it back in 1555 and assigned it to Akbar.[4] During Akbar's reign (1556–1605) Hisar became once more a place of considerable importance.[4] The city remained under the rule of Mughals until 1760.[4]
British era
Hisar was occupied by George Thomas, an Irish adventurer, in 1798. The arrangement continued until 1801, when Thomas was driven out by the Sikh-Maratha-French confederacy.[3] The region came under the rule of British East India Company in 1803 and remained a part until the Indian Rebellion of 1857 when Muhammad Azim and Rao Tula Ram conquered it away for a short period. The company sent forces under General Van Cortlandt, who defeated Azim and Tula Ram on 16 November 1857.[3] Between 1803 and 1879, British constructed a 4,000-km-long Great Hedge of India, for levying the customs duty on salt and sugar, that ran through Hisar and Hansi. Hisar became a municipality in 1867.[9]
The city remained as a major center of the Indian independence movement from the rebellion of 1857 until the independence, as many national leaders visited the city during the movement such as Lala Lajpat Rai in 1886,[10] Subhas Chandra Bose in 1938,[4] and Jawaharlal Nehru in 1946.[11]
After independence
After independence, the city became a part of Punjab and later Haryana in 1966.
Geography
Hisar is located at 29°05′N 75°26′E / 29.09°N 75.43°E in western Haryana. It has an average elevation of 215 m (705 ft) above mean sea level. The region is part of the alluvial Ghaggar-Yamuna plain and its southern and western portions mark a gradual transition to the desert.[4] Ghaggar[12] and Drishadvati[13] Rivers once flowed through the city. According to tectonic map, the district lies on Delhi-Lahore Ridge which is bounded by thrusts and no earthquake of any significance has originated in the zone in the past.[4] Only one instance has been recorded of a famine occurring in the city in 1837–38.[14]
Climate
Hisar has a continental climate, with very hot summers and relatively cool winters.[15] The main characteristics of climate in Hisar are dryness, extremes of temperature, and scanty rainfall.[16] The maximum daytime temperature during the summer varies between 40 and 46 °C (104 and 115 °F). During winter, its ranges between 1.5and 4 °C.[17] Maximum temperature recorded is 48.3 °C (118.9 °F) in May 1944, whereas the minimum temperature recorded is −3.9 °C in January 1929. Annual average maximum and minimum temperature is 31.5 °C (88.7 °F) and 16.2 °C (61.2 °F), respectively. Relative humidity varies from 5 to 100%.[16]
Hisar is located on the outer margins of the south-west monsoon region. The average annual rainfall is around 450 mm (18 in), most of which occurs during July and August. The annual highest rainfall of 793.6 mm (31.24 in) was recorded in 1976 and the lowest of 145.2 mm (5.72 in)in 2000. Dew is observed in December and January. Hot winds, locally known as loo, are strong and frequent from May to July.[16] Occasionally, dust-storms are experienced during summer and hail-storms during February to April. Fog prevails generally in December and January. Thunderstorms also occur during postmonsoon season and summer.[16]
| Climate data for Hisar (1951–1980) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 21.4 (70.5) |
24.7 (76.5) |
30.5 (86.9) |
36.8 (98.2) |
40.7 (105.3) |
41.0 (105.8) |
37.0 (98.6) |
35.1 (95.2) |
35.4 (95.7) |
34.3 (93.7) |
29.1 (84.4) |
23.5 (74.3) |
32.5 (90.5) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 5.5 (41.9) |
8.3 (46.9) |
13.7 (56.7) |
19.4 (66.9) |
24.2 (75.6) |
27.7 (81.9) |
27.0 (80.6) |
26.0 (78.8) |
23.7 (74.7) |
17.8 (64) |
11.0 (51.8) |
6.5 (43.7) |
17.6 (63.7) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 013.4 (0.528) |
015.5 (0.61) |
012.1 (0.476) |
005.6 (0.22) |
020.3 (0.799) |
042.9 (1.689) |
140.7 (5.539) |
146.9 (5.783) |
065.0 (2.559) |
014.8 (0.583) |
006.1 (0.24) |
007.3 (0.287) |
490.6 (19.313) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 0.6 | 1.3 | 3.0 | 6.9 | 7.5 | 3.5 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 28.5 |
| Source: India Meteorological Department[18] | |||||||||||||
Civic administration
| Hisar City officials | |
|---|---|
| Member of Parliament | Dushyant Chautala[19] |
| Member of Legislative Assembly | Kamal Gupta[20] |
| Municipal Commissioner | Nikhil Gajraj[21] |
| Superintendent of Police | Ashwin Shainwi[22] |
Hisar became a municipality in 1867.[10] It was made the headquarters of the Hisar district in 1832. The Municipal Corporation of Hisar, consisting of 20 wards, is headed by a mayor. Law and order in the city are maintained by Haryana Police, which is headed by Superintendent of Police.[23] The city also serves as headquarters of the Hisar Range of Haryana Police which covers Sirsa, Jind, Bhiwani, and Hisar and is headed by Inspector General of Police.[24] District court was set up at Hisar in 1832[25] and was upgraded as a Sessions Division in 1915. It is headed by Chief Judicial Magistrate.[25] The district court has a bar association which was founded in 1870.[4]
Hisar elects its member to the legislative assembly for Hisar (Vidhan Sabha constituency) and a member to the parliament for Hisar Lok Sabha constituency. It serves as the headquarters of 33rd Battalion of Border Security Force[8] and 3rd Battalion of Haryana Armed Police.[23] The 33rd Armoured Division of Indian Army is stationed at Hisar[26] and is a part of I Corps. In 1996, Brigade of the Guards arrived here for conversion to mechanized profile and the unit is now a fully mechanized battalion.[27]
Economy

The city has a large steel industry and is known as the 'city of steel'.[28][29] As of June 2012, Hisar is India's largest manufacturer of galvanized iron.[30] Textile and automobile industry is also a major contributor to the economy of the city.[4][31] It also has a large number of livestock farms with the Central Livestock Farm, established in 1809 being one of the Asia's largest cattle farms.[32][33] The Jindal Group headed by Savitri Jindal, the 10th-wealthiest woman in the world is based in Hisar.[34] The city has been identified as a counter-magnet city for the National Capital Region to attract migrants and develop as an alternative center of growth to Delhi.[35]
Demographics
According to the 2011 census of India, Hisar has a population of 301,249[36] and is currently the 141st-most populated city in India.[37] Males constitute 54% of the population and females 46%, with 844 females per thousand males. Hisar has an average literacy rate of 81.04%, higher than the national average: male literacy is 86.13% and female literacy is 75.00%. In Hisar, 11% of the population is under 6 years of age and the child sex ratio is 860 girls per thousand boys. Although Hisar city has population of 301,249, its urban population is 306,893, of which 166,623 are males and 140,270 are females.[1] The decadal growth rate was 27.06%.[38]
Religion
Over 97% of the city's population are followers of Hinduism. The remaining 3% are followers of Sikhism, Jainism, Islam, and Christianity.[1] The city had a major Muslim population before Indian Independence in 1947, following which most Muslims migrated to Pakistan during the Partition of India.[4] It was also a major centre of learning for Digambara Jains and was once the seat of Bhattaraka, head of Digambara Jain institutions.[39]
Culture

Most of the popular Indian festivals are celebrated in the city, the most important being Diwali, Dussehra, Ram Navami, Janamashtami, Shivratri, Gugga Navami, Holi, Basant Panchami, Teej, and Makar Sankranti. The festivals of Jains, Christians, Sikhs and Muslims are also celebrated.[4] Sweets are popular, with Hansi ka Peda being the most popular amongst them.[40] Ghoomar is the primary folk dance performed by people during festivals and other occasions and Saang is the folk-theatre of the region.[4] Classical Indian vocalist Jasraj and poet Vishnu Prabhakar belong to Hisar.[41]
Architecture
Signs of pre-Harappan settlements have been found at Siswal and Lohari Ragho.[42] One of the four pre-Harappan phases has been named Sothi-Siswal period (3200–2600 BC)[43] on this site.[44] Harappan settlements can be found as well in Rakhigarhi. The site covers 2180 hectares, making it the largest Harappan site known in India and the second-biggest overall after Mohenjodaro.[45] All the sites are maintained by Archaeological Survey of India. Agroha is another place of historical importance. It is situated about 24 km from the city and was once the capital of king Agrasena, who is believed to have lived during the last stages of Dwapar Yuga in the Mahabharat era. Remains of his capital have been excavated, known as Agroha Mound or locally as Ther, and belong to around 3000 BC. The city was also a major centre during the Mauryan period as Buddhist and Jain temples have also been revealed in the excavations.[46]
Firoz Shah Palace Complex is another prominent historical site located inside the city. It was built by Firuz Shah Tughlaq in 1354.[4] Asigarh Fort, a centrally protected monument, was built in 1304–1305.[8] Historical places from the British era include St. Thomas Church and Jahaj Kothi Museum, a Jain temple converted to a museum.[10]
Places of interest

Siswal, Banawali, Kanwari, and Rakhigarhi are some of the sites of Indus Valley Civilization of now lost ancient Drishadvati river flowing through Hisar, Drishadvati river was a tributary of ancient Sarasvati River which still flows as remnant Ghaggar-Hakra River.[4] Historic Agroha Mound and Agroha Dham is a prominent religious place located on the outskirts of the city about 22 km away on Fatehabad-Sirsa-Bhatinda road.[47] A local deity Banbhori is worshipped by local people. Delhi Sultanate era Firoz Shah Palace Complex and Pranpir Badshah tomb are located in the city.[48][49]
The oldest park located in the city is the Krantiman Park, located across the historic St. Thomas Church. The park was built in the 19th century and was then known as Company Bagh.[10] Other parks include Madhuban Park, Town Park, and O. P. Jindal Knowledge Center.[4] The O. P. Jindal Knowledge Centre, inaugurated in 2009 a museum, library, park and houses a 25-storied, 282-ft- high steel tower modeled on the Space Needle in Seattle.[50] Haryana Rural Antique Museum, which is maintained by CCS HAU in its Gandhi Bhawan, exhibits evolution of agriculture and vanishing antiques.[4] Jahaj Kothi Museum, named after George Thomas, is located inside Firoz Shah Palace Complex and maintained by the Archaeological Survey of India.[51] Rakhigarhi Indus Valley Civilisation Museum is located at Rakhigarhi, which is an Indus Valley civilisation site 60 km away.[52]
Blue Bird Lake, an artificial lake and tourist complex maintained by the Haryana Tourism, offers boating and watersports, birding, picnicking, and recreation.[53] The deer park and Shatavar Vatika Herbal Park are located at the outskirts of the city and maintained by the Haryana State Forest Department.[54] It was established in 1971 and endangered species such as blackbuck, chital, sambar, and nilgai can be found here.[54] Hisar Police Lines Golf Course is located near the Hisar Airport.
Media
Doordarshan Kendra was set up in 2002.[55] Besides Doordarshan, local cable operators broadcast channels in the city.[56] An All India Radio station is located at Hisar.[57] Private FM stations operating in Hisar are BIG FM, My FM, Radio Mantra, Radio Dhamaal and Radio Tarang.[58] CCS HAU community radio station was started in 2011.[59]
Facilities
Utility services
Before independence of India, monsoon or groundwater were the main sources of irrigation.[60] The main source of water now is Balsamand branch of Western Yamuna Canal.[61] Municipal Corporation of Hisar supplies potable water to the city.[62] The city first got electricity in 1936.[10] Power is distributed by Dakshin Haryana Bijli Vitran Nigam Limited.[63] Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL) provides landline and broadband services.[64] Cell phone coverage is extensive, and the main service providers are Vodafone Essar, Airtel, MTNL, Reliance Communications, Idea Cellular and Tata Indicom. The planning of the city is done by Haryana Urban Development Authority.[65]
Healthcare
People from Punjab and Rajasthan come to Hisar for medical treatment.[66] The district Red Cross Society caters to specially abled people.[67]
Transport
Road
The city lies on National Highway 10 and National Highway 65. National Highway 10 from Delhi to Fazilka connects it to Rohtak and Sirsa and National Highway 65 from Ambala to Pali connects it to Kaithal and Jodhpur. The state highways of Haryana that pass through Hisar are State Highways 10, 13, and 20.[68] Besides, there are district roads, village link roads and canal inspection roads.[4] In 1947, the total metalled road length in the city was 137 km (85 mi) which increased to 1,188 km (738 mi) in 1978.[4]
Bus service is the major means of transport in the town.[69] Bus services are provided by Haryana Roadways and other private operators. Hisar bus depot was established on 11 August 1969 and has a subdepot at Hansi.[69] As of 2012, the depot has a total of 198 buses with daily ridership of 73,500.[69] All the 290 villages of Hisar district are connected to the city through either public transport provided by Haryana Roadways or through private buses.[69] Auto rickshaws are a major means of transport for travelling within the city.[4] In August 2012, city bus service was started in the city.[70] The city is a part of Delhi Mumbai Industrial Corridor Project which aims at developing strong road and rail connections between the cities lying on it and develop them as an industrial area.[71]
Rail
Hisar is a railway junction station, and it falls under Bikaner division of North Western Railway Zone.[72] The first railway line to the city was laid down in 1883 when Delhi Rewari Railway was extended to Bhatinda.[10] Currently, four broad gauge railway lines are at the station.[4] The railway station is a part of Western Dedicated Rail Freight Corridor according to which the city is to be developed as an export-oriented industrial unit.[73] The city is well connected to the neighboring states through rail links.[74]
Air
Hisar Airport is located on the outskirts of the city. In August 2012, the DGCA approved the Haryana state government's plan to develop the airport to operate domestic passenger services. Its 4,000-foot (1,200 m) runway will be extended to 6,000 ft (1,800 m) to accommodate air service.
Education
Before the British Raj, indigenous schools provided elementary education. Till 1892, the city had only one middle school.[4] The first private school, CAV High School, was set up by Arya Samaj in 1918.[10] Chaudhary Charan Singh Haryana Agricultural University, one of Asia's biggest agricultural universities was the first university established in Hisar, in 1971.[75] Other universities located in the city are Guru Jambheshwar University of Science and Technology, Lala Lajpat Rai University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences and Shanti Niketan Vidyapeeth, Hisar.[15] Commercial and private pilot license training is provided by the Haryana Institute of Civil Aviation (HICA) from Hisar Airport built in 1965.[76][77]
A few agricultural and veterinary research centers are also situated in the city such as National Research Centre on Equines,[78] Central Sheep Breeding Farm,[33] Government Livestock Farm, Hisar[15] Northern Region Farm Machinery Training and Testing Institute,[79] Regional Fodder Station, Hisar[80] and Central Institute for Research on Buffaloes.[81] In 1988, the city hosted the 2nd World Buffalo Congress.[81] The major library in the city is Nehru Library.[82]
Sports
Mahabir Stadium, Haryana Agricultural University Stadium and HAU Giri Centre host state sponsored sports academies.[83][84] Hisar hosted the 51st National Boxing Championship in 2004[85][86] and 22nd Haryana State Women Sports Festival in 2008.[87] It has a sports center run by Sports Authority of India at Chaudhary Charan Singh Haryana Agricultural University which has a synthetic track of international standard apart from other facilities.[88] Other major sporting venue in Hisar is Mahabir Stadium for multiple sports which was completed in the year 1972, run by District Olympic Association .[10] Sports persons from Hisar include Chandgi Ram, Geetika Jakhar in wrestling, Krishna Poonia in discus throw, Manvinder Bisla in cricket, Nirmala Devi in wrestling, Udey Chand, and Vikas Krishan Yadav in boxing. In April 2012, 18-year-old Ajay Kumar from Hisar qualified for 2012 Summer Olympics.[89]
References
- 1 2 3 "Census of Hisar city". Government of India. Retrieved 23 May 2012.
- 1 2 3 Cities having population 1 lakh and above (PDF). censusindia (Report). The Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved 28 May 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Imperial gazetteer of India". University of Chicago. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 "Hisar gazeteer" (PDF). Haryana Gazeteers Organisation. Retrieved 23 May 2012.
- ↑ "Indian archaeology" (PDF). ASI. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "Ain-e-Akbari". Abul Fazl. Retrieved 23 May 2012.
- ↑ Sen, Sailendra (2013). A Textbook of Medieval Indian History. Primus Books. p. 98. ISBN 978-93-80607-34-4.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Hisar". District administration, Hisar. Retrieved 23 May 2012.
- ↑ Mohan, Lalit (23 December 2003). "Hisar: Hub of Haryana's history". The Tribune. Retrieved 24 March 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "Hisar jano" (PDF). Jambh Shakti Trust. Retrieved 23 May 2012.
- ↑ "Jawahar Lal Nehru in Hisar". District Administration, Hisar. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "Archaeological sites- I (Early Harappa and Harappa)" (PDF). Indira Gandhi National Open University: 12. Retrieved 7 June 2012.
- ↑ Hasan Dani, Ahmad (1999). "Pre Indus and early Indus cultures of Pakistan and India". In Vadim Mikhaĭlovich Masson. History of civilizations of Central Asia (3rd ed.). Motilal Banarsidass Publications. p. 279. ISBN 978-92-3-102846-5.
- ↑ "The 1837–38 famine in U.P.: Some dimensions of popular action". Indian Economic and Social History Association. Retrieved 31 May 2012.
- 1 2 3 "Climate of Hisar". PPU. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 "Climate of Hisar". District Administration, Hisar. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "More snowfall in Himachal". The Hindu. Retrieved 24 March 2016.
- ↑ "Climatological table of Hisar, India". India Meteorological Department. Retrieved 19 April 2012.
- ↑ "HJC's Kuldeep Bishnoi wins Hisar bypoll, Cong pushed to third place". The Times of India. 17 October 2011. Retrieved 21 April 2012.
- ↑ "Congress blames internal sabotage for Hisar defeat". Hindustan Times. 21 October 2012. Retrieved 21 April 2012.
- ↑ "Haryana government transfers 71 IAS officers". jagran.com. Retrieved 20 March 2016.
- ↑ "Mayyar incident: Agitation slows down investigations". The Times of India. 5 March 2011. Retrieved 21 April 2012.
- 1 2 "Hisar police official website". Hisar Police. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "Hisar police organisational setup" (PDF). Hisar Police. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- 1 2 "History of district court Hisar". Punjab & Haryana High Court. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "Army exercise". The Telegraph. Calcutta, India. 5 April 2012. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "Battalion celebrates Hilli day". The Tribune. 24 November 2011. Retrieved 31 May 2012.
- ↑ Saini, Manaveer (29 June 2015). "Hisar, the City of Steel". Times of India. Retrieved 24 March 2016.
- ↑ Hisar:Changing the face of Haryana (PDF). Government of Haryana (Report). Retrieved 24 March 2016.
- ↑ Singh, Amardeep (26 June 2015). "Scodix at Hisar's Aggarwal Digital Studio". Print Week. Retrieved 24 March 2016.
- ↑ "About Hisar". Guru Jambheshwar University. Retrieved 23 May 2012.
- ↑ "Central livestock farm". The Tribune. 9 June 2005. Retrieved 2 June 2012.
- 1 2 "Central sheep breeding farm". Department of Animal Husbandry, Dairying & Fisheries, GoI. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "World's richest women 2012". Forbes. Retrieved 10 June 2012.
- ↑ "How to Handle Delhi's Influx of Migrants". Forbes India. 14 September 2011. Retrieved 10 June 2012.
- ↑ "Census 2011 of Hisar district". Ministry of Home Affairs, GOI. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "Cities having population 1 lakh and above, Census 2011" (PDF). Census of India, 2011. Retrieved 31 May 2012.
- ↑ "Census 2001" (PDF). Ministry of Home Affairs, GOI. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ Adinath Sangave, Vilas (2001). "The Bhattaraka Tradition". Facets of Jainology: Selected research papers on Jain society, religion, and culture. Popular Prakashan. p. 134. ISBN 81-7154-839-3.
- ↑ "Hansi ka Peda" (PDF). Science & Technology Department, Haryana. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "Literature of Haryana". preservearticles.com. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "Sothi-Siswal ceramic assemblage: A reappraisal". Ancient Asia Journal. Retrieved 28 May 2012.
- ↑ Possehl, Gregory L. (2002). "The Beginnings of the Indus Age". The Indus civilization: A contemporary perspective. Pennsylvania: Rowman Altamira. p. 29. ISBN 0-7591-0172-8.
- ↑ Higham, Charles (2004). "S". Encyclopedia of ancient Asian civilizations. Dunedin: Infobase Publishing. p. 329. ISBN 1-4381-0996-2.
- ↑ "Rakhigarhi". Global Heritage Network. Retrieved 28 May 2012.
- ↑ "Mound Agroha" (PDF). Archaeological Survey of India. Retrieved 25 June 2012.
- ↑ "Krishi Darshan expo". Ministry of Agriculture, GoI. Retrieved 28 May 2012.
- ↑ "Pranpir gumbad". Haryana Tourism. Retrieved 22 April 2016.
- ↑ "Feru Shah palace and Tehkhana". Haryana Tourism. Retrieved 22 April 2016.
- ↑ Sharmila Banerjee (June 2009). "Learning for all- O.P. Jindal knowledge centre inaugurated". JSW Connect. JSW Group (6): 61. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "Jahaj Kothi museum". Haryana Tourism. Retrieved 26 April 2016.
- ↑ "Harappan museum at Rakhigarhi". Times of India. Retrieved 26 April 2016.
- ↑ "Blue bird Hisar". Haryana Tourism Department. Retrieved 28 May 2012.
- 1 2 "Deer park Hisar". Haryana Forest Department. Retrieved 28 May 2012.
- ↑ "About DD Hisar". DD Hisar. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "Siti Hisar dancing star". Essel Group. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "Radio stations". All India Radio. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "Radio Tarang". Radio & Music. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "HAU community radio". EK duniya anEK awaaz. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "District profile of Hisar" (PDF). Central Ground Water Board, GoI. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "Haryana irrigation patterns". Haryana Irrigation Department. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "Municipal corporation, Hisar". District Administration, Hisar. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "Hisar electricity map". Dakshin Haryana Bijli Vitran Nigam. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "BSNL to add 8 lakh new GSM lines in 4 Haryana districts". Web India. 19 June 2012. Retrieved 21 June 2012.
- ↑ "About HUDA". HUDA. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "About Hisar". District Administration, Hisar. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "List of NGOs" (PDF). Department of Social Justice and Empowerment, Haryana. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "State highways of Haryana". Public Works Department, Haryana. Retrieved 30 June 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 "Hisar at a glance". Haryana Transport Department. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "Haryana to expand city bus service". Times of India. 21 August 2012. Retrieved 1 September 2012.
- ↑ "Strike a hot deal". Business Today. Delhi. 1 December 2011. Retrieved 30 June 2012.
- ↑ "North Western Railway System Map" (PDF). www.nwr.indianrailways.gov.in. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ↑ "DMIC- Haryana". DelhiMumbaiIndustrialCorridor.com. Retrieved 30 June 2012.
- ↑ "Railway station, Hisar". Indian Rail Info. Retrieved 30 June 2012.
- ↑ "About HAU". Haryana Agricultural University. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "Hisar jano" (PDF). Jambh Shakti Trust. Retrieved 23 May 2012.
- ↑ "Haryana Institute of Civil Aviation". District Administration, Karnal. Retrieved 30 June 2012.
- ↑ "Vision 2030" (PDF). National Research Centre on Equines. Retrieved 7 June 2012.
- ↑ "About us". Northern Region Farm Machinery Training and Testing Institute. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ Regional Fodder Station, Hisar website
- 1 2 "About CIRB". Central Institute for Research on Buffaloes. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "Nehru library". Haryana Agricultural University. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "Haryana player preparing for Rio olympics". Hindustan Times. Retrieved 22 April 2016.
- ↑ "Wrestling dreams". India Today. Retrieved 22 April 2016.
- ↑ "Asian women ready to fight for supremacy". The Hindu. Chennai, India. 19 November 2003. Retrieved 2 June 2012.
- ↑ "Nationals in Hissar from August 3". The Hindu. Chennai, India. 9 July 2007. Retrieved 2 June 2012.
- ↑ "Haryana women sports festival". One India News. 15 September 2008. Retrieved 2 June 2012.
- ↑ "About HAU". HAU. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "India's jewelbox". Indian Express. 15 April 2012. Retrieved 2 June 2012.
Further reading
- Juneja, M.M. History of Hisar: From Inception To Independence, 1354–1947 1989, Haryana: Modern Book Co., 484 pp. OCLC 21197085
- Juneja, M.M. Hisar City: Places & Personalities 2004, Haryana: Modern Publishers, 744 pp.
- Gazetteer Of The Hisar District 1883–84 2001, Haryana: Sang-E-Meel Publications, 72 pp. ISBN 978-969-35-1114-7
- Ojha, J.S.B.S. Resource Planning Atlas Of Western Haryana: Sirsa And Hisar Districts 1996, Haryana: National Book Organisation, 207 pp. ISBN 81-85135-81-9
- Shokoohy, M. & Shokoohy, N.H. Hisar-i Firuza: Sultanate and Early Mughal Architecture in the District of Hisar, India 1988: Araxus Books, 172 pp. ISBN 1-870606-01-9