Autoroutes of France



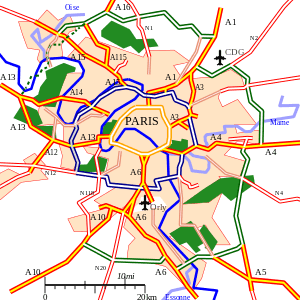
The Autoroute system in France consists largely of toll roads, except around large cities and in parts of the north. It is a network of 11,882 km (7,383 mi) worth of motorways in 2014. Autoroute destinations are shown in blue, while destinations reached through a combination of autoroutes are shown with an added autoroute logo. Toll autoroutes are signalled with the word péage (toll).


Numbering scheme
Unlike other motorway systems, there is no systematic numbering system, but there is a clustering of Autoroute numbers based on region. A1, A3, A4, A5, A6, A10, A13, A14, A15, A16 radiate from Paris with A2, A11, and A12 branching from A1, A10, and A13, respectively. A7 begins in Lyon, where A6 ends. A8 and A9 begin respectively near Aix-en-Provence and Avignon. The 20s are found in northern France. The 30s are found in eastern France. The 40s are found near the Alps. The 50s are near the French Riviera. The 60s are found in southern France. The 70s are found in the centre of the country. The 80s are found west of Paris.
Named routes
Some of the autoroutes have their own name in addition to a number:
- A1 is the autoroute du Nord (Northern motorway).
- A4 is the autoroute de l'Est (Eastern motorway).
- A6 and A7 are autoroutes du Soleil (Motorways of the Sun), for they lead from northern to southern France and its sunny beach resorts.
- A8 is named La provençale as it cross Provence.
- A9 is named La Languedocienne as it crosses the Languedoc
- A10 is named L'Aquitaine because it leads to Bordeaux, which is situated in the part of France named Aquitaine.
- The A13 is named the autoroute de Normandie as it traverses Normandy.
- A20 is named L'occitane as it leads to the south-west of France, this part of France was historically called Occitanie.
- The A26 is the autoroute des Anglais as it leads from Calais, the main point of arrival for cars and lorries from the UK. It continues to Troyes, and just happens to pass straight through the Champagne region, whose wines are so loved by the British. In addition it threads through and close to the sites of the most famous battles fought by the British Army in World War I, such as Arras, Cambrai and the Somme and not far from Ypres and Mons in Belgium. It also passes sites of earlier UK interest such as Crecy and The Field of the Cloth of Gold.
- The A29 is part of the route des Estuaires, a chain of motorways crossing the estuaries of the English Channel.
- The A40 is named the autoroute blanche (white motorway) because it is the road that goes to Chamonix and other French winter resort towns.
- The A62 and A61 are named autoroute des deux mers (the two seas motorway) because these roads connect the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea from Bordeaux via Toulouse to Narbonne.
- A68 is called autoroute du Pastel because it leads to Albi and to the Lauragais where woad was cultivated to produce pastel.
- The N104, one of Paris's beltways, is also known as La Francilienne because it circles the region of Ile-de-France.
Administration
The status of motorways in France has been the subject of debate through years, from their construction until recently. Originally, the autoroutes were built by private companies mandated by the French government, and followed strict construction rules as described below. They are operated and maintained by mixed companies held in part by private interests and in part by the state. Those companies hold concessions, which means that autoroutes belong to the French state and their administration to semi-private companies. Vinci controls around 4,380 km (2,720 mi) of motorway. The different companies are as follows:
- ALIS (SEM, SAPN 8%, Bouygues 20.2%, Ixis 26%, DTP Terrassement 13.44%), concessionnaire de l'A28 Rouen-Alençon 125 km, Alis, official site
- SAPRR (Autoroutes Paris-Rhin-Rhône), 1801 km, SAPRR, official site
- AREA (Société des Autoroutes Rhône-Alpes, SAPRR Subsidiary at 99.82%), 381 km, AREA, official site
- ASF (Autoroutes du sud de la France), 2325 km, ASF, official site (bought by vinci-autoroutes.com Vinci)
- ATMB Autoroutes et tunnels du Mont-Blanc, 107 km, ATMB, official site
- CEVM (Viaduc de Millau, groupe Eiffage), 2.5 km, CEVM, official site
- Cofiroute (Compagnie Industrielle et Financière des Autoroutes, private company part of Vinci group), 896 km, Cofiroute, official site
- Escota (Société des Autoroutes Esterel-Côte d'Azur, ASF group), 460 km, Escota, official site (bought by vinci-autoroutes.com Vinci)
- Sanef (Société des autoroutes du Nord et de l'Est de la France), A.C.S. group (Spain), 1317 km, SANEF, official site
- SAPN (Société des autoroutes Paris-Normandie, SEM, groupe Sanef), 366 km, SAPN, official site
- SFTRF, Société française du tunnel routier du Fréjus, 67 km, SFRTF, official site
Only in the Brittany region do most of the autoroutes belong to the government. They are operated by the regional council and are free from tolls.
Safety on French autoroutes
France has the following speed limits for limited access roads:
- Under normal conditions - 130 km/h (81 mph)
- In rain or wet road conditions - 110 km/h (69 mph)
- In heavy fog or snowy/icy conditions - 50 km/h (31 mph)
In normal conditions, there is a minimum speed of 80 km/h (50 mph) in the lane most left (no minimum speed on the others' right lanes, but speed should be adapted for each situation: not too slow).
The autoroutes are designed to increase the safety of drivers; this allows a higher speed limit (130 km/h or 81 mph) than on the normal roads (90 km/h or 56 mph) with an acceptable risk of accident.

The safety measures are:
- one way driving: the lanes driving in the opposite direction are separated by at least a crash barrier, which is designed to resist the oblique impact of a car at up to 180 km/h (113 mph); no intersecting roads but bridges and tunnels;
- wider carriageways, at least 2 (often 3) lanes driving in the same direction, with a larger turning radius - some recently built autoroutes have one-lane-only sections;
- long acceleration and slowing lanes to get in or out of the autoroute without disturbing the traffic;
- presence of an additional emergency lane where it is forbidden to drive (except for the emergency services) and to park (except in case of emergency);
- presence of emergency call boxes every 2 km (1.2 mi) on each side, that allow to call for help with the possibility to locate the call; some call boxes have flashing light that warn when there is a problem ahead;

- presence every 10 km (6.2 mi) (4–6 minutes of driving) of resting zones (aire de repos, i.e. car parks with public toilets), and every 40 km (25 mi) (20–30 minutes of driving) of a resting zone with a restaurant and a gas station - on most recently built autoroutes these distances are longer;
- regular patrols of the security services, to clear any obstacle and protect drivers in trouble (usually a breakdown or a flat tyre) with appropriate warning signs and beacons;
- dynamic information panels that warn about possible difficulties ahead (accident, people at work, traffic jam);
- an FM radio station (107.7 MHz) dedicated to information about traffic conditions on most of the network;
- on heavy traffic days (e.g. beginning and end of school holidays): organisation of specific information and recreation events at rest areas;
- radars automatiques (speed cameras) currently being installed in many locations.
Economics
The toll roads were granted as concessions to mixed-economy corporations; the free roads are directly administered by the national government. Tolls are either based on a flat-rate for access to the road or on the distance driven. The latter case is the most common for long distances; users take a ticket from an automatic machine when they enter the autoroute, and pay according to the distance when exiting; toll booths accept multiple payment methods.

In 2005, the Villepin government proposed a controversial plan to sell all of the state's holdings in autoroute companies to private investors. Critics contend that the price announced is well below the profit forecasts for these companies, and thus that the government sacrifices the future to solve current budgetary problems.[1]
List of Autoroutes
A1 - A9
- A1 : Autoroute du Nord Paris Porte de la Chapelle - Lille
- A2 : Combles - Belgium
- A3 : Paris Porte de Bagnolet - Paris-Nord
- A4 : Autoroute de l'Est Paris Porte de Bercy - Strasbourg
- A5 : Vert-Saint-Denis (Seine-et-Marne) - Langres
- A6 E15 : Autoroute du Sud and Autoroute du Soleil : Paris - Lyon
- A7 E15 : Autoroute du Soleil : Lyon - Marseille
- A8 La Provençale : La Fare-les-Oliviers - Italy
- A9 La Languedocienne/La Catalane Orange - Narbonne - Spain
A10 - A20
- A10 L'Aquitaine : Rungis - Orly - Bordeaux
- A11 L'Océane : Saint-Arnoult-en-Yvelines - Nantes
- A12 : A13 (Rocquencourt) - Trappes
- A13 Autoroute de Normandie : Paris (Porte d'Auteuil) - Caen (Porte de Paris)
- A14 : Orgeval - La Défense
- A15 : Gennevilliers - Cergy (and formerly - Pont de Tancarville - Le Havre)
- A16 L'Européenne : L'Isle-Adam - Beauvais - Amiens - Abbeville - Boulogne-sur-Mer - Calais - Dunkerque - Belgium
- A19 : Orléans (A10 at Artenay) - Sens
- A20 L'Occitane : Vierzon - Montauban
A21 - A29
- A21 Rocade Minière : Lens - Douai - Denain
- A22 : Lesquin - Belgium
- A23 : Lesquin - Valenciennes
- A24 : Amiens - Lille - Belgium (proposed)
- A25 : Lesquin - Dunkerque
- A26 Autoroute des Anglais : Troyes - Calais
- A27 : Lesquin - Lille - Belgium
- A28 Autoroute des Estuaires : Abbeville - Tours
- A29 : A13 - Pont de Normandie - Amiens – Saint-Quentin
A30 - A39
- A 30 : Uckange - Crusnes
- A 31 : Beaune - Luxembourg
- A 32 : Freyming-Merlebach - Germany
- A 33 : Nancy - Hudiviller (local autoroute around Nancy)
- A 34 : Reims - Charleville-Mézières - Belgium
- A 35 : Lauterbourg - Switzerland (Basel)
- A 36 La Comtoise : (A 31) Ladoix-Serrigny - Germany
- A 38 : Pouilly-en-Auxois - Dijon
- A 39 Autoroute Verte : Dijon - Bourg-en-Bresse

A40 - A49
- A40 E62 Autoroute Blanche, Autoroute des Titans : Mâcon - Mont Blanc Tunnel
- A41 : Switzerland (Geneva) - Grenoble
- A42 E611 : Lyon - Bourg-en-Bresse
- A43 : Lyon - Italy
- A44 : (project) bypassing Lyon by west
- A45 : Lyon - Saint-Étienne
- A46 : Anse - Givors (bypassing Lyon by east)
- A47 E70 : Lyon - Saint-Étienne
- A48 : Lyon - Grenoble
- A49 : Grenoble - Valence

A50 - A59
- A50 : Marseille - Toulon
- A507/L2 : (under construction, planned since 1935) ring of Marseilles.
- A500 : access to Monaco
- A51 : Marseille - Grenoble, Val de Durance
- A516 : Autoroute link between A51 from Marseilles and the city center of Aix-en-Provence
- A52 : Autoroute link between A8 and A50, great ring of Marseilles.
- A520 : Autoroute link between A52 and Auriol, access to Saint Maximin via the Sambuc pass
- A54 : Nîmes - Salon Sud (link with A7)
- A55 : (Nîmes) - Martigues - Marseille
- A557 : one-direction ring of Marseilles downtown
- A56 : (under construction), link between A54 and A55 from Salon to Fos freight port
- A57 : Toulon – Vidauban, link with A8

A60 - A69
- A61 E80 Autoroute des Deux Mers: Toulouse - Narbonne
- A62 E72 Autoroute des Deux Mers: Bordeaux - Toulouse
- A63 E05 Autoroute de la Côte Basque : Bordeaux - Biriatou
- A64 E72 La Pyrénéenne : Toulouse - Bayonne
- A65 E7 : Bordeaux - Pau
- A66 : Toulouse - Pamiers
- A68 : Toulouse – Albi
A70 - A79
- A71 : L'Arverne Orléans (A10) - Clermont-Ferrand (A75)
- A72 : Saint-Étienne - Clermont-Ferrand
- A75 La Méridienne : Clermont-Ferrand - Béziers (A0)
- A77 Autoroute de l'Arbre Poligny (A6) - Nevers - Challuy
A80 - A89
- A81 : Le Mans - La Gravelle
- A83 : Nantes - near Niort
- A84 : Rennes - Caen
- A85 : Angers - Vierzon
- A86 : the second ring road around Paris
- A87 : Mûrs-Erigné - La Roche-sur-Yon
- A88 : Caen - Falaise - Sées
- A89 : Lyon - Arveyres
Others

- A1(972) : Around Fort-de-France. Autoroute in Martinique, a French overseas territory.
- A104 : The Francilienne around the Île-de-France (Paris) region
- A105 : Combs-la-Ville
- A110 : Ablis - Tours (proposed)
- A115 : A15 (Sannois) - Méry-sur-Oise
- A131 : Bourneville (A13 exit 26) - Le Havre
- A132 : A13 / Pont-L'Évêque - Canapville
- A154 : A13 - Louviers
- A199 : Torcy - Champs-sur-Marne (downgraded into RD 199)
- A203 : Charleville-Mézières - Glaire
- A211 : A21 - N17
- A216 : A16/A26 - N216 Calais
- A260 : Boulogne-sur-Mer - A26
- A320 : A4 - Germany
- A330 : Nancy - Richardménil
- A391 : A39 - RN83
- A404 : Saint-Martin-du-Frêne - Oyonnax - Arbent
- A406 : Mâcon
- A430 : Chamousset - Gilly-sur-Isère
- A432 : Saint-Laurent-de-Mure - Montluel
- A508 : Tunnel (access to Monaco)
- A570 : A57 - Hyères
- A620 : A61 - A62 ( West ring of Toulouse)
- A621 : Toulouse - Blagnac
- A623 : A620 - A61
- A624 : Toulouse - Colomiers
- A630 : Lormont - Bègles
- A631 : Bègles
- A641 : Oeyregave - Orthevielle
- A645 : Ponlat-Taillebourg - Seilhan
- A660 : Mios - Gujan-Mestras
- A680 : Castelmaurou - Verfeil
- A710 : Gerzat - Clermont-Ferrand
- A711 : Lempdes - Pont-du-Château
- A712 : Lempdes - Pont-du-Château
- A714 : Bizeneuille - Saint-Victor
- A719 : Gannat - Monteignet-sur-l'Andelot
- A750 : A75 to Clermont-l'Hérault - Montpellier
- A810 : La Rochelle - A10
- A811 : Carquefou - Sainte-Luce-sur-Loire
- A813 :Banneville-la-Campagne-Frénouville
- A831 : Rochefort - La Rochelle - Fontenay-le-Comte
- A837 Autoroute des Oiseaux : Rochefort - Écurat (A10)
- A844 : A11-A82
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Autoroutes in France. |
References
- ↑ Press release of 12-14-2005 Archived November 20, 2006, at the Wayback Machine.
External links
- Official Website of the ASFA, with information on the Autoroute network and instructions on how to use them
- Motorway numbers in France (route log)
- The automatic tolling system in France: Liber-t
- Driving in France - autoroutes and other routes

