Speed limits by country
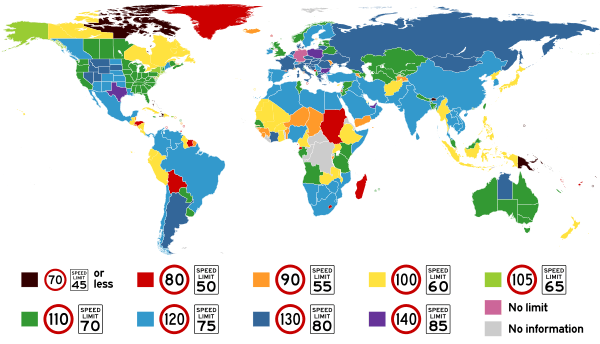
A road speed limit is the limit of speed allowed by law for road vehicles, usually the maximum speed allowed. Occasionally there is a minimum speed limit.[1] Speed limits are commonly set by the legislative bodies of national or local governments.
Overview
The following tables show various jurisdictions' default speed limits (where applicable) that apply to different types of vehicles travelling on three different types of road. Actual speed limits may range beyond these values. Speeds are listed in kilometers per hour. The enforcement tolerance is specified in km/h or percentage above the stated limit. For the United Kingdom and the United States, the speed limit is also listed in miles per hour in brackets.[fn 1] Germany, with its Autobahns, is the only country without a general speed limit on its highways.[2] The Isle of Man is the only jurisdiction without a general speed limit on rural two-lane roads.

Germany has a variable speed limit: where no general limit is enforced by signage of miscellaneous type, the advisory speed limit is 130 km/h (81 mph), referred to in German as the Richtgeschwindigkeit. The advisory speed is not enforceable; however, being involved in an accident driving at higher speeds can lead to the driver being deemed at least partially responsible due to "increased operating danger" (Erhöhte Betriebsgefahr).
The Federal Highway Research Institute (Bundesanstalt für Straßenwesen) solicited information about speed regulations on autobahns from the sixteen States and reported the following, comparing the years 2006 and 2008:
| Parameter[3] | 2006 | 2008 | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Autobahn Carriageway-Km | 24,735 km | 25,240 km | +505 km |
| Advisory Limit Only | 69.2% | 65.5% | -580 km |
| Variable Limit (with Advisory Maximum) | 4.2% | 4.1% | -5 km |
| Permanent or Conditional Speed Limit | 26.7% | 30.4% | +1,090 km |
Except at construction sites, the general speed limits, where they apply, are usually between 100 km/h (62 mph) and 130 km/h (81 mph); construction sites usually have a speed limit of 80 km/h (50 mph) but the limit may be as low as 60 km/h (37 mph).[4] In rare cases, sections may have limits of 40 km/h (25 mph),[5] or on one ramp 30 km/h (19 mph)![6] Certain stretches have lower speed limits during wet weather. Some areas have a speed limit of 120 km/h (75 mph) in order to reduce noise pollution during overnight hours (usually 10pm – 6am) or because of increased traffic during daytime (6am – 8pm).
Some limits were imposed to reduce pollution and noise. Limits can also be temporarily put into place through dynamic traffic guidance systems that display the according message. More than half of the total length of the German autobahn network has no speed limit, about one third has a permanent limit, and the remaining parts have a temporary or conditional limit.
Countries
| Country | Within towns | Automobiles & motorcycles (single carriageway) | Automobiles & motorcycles Expressways/motorways (dual carriageway) | Trucks or automobiles with trailer | Trucks or automobiles with trailer Outside built-up areas/highways | Enforcement tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 50 | 70–90 | ||||
| | 40 | 80–90 | 110 | 60–70 | 80 | |
| | 40–70[fn 2] | 80–110 | 120–130 (100 in Buenos Aires City) | 80 | 110 | |
| | 40–60 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | Up to 10 km/h over the limit |
| | 50 | 80 | ||||
| | 50–60[fn 3] | 100 (100 limit on Learner and Provisional licence holders) (110 zones widely used, 130 on four NT highways) | 100–110 | 80–100 trucks and road trains only | 80–110[fn 4] | in Victoria 3 km/h strictly enforced by fixed speed camera and at the discretion of Victoria Police
7 km/h over in Western Australia Generally 10% over speed limit in other states, but a ticket will be given for less when detected by fixed speed camera. However, new laws may see the drivers issued with a ticket for exceeding 2 km/h over the posted speed limit. Heavy penalties apply for speeding in Australia. |
| | 40 | 90 | N/A | |||
| | 50 (30 in many residential areas) | 100 | 130 (motorways) 100 (expressways)[fn 5] | 70–100[fn 6] | 80–100[fn 7] | |
| | 60 (20 in residential areas) | 90 | 110 | 10 km/h tolerance set by law. | ||
| | 50 | 80 | 100 | 80 | ||
| | 32 (20 mph) | 80 (50 mph) | ||||
| | 60 | 80 | 100 | |||
| | 60 | 90 | 110 ( | 70 | 90 | Up to 10 km/h over the limit |
| | 50 (30 in many residential areas) | 90 | Motorways: 120, Expressways: 120 (90 if no central reservation) | 60–90 | 90 | 6 km/h tolerance under 100 km/h, 6% over 100 km/h |
| | 40–64 (25–40 mph) | 88 (55 mph) | N/A | |||
| | 50 | 90 | 90 | |||
| | 8–20 (30 km/h fastest speed limit in an urban area.) | 50 km/h | 50 km/h | |||
| | 50 | 80 | 130 (motorways) 100 (expressways) | 80 | ||
| | 40–60 | 60–80 | 80–120 | 80 (90 for buses) | 80–100 | 7 km/h when speed limit = or < 100 km/h and 7% when speed limit > 100 km/h |
| | 50 | 80 | 100 | 80 | 80 | |
| | 50 | 90 ( | 140[fn 8][fn 9] ( | 70 | 100 | Speed cameras have 10 km/h tolerance. |
| | 60–80 | 90 | 120 | 80 | 100 | |
| | 60 | 100 | 100 | |||
| | 30–80 (20–50 mph) | 60–100 (40–60 mph) | 70–120 (45–75 mph)[fn 10] | 60–100 (35–60 mph) | 70–120 (45–75 mph) | 20% to 40% unofficially (depends on police officer, province, type of road). Speed limits are more strictly enforced in school zones and construction zones where road workers are present. Tickets can be given from 1 km/h above the speed limit. |
| | 30–60 | 60–80 | 100–120 (Motorcycles not allowed on Toll sections of Expressways) | N/A | N/A | |
| | 40–60 | 80–100 | 100–120 | 100 (90 for trucks) | 100 | |
| | 40 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 90 | |
| | 30–60 | 80–90 | 90–100 | 60 | 90 | |
| | 45 | 60 | 80–100 | 60 | 80 | |
| | 55 | 80–120 (130 in some exception.) | 90 (buses), 75 (heavy goods) | |||
| | 50 | 90 | 130 (motorways) 110 (expressways) | 80 | 80 | 10% in all cases; additionally, outside towns there is no penalty for 10 km/h speeding |
| | 40/50 (special suburban areas where children can play); 60 (other urban areas) | 60 | 100 | |||
| | 40 | 80 | 80 | |||
| | 50 | 80 | 100 | 80 | 100 | 20% unofficially (depends on police officer). Tickets can be given from 1 km/h more than speed limit |
| | 50 | 90 | 130 (motorways) 80 (urban areas) | 80 | 80 | 3 km/h under 100 km/h, 3% over 100 km/h[16] |
| | 50 | 80 | 130 (motorways) 80–90 (expressways) | 80 | 80 (90 for buses) | 10% in all cases |
| | 60 | 80 | 80–100 | |||
| | 50 | 60–100 | 60–100 | 40–70 (50–90 for buses) | 90 | |
| | 60 | 90 | 100 (120 on the Ayn Sukhna road) | |||
| | 50–70 (20 in many residential areas) | 90 | 110 (90 in winter) | 90 | 90 | 6 km/h even with fixed cameras. |
| | 30–50 | 60–100 | 100 | |||
| | 50 | 80 | ||||
| | 20–30 (in school and industrial areas), 50 (in town, city or densely populated areas) | 80 | ||||
| | 50 | 80–100[fn 11] | 100–120[fn 11] | 80 | 80 | 10 km/h in all cases; fixed speed cameras activate at 6 km/h and a notification is sent by mail with no consequences up to 10 km/h over the limit
Beyond 20 km/h fine is net income based with no upper limit (!) |
| | 50 (30 in many residential areas) | 90 (80 in rain) | 110 (100 in rain)-expressways 130 (110 in rain)-motorways | 60[fn 12]-110 | 80[fn 13]-130 | 5 km/h tolerance under 100 km/h, 5% over 100 km/h |
| | 60–80 (on embankments in Tbilisi 70, Tbilisi airport highway and Vera-Vake highway – 80 | 90 | 110 | 15 km/h since 2012. Advisory screens showing your current speed on Highway S1/E60 | ||
| | 50 (30 in many residential areas) | 100 (no / 130 advisory with two or more lanes per direction)[23] | No Speed Limit (only 130 advisory)[fn 14] | 80 (trucks) / 100 (automobiles with trailer and buses) | 100 | Up to 100 km/h: 3 km/h, over 100 km/h: 3% (rounded up) for fixed speed cameras. Up to 100 km/h: 7 km/h, over 100 km/h: 7% (rounded up) for moving speed cameras. |
| | 30–50 | |||||
| | 50 | 90 ( | 130 ( | 80 (School buses 60) | 80 (School buses 60) | 20 km/h above the speed limit, unofficially. However, it can depend on traffic officer, type of road and type of vehicle. |
| | 50 | 80 | ||||
| | 40 (25 mph) | 56 (35 mph) | N/A | N/A | 56 (35 mph) | |
| | 50 | 80 | 100 | |||
| | 50 | 50–70[fn 16] | 70–110[fn 17] | 70[fn 18] | 30–70[fn 19] | |
| | 50 | 90 | 110 (expressways) 130 (motorways) | 70 | 80 (express buses 100) | ~10% if stopped, cameras: 14 km/h up to 100 km/h, 19 km/h over 100 km/h |
| | 50 | 90 (80 on gravel) | 90[fn 20] | 80 | 80 | Up to 3 km/h over the limit |
| | 50–70 | 80 | 80–120[24][25] | 65 | 50 | No speed limit on new expressways. |
| | 40–50 | 60–80 | 100 ( | 80 | 80 | |
| | 50 | 70–110 | 70–120 (motor cycle prohibited on any free way with 120 limit) | 70–110 | 70–110 | under 60 limit up to 30 km/h above up to 20 fixed cameras have no tolerance |
| | 50 (normal built-up) 30–60 (special limits) | 80–100[fn 21] | 120 (80–100*[fn 21]) | 80–90 | 80–100 | |
| | 48 (30 mph) | No Speed Limit | N/A | N/A | No Speed Limit | |
| | 50 | 80–90 | 110–(120 at road 6) | 80 | 90 | 10 km/h |
| | 50 (70 where there are two carriageway) | 70–90 | 110 (90 in adverse weather)-expressways 130 (provisions trying to raise to 150)[26] (110 in adverse weather)-motorways[fn 22] | 70 | 80 | 5 km/h tolerance under 100 km/h, 5% over 100 km/h [27] |
| | 50 | 80 | 80–110 | |||
| | 40 | 50–60 70–80 (single carriageway expressways) | 80–100 | 50–60 | 50–60 | |
| | 48 (30 mph) | 64 (40 mph) | N/A | N/A | 64 (40 mph) | |
| | 60/80/100 | 90–100 | 110 | |||
| | 50 | 80 | 130 | 80 | ||
| | 60–80 | 80–120 | 100–120 | 70–100 | 120 | Up to 20–25 km/h over the limit is tolerated on highways |
| | 20 (residential area's), 60 (other built-up areas) | 60–90 | 90–110 | 70 | 90-70 | |
| | 50 | 80–110 | 100–120 | 90 | 100 | 10 km/h |
| | 50 | 90 | 90; 110 (motorways) | 80 | 80–90 | Up to 20 km/h over the limit is tolerated on highways |
| | 50 | 100 | ||||
| | 50 | 80 | 80 | |||
| | 50 | 90 – Asphalt/Concrete roads 70 – Other roads | 120/110* – motor roads (expressways) 130/110* – motorways (*summer/winter period)[fn 23] | 70–80–90 | 90 | Speed cameras have 7–13 km/h tolerance. No fine (warning) issued 0–9 which makes 9–19 km/h depending on situation. |
| | 50 | 90 | 130 (110 in rain) | 90 | 90 | |
| | 50 | N/A | No speed limit [30] | N/A | N/A | |
| | 20–60 | 50–80 | 60–80 | N/A | N/A | 10 km/h |
| | 50 | 80–100 | 130 | |||
| | 50–60 | 80–100 | 100 | 80 | ||
| | 50–70 | 80–90 (80 km/h speed limit on federal and state roads during festive seasons) | 110 | 50–70 | 80–90 | 10% over the speed limit[33] |
| | 40–60 | 100 | 100 | |||
| | 25–45 | 60–80 | 60 | |||
| | 40 | 80 | 110 | |||
| | 60 | 90 | 90 | |||
| | 60 (40 in many residential areas) | 100 | 120 | N/A | 100 | 10% (max 7 km/h) |
| | 50 | |||||
| | 60 | 70–110 | 130 | |||
| | 50 | 80 | ||||
| | 30–70 (20–45 mph) | 80–120 (50–75 mph)[fn 24] | 100–120 (60–75 mph) | 95 (60 mph) | ||
| | 60 | 80/120 | 120 | |||
| | 8–32 (5–20 mph) | 32 (20 mph) | N/A | |||
| | 60 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 110 | |
| | 50 (30 in many residential areas) | 80 100 (single carriageway expressways) | 130 (motorways, 120 or lower on many stretches) 100 (dual carriageway expressways) | 80–90[fn 25] | 80 | 3 km/h for up to 100 km/h measured, 3% of the measured speed otherwise.[37] From 01–01–2012, the higher 9 km/h tolerance for speeds over 130 km/h has been abolished in favour of the 3% rule (resulting in fines being issued from 136 km/h).[38][fn 26] |
| | 30–60 (usually: 50 km/h) | 60–110 | 110 | |||
| | 10–70 (10 for shared pedestrian zones, 30–60 for residential streets and 50–70 for arterial routes)[39] | 80–100 | 80–100 (110 proposed) | 90 | 80–100 | 4 km/h (school zones and holiday periods) or 10 km/h (otherwise) when enforced by police. Speed cameras have no tolerance. You get a ticket for 105 km/h at 100 km/h area. |
| | 40 | 60 | N/A | |||
| | 40 | 80 | 120 | |||
| | 30–40 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 50 | |
| | 70 (third lane), 60 (second lane), 40 (first lane) | up to 100 | up to 100 | |||
| 50 (30 in many residential areas) | 80–90 | 90–110[40] | 80, 60 without brakes on trailer | 80 | Speed cameras have a 5 km/h tolerance. Police generally apply a tolerance of 5–10 km/h, but up to 20–25 km/h on motorways when driving conditions are favorable. | |
| | 25–30 | 100 | 100–120 | 100 | ||
| | 60 | 75 | ||||
| | 40–70 | 60–100 | 120 (motorways)
100 (expressways) |
70–80 | 110 (90 buses) | Motorway Police allows up to 10 km/h exceed in legal speed to lighter vehicles only. |
| | 60 (on avenues) 40 (on streets) 30 (near schools and hospitals) | 100 (on paved highways in rural areas) | 80 (urban areas) 100 (rural areas) | 90 (buses) 80 (for trucks) 70 (for school buses and dangerous goods) | 70–100 (paved highways) 60 (unpaved roads) | Speed cameras are widely used in Lima and have no tolerance. On national paved roads in rural areas speeding is very common (up to 110 km/h) and speed limits are seldom enforced. Police offices can give fines at their own discretion. |
| | 40–60 | 20–60 | 60–100 | 40–80 | 40–60 | Trucks/buses are only allowed to reach 80 km/h at expressways. |
| | 50 (60 at night) can be increased up to 80 on main transit routes[fn 27] | 90 (single carriageways) 100 (dual carriageways) | 140 (motorways) 120 (dual carriageway expressways) 100 (single carriageway expressways) | 70 | 80 | 10 km/h |
| | 50 | 90–100 | 120 | 70–80 | 100 | |
| | 60–100 | 100–120 | 120 | |||
| | 50 70 (some DN stretches) | 90 100 (E-roads) | 130[fn 28] (motorways) 100 (expressways) | 80 90 (E-roads) | 90 (expressways) 110 (motorways) | 10 km/h |
| | 60 (can be increased by regional government up to 110)[44] | 90 (can be increased by regional government up to 110)[44] | 110[44] ( | 70–90 | 90 | 20 km/h (since September 1, 2013) |
| | 24 (15 mph) | 40 (25 mph) in almost every road outside town. (72 or 45 mph is the fastest speed limit in the whole country.) | ||||
| | 50 | 90 | 110 | |||
| | 50 (40 in many residential areas) | 80 | 120 (motorways) 100 (expressways) | 60 | 70 (car) 80/90 (truck) | 10% above the speed limit. However, it can depend on traffic officer. |
| | 50 | 70–90 | 90 | 60 | 60 | |
| | 50 | 90 | 90 (urban expressways & motorways) 130 | 90 | 90/130 | 0 km/h but up to 6 km/h for no fee and speaking with policeman[46] |
| | 50 (30 in many residential areas) | 90 | 130 (motorways) 110 (expressways) | 80 | 80 | 7 km/h up to 100 km/h, 8 km/h between 100 and 150 km/h and 9 km/h above 150 km/h |
| | 40–80 | 100–120 | 120 125 (section of Highway 40 – Riyadh-Mekka) | 80 | 80 | 10% above the speed limit. |
| | 40–65 | 50–90 | 110–120 (Freeways | 40–80 | 80–100 | 9 km/h |
| | 40 | 60–100 | 100 | 60 | 60–80 | Up to 10km/h over, at the officer's discretion. Fines can be issued from 1 km/h over the speed limit.[47] |
| | 30–80 | 60–80 | 80–120 ( | 40–60 | 80 | 10 km/h over, reduced penalties less than 20 km/h over. 22 km/h tolerance with speed cameras on expressways with a speed limit of 100 km/h or higher. |
| | 50 (30 in many residential areas) | 90–100[fn 29] | 120 (from 1 July 2011) | 70–80[fn 30] | 80–90[fn 31] | |
| | 50 (31 mph) | 70 (43 mph) | 70–100 (43–62 mph)( 100 in Expressways | 40 (25 mph) (TukTuk) | 40–70 (25–43 mph) | |
| | 60 | 70–90 | 120 | |||
| | 40–50 | 80 | 80 | none | 80 | |
| | 30–60[fn 32] | 60–100[fn 32](110) | 110–120[fn 32] | 80 (90 km/h for trucks without a connected trailer and only on motorways/dual carriageways) 90 & 100 for buses | 80 | No tolerance on any road; massive use of speed cameras
new 120 km/h limit is now enforced[fn 33] |
| | 50 (30 in many residential areas) | 80–100 | 120 | 80 | 80 | Up to 100 km/h: 5 km/h, 101 to 150 km/h: 6 km/h, over 150 km/h: 7 km/h for fixed speed cameras. Up to 100 km/h: 3 km/h, 101 to 150 km/h: 4 km/h, over 150 km/h: 5 km/h for laser speed cameras. |
| | 40–60 | 50–80 | 100–110 (Freeways | 60–80 | 80–90 | 9 km/h |
| | 60 | 80–100 | 110 | 100 | N/A | 9 km/h over the speed limit |
| | 60 | Bangkok Metropolitan & Pattaya City: 80 Others: 90 | 90 Intercity Highway 120 Motorway(Motorways | Truck Bangkok Metropolitan & Pattaya City: 60 Others: 80 Long Vehicle Bangkok Metropolitan & Pattaya City: 45 Others: 60 | 80–90 | No tolerance on any road when speed cameras are in operation. |
| | 50 | 80 | 80 | |||
| | 50 (70 on urban fast traffic roads) | 90 | 110 | |||
| | 50 | 90 ( | 120 (motorways) ( 110 (dual carriageways) ( | 80 | 90 (motorways) 85 (dual carriageway) | 10% over the limit, except for motorways which have zero tolerance |
| | 60 | 90 | 110 | |||
| | 30 (close to schools and hospitals), 40 (other streets in the cities), 50 (city roads connecting the main highways and motorways) [51] | 80 | 80–100 | |||
| | 60 | 90 ( | 110 (dual carriageway) 130 (motorway) ( | 70–90 | 80 | 20 km/h |
| | 50–60 | 100–120 | 100–140 (formerly 160 or 100 mph, which would've been the fastest in the world) | 50–80 | 100–140 ( | +20 km/h unless maximum speed limit is stated (e.g.140). Temporary speed cameras can be expected in any roads and most do not have tolerance. |
| | 48 (30 mph)[fn 36] | 97 (60 mph)[fn 36] | 113 (70 mph) (both Motorways and trunk Dual-carriageways)[fn 37] | 80–97 (50-60mph) dependent on class (64–97 (40-60mph) in Scotland)[fn 38] | 97–113 (60–70 mph)[fn 38] dependent on class (Motorways) 97–113 (60–70 mph) (80–113 (50–70 mph) in Scotland, ditto (trunk Dual-carriageways) | 10 per cent over the speed limit plus 2 mph (3 km/h)[52] |
| | 40–120 (25–75 mph) | 72–120 (45–75 mph)[fn 39] | 97–129 (60–80 mph).[fn 40] 137 (85 mph) is allowed on one highway in Texas [fn 41] | Restrictions only in few states, typically 16 km/h (10 mph) lower. | 89–129 (55–80 mph)[fn 40] | States have jurisdiction over speed limits. Enforcement varies, from warning (e.g., Nebraska) to fines to jail (e.g., Wyoming above 100 mph). Typically, ~5 mph over in speed limit zones 50 mph and under and ~10 mph in zones 55 mph and over (highway speeds.) ; can be as little as 1 mph.[53] |
| | 50 | 75–90 | 90–110 | none | ||
| | 70 | 100 | 100 | 70 | 90/80 | |
| | usually up to 60 km/h (50 in Luganville [56]) | 60–80 | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| | 30 | |||||
| | 15–30 | 80–120 | N/A | 40–60 | 60–120 | |
| | 60 ( | 90 ( | 80–120 ( | 70 | 70 | 5 km/h |
| | 60 | 80–120 | 80–120 | 80 | 60–80 |
|
Footnotes
- 1 2 Signs are posted in mph. Until recently, speed limit signs on a stretch of Interstate 19 in southern Arizona were the only ones based on the metric system. As part of the 2009 American Recovery and Reinvestment Act, the federal government funded a project where the state of Arizona replaced the km/h signs on that stretch with miles-based speed limit signs.
- ↑ "Speed limit in Av. Libertador and Av. Figueroa Alcorta". 31 August 2010. Retrieved 1 July 2015.
- ↑ Default speed limits in Australia vary between states and territories. See Speed limits in Australia for more details.
- ↑ No special limit applies for automobiles with trailers. A 100 km/h speed limit applies for heavy vehicles with a gross vehicle mass of 12 tonnes or more. A 100 km/h limit applies for buses with a gross vehicle mass of 5 tonnes or more. In some Australian states, Road Trains are limited to 90 km/h. In some cases, over steep descents or other potentially dangerous stretches of road, heavy vehicles may have other special speed limits as indicated by signage.
- ↑ A provisional increase to 160 km/h was in place on a 12 km stretch on the A10 (between Spittal an der Drau and Paternion) in May and June 2006. The 160 km/h speed limit was displayed only during the day (from 5 till 22) and under optimal conditions. In the night (from 22 till 5) the speed limit could be only up to 110 km/h. In bad weather or traffic conditions the displayed speed limit could be lowered. In very poor conditions, the rate was reduced to 80 km/h.
- ↑ Cars with heavy trailer: 80 km/h; lorries with heavy trailer: 70 km/h.
- ↑ Cars with heavy trailer: 100 km/h; lorries with heavy trailer: 80 km/h.
- ↑ "Bulgaria Ups Hwy Speed Limit to 140 km/H". 26 June 2012. Retrieved 15 March 2013.
- ↑ "Bulgarian MPs Seal 140 km/h as Highway Speed Limit". 12 June 2012. Retrieved 15 March 2013.
- ↑ Speed limit is 110 km/h in several provinces, 100 km/h in others. It's 120 km/h on some highways in British Columbia. It's 70 km/h in Montreal's Metropolitan Expressway. It's 80 km/h-90 km/h in Toronto's Municipal Expressway System.
- 1 2 During winter, when conditions are often bad, all Finnish motorways have a speed limit of 100 km/h or less. Also most roads with 100 km/h speed limit in summer have 80 km/h limit during winter.
- ↑ Speed limit is 60 km/h for trailers on 2-lane non-priority roads.
- ↑ Speed limit is 80 km/h for lorries and trailers transporting dangerous goods.
- ↑ 130 km/h is the recommended maximum speed on motorways, as indicated by a square blue sign (round blue sign = minimum speed). Many sections of the German motorway network are now covered by speed limits, usually ranging from 80 to 130 km/h (140 km/h as speed limit is being tested in Lower Saxony -some politicians are against it, because 140 km/h is over the recommended maximum speed, depending on local conditions (i.e., frequent traffic, terrain, etc.). It is usual for drivers involved in crashes who were exceeding the 'recommended' speed limit to be held to be at least partly at fault, regardless of the circumstances of the crash, and insurance companies have the right to withhold payment. Already more than 50% Autobahns now have a (partially variable) speed limit. Vehicles also must be able to go faster than 60 km/h.
Roughly 30% of german Autobahn have permanent limits. An additional 17% have at least partial limits depending on time, weather or traffic. Study on the speed limit on german Autobahn. Archived 25 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine. - ↑ Speed limits have been signed in kilometres per hour since the 1980s. The unit "km/h" was signed below the number before the late 1990's.
- ↑ Type restriction is not prescribed for private motor vehicles or motor cycles as opposed to goods vehicles and buses. The default speed limit is 50 km/h unless signed otherwise.
- ↑ No default speed limit is mandated on expressways. The lowest signposted limit on main lines is 70 km/h, which is the norm for examples from the 1970's and 80's usually found in urban areas. More commonly, however, 80 km/h is signed. The rural standard is 100 km/h and is signed whenever practicable in the New Territories. The highest limit, 110 km/h, is only used on the island of Lantau.
- ↑ Buses, as well as goods vehicles with a laden weight of 7.5 tonnes, are limited to 70 km/h, minibuses to 80 km/h. Most buses and all minibuses are mechanically restricted. The restriction for goods vehicles is not enforced by the police.
- ↑ The default speed limit in the territory is 50 km/h. 30 km/h may be signed on less used roads built on rough terrain.
- ↑ Iceland does not have expressways/motorways in the traditional sense. There is only one true 'expressway', road 41(Reykjanesbraut), which is built to motorway standard most of its route – grade separated, 2 lanes each direction. However it does not have a higher speed limit. Other such expressways are located within Reykjavík city limits, and the maximum speed is 80 km/h.
- 1 2 100 km/h is default limit on all National Routes regardless of design standard when local limits do not apply; regional and minor routes have an 80 km/h limit. All limits are signposted either way. *On urban motorways such as the M50 (100km/h or 80 km/h) or M1 (as low as 80km/h in places) or in tunnels (80km/h).
- ↑ Two and three-lane motorways (autostrada): 130 km/h; since 2003 on some three-lane autostrade a 150 km/h limit was introduced, but is not operative).
- ↑ "Lithuanian parliament official speed limits. See XV article.". 8 April 2008. Retrieved 19 January 2014.
- ↑ Some two lane Federal highways are posted at 110 km/h provided they have a paved shoulder.
- ↑ In the Netherlands, only cars or vans pulling a trailer with a total weight of less than 3.5 metric tons (with the trailer weighing less than 750 kg) are allowed to drive 90 km/h, except where a lower speed limit is posted. Vehicles of other categories (i.e. trucks), as well as cars or vans with a trailer weighing more than 3.5 tons are restricted to 80 km/h.
- ↑ This is because the 3% are rounded up. 3% of 136 km/h is 4.08, which after rounding up results in a tolerance of 5 km/h. Thus after correction for tolerance, a measured speed of 136 km/h results in a fine for driving 131 km/h, or 1 km/h over the speed limit.
- ↑ 50 km/h in built-up areas during the day (from 5 till 23) and 60 km/h at night (from 23 till 5)
- ↑ Speed limit is 130 km/h, but no legal sanction is established for driving within 10 km/h over the speed limit.
- ↑ 100 km/h on: a) one-way roads, b) roads with more than two lanes, or c) roads with shoulders at least 1.5 m wide; 90 km/h elsewhere.
On two-way roads, cars and motorbikes are allowed to go 20 km/h over the speed limit in order to overtake a slower vehicle in a shorter amount of time. - ↑ On roads with a speed limit of 100 km/h for cars and motorbikes: 90 km/h for buses, vans and vehicles with a trailer weighing 750 kg or less, 80 km/h for trucks and vehicles with a trailer weighing more than 750 kg.
On roads with a speed limit of 90 km/h for cars and motorbikes: 80 km/h for buses, vans and vehicles with a trailer weighing 750 kg or less, 70 km/h for trucks and vehicles with a trailer weighing more than 750 kg. - ↑ 100 km/h for buses and vans, 90 km/h for trucks and vehicles with a trailer weighing 750 kg or less, 80 km/h for vehicles with a trailer weighing more than 750 kg.
- 1 2 3 Sweden introduced new speed limits in 2008/2009, where the regular limits 30, 50, 70, 90 and 110 km/h are complemented by 40, 60, 80, 100 and 120 km/h. Please see this document for more information In general speed limits of 110 and 120 km/h apply on freeways only (4 lanes). However speed limits of 110 km/h remain on fence-divided 2–3 lane highways in the northern part of the country. Parts of the east-coast European Route E4 north of the city of Gävle towards Haparanda is an example of this. All other 2–3 lane highways previously zoned at 110 km/h have been lowered to either 90 or 100 km/h respectively.
- ↑ The 120 km/h limit is currently unenforced by the police due to lack of clarity in the legal text, per Teknikens Värld, 3 January 2012.
- ↑ In June 2010, a motion has taken by the Turkish Grand National Assembly to increase the speed limit in double lane highways in rural areas from 90 km/h to 110 km/h. New law is expected to be valid from July 2010.
- ↑ New speed limits in Ukraine effective from 22 April 2009.
- 1 2 UK roads only have three blanket limits for non-towing private vehicles (separate from those for trucks, buses and towing vehicles). 30 mph (48 km/h) in towns (including dual carriageways), 60 mph (97 km/h) on non-urban single carriageway roads, and 70 mph (113 km/h) on all dual-carriageway roads and motorways (including rare single-carriageway motorway sections, and slip roads), which apply without needing signs. Any other limits in force must be clearly posted. For example, 20 mph (32 km/h) limits are sometimes seen in residential estates and city-centre areas and outside primary schools, whereas 40 mph (64 km/h) limits are common on major urban through-routes, including many 2-lane single-carriageway residential urban roads, and usually come with both zone start/end signs and small repeaters (with 30 mph areas also usually having start/end signs for clarity, but rarely repeaters; 60/70 sections tend to be marked with struck-circle "de-restriction" signs, but very occasionally zone-start and repeaters for clarity or preserving the higher limit on limited-access routes that would otherwise technically class as an urban road). Higher limits in urban areas are usually reserved for limited-access dual carriageways. Lower limits are common on sections of dual carriageways, even on some major intercity routes. Permanent, mandatory lower motorway limits are rare but do exist, e.g. 50 mph (80 km/h) is generally applied on tidal flow sections, in tunnels, some bridges or sections of substandard alignment and junction structure. Variable, legally-enforceable limits for traffic control (including hard-shoulder running at up to 50~60 mph) are being gradually introduced (at time of writing, on sections of the M25, M42 and M6) and may go as low as 20 mph (32 km/h) in 10 mph steps. Any other speed signs on motorways are usually advisory-only but may be used for apportioning liability for accidents.
- ↑ In general, non-urban, all-purpose (i.e. not limited to motor traffic, except in the case of "A(M)" roads) dual carriageways are subject to the same 70 mph limit for light vehicles as motorways, but lower limits (50 and 60 mph) are in place for heavy trucks, buses/minibuses and towing vehicles. These roads take the place of motorways where a high-traffic trunk route is required but building a motorway would be impractical for reasons of cost and/or geography. For instance, steeper or more winding alignments and less forgiving junctions than would be found on motorways necessitate lower limits for some stretches – as low as 30 mph in some cases, e.g. around Penmaenbach on the A55 in Wales, or a less severe 60 mph restriction on some parts of the A38 and A45.
- 1 2 Generally in the UK, lorries over a laden weight of 7500 kg are mechanically or electronically speed-limited to 56 mph (90 km/h) because of overriding European law, even on motorways where they are legally permitted (under UK law) to travel at 60 mph. Some heavier machines are further limited to 53 (85 km/h) for the same reasons, and carry warning plates to this effect. Some lorries or trucks with a laden weight between 3500 kg and 7500 kg are also speed-limited to 56 mph (90 km/h) on all roads. On non-motorway roads, heavier trucks are legally limited to 50 (single-carriageway) or 60 (dual carriageway) mph (80 and 97 km/h) except in scotland where they are limited to 40 (single-carriageway) or 50 (dual carriageway (as of 6th April 2015), Medium trucks and buses/commercial van-based minibuses to 50 and 60 mph (80 and 97 km/h), though the latter are further subdivided: some are allowed a motorway speed of 60 mph (97 km/h) and others 70 mph (113 km/h). Light commercial vans are subject to the same 60/70/70 mph limits as private cars and motorcycles, and towing cycles/cars/vans subject to medium truck 50/60/60 limits.
- ↑ The lower speed limit in large inner-cities may be as low as 45 mph (72 km/h) for example on I-90/94 which goes through Chicago. In many urban areas, controlled-access highways typically take 5 – 15 mph off the speed limit. For example, in Cleveland and Cuyahoga county, the speed limit is 60 mph (97 km/h). Once out of the county, the speed limit returns to 65 mph (105 km/h).
- 1 2 The state of Hawaii posts a 55 mph (89 km/h) speed limit on many Interstate highways.
- ↑ One toll road near Austin, TX has a speed limit of 85 miles per hour. 85 MPH Highway Opens
- ↑ There are no specific speed limits in Venezuela. The standard within towns is 60 km/h and from 80 to 120 km/h in highways however it varies depending on road conditions therefore speed limits are set by transit authorities through signals. Ley de Transito Terrestre, 3 November 2007.
Country specific
United States
American interstate highways are frequently patrolled by law enforcement, typically referred to as Highway Patrol, State Patrol or State Police. Speed limit enforcement is the most profitable part of their duty, but other traffic laws are sometimes enforced. Enforcement varies notably between states and traffic conditions. Montana and Nebraska have high tolerance toward speeding. More states are experimenting with variable speed limits, with electronic speed limit displays replacing fixed-number signs. The New Jersey Turnpike has long been equipped with variable-limit signs; in 2011, the same system was put in place along a stretch of Interstate 80 through Wyoming. The idea is to vary speed limits with traffic and weather conditions, the latter being the most immediate concern in Wyoming.
European countries
In some countries in Europe, traffic calming is gradually becoming a regular part of urban traffic management, after a long evolution of opinions and attitudes towards car use and vulnerable road users. From 1980, regulations for 30 km/h zones were enacted and have been widely applied. New urban policies have been defined with a view to encouraging a switch from car use to public transport and non-motorised modes (cycling, walking), with the additional condition of lower speeds to improve safety of vulnerable road users, for example national policies such as Duurzaam Veilig ('sustainable safety') in the Netherlands or "Vision Zero" in Sweden.
See also
- Category:Speed limits by country
References
- ↑ "Speeds on Rural Interstate Highways Relative to Posting the 40 mph Minimum Speed Limit | Bureau of Transportation Statistics". www.rita.dot.gov. Retrieved 2015-11-29.
- ↑ "Fun, fun, fun on the autobahn". 2013-09-16. Retrieved 2010-11-25.
- ↑ "Tempolimit auf Autobahnen 2008 (Speed limits on autobahns 2008)" (PDF). Bundesanstant fuer Strassenwesen (Federal Highway Research Institute). Retrieved 2014-04-08.
- ↑ http://www.derwesten.de/staedte/nachrichten-aus-dinslaken-huenxe-und-voerde/60-km-h-erlaubte-hoechstgeschwindigkeit-auf-der-autobahn-59-id7114757.html
- ↑ Christoph Koopmeiners (29 September 2011). "A 29: An neun Baustellen gilt Tempo 40". NWZonline. Retrieved 14 April 2016.
- ↑ NDR. "Tempo 30: Es blitzt und blitzt an der Autobahn". Retrieved 14 April 2016.
- ↑ "Kodiak Rigorous i Republics st Shqipërisë" (in Albanian). Sq.wikibooks.org. 2010-11-15. Retrieved 2010-11-25.
- ↑ DEATHTRAP Archived 13 June 2010 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ http://www.adcidl.com/Driving-in-Bahamas.html
- ↑ https://www.justlanded.com/english/Bahrain/Bahrain-Guide/Travel-Leisure/Traffic-regulations-in-Bahrain
- 1 2 https://www.toi.no/getfile.php?mmfileid=4345
- ↑ http://www.keithlane.com/page15.htm
- ↑ http://www.adcidl.com/Driving-in-Bhutan.html
- ↑ http://livingabroad.com/clients/lafarge/driving/Driving%20in%20Cameroon.pdf
- ↑ http://www.adcidl.com/Driving-in-Cuba.html
- ↑ http://www.cdv.cz/mereni-rychlosti-radary-a-tolerance-mereni-v-ceske-republice-a-v-jinych-statech/
- ↑ "LBK nr 1100 af 08/11/2006". retsinformation.dk. Retrieved 2011-11-26.
- ↑ http://www.worldtravelguide.net/dominican-republic/getting-around
- ↑ "Reglamento General para la aplicación de la LOTTTSV" (in Spanish). 25 Jun 2012. p. 29. Retrieved 9 Aug 2012.
- ↑ http://www.instantcars.eu/en/car_rental_in_egypt.html
- ↑ http://www.adcidl.com/Driving-in-Ethiopia.html
- ↑ http://www.fiji.gov.fj/Media-Center/Cabinet-Releases/23-4-13---FIJI-ROAD-SPEED-LIMITS-TO-BE-REVIEWED.aspx
- ↑
- ↑
- ↑ http://ibnlive.in.com/news/orr-to-be-drivers-delight/176822–60–121.html
- ↑ http://driving.drive-alive.co.uk/driving-in-italy.htm
- ↑ http://www.mit.gov.it/mit/site.php?p=normativa&o=vd&id=259
- ↑ http://coming-to-jamaica.com/?page_id=118
- ↑ http://www.adcidl.com/Driving-in-Kyrgyzstan.html
- ↑ http://www.who.int/violence_injury_prevention/road_safety_status/country_profiles/libyan_arab_jamahiriya.pdf
- ↑ https://books.google.com/books?id=2pBkhHmxu5YC&pg=PA74&lpg=PA74&dq=speed+limits+malawi&source=bl&ots=PO5l0yqCMA&sig=5qN7QdvgQZWyHpeEX6q57sraAT0&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0CE0Q6AEwBmoVChMIksyxyN3-yAIVR-0UCh26CgVI#v=onepage&q=speed%20limits%20malawi&f=false
- ↑ http://www.adcidl.com/Driving-in-Malawi.html
- ↑ "Tinted car windows fine is only RM300, says JPJ". Free Malaysia Today. BERNAMA. 10 February 2016. Retrieved 14 November 2016.
- ↑ http://www.adcidl.com/Driving-in-Mali.html
- ↑ http://www.adcidl.com/Driving-in-Mauritius.html
- ↑ http://www.countryreports.org/travel/Micronesia/traffic.htm
- ↑ "Openbaar Ministerie – Snelheid en overtredingen" (in Dutch).
- ↑ "Flitsmarge bij 130 km/uur omlaag". Infopolitie (in Dutch). 15 May 2011. Retrieved 13 September 2012.
- ↑ http://www.drivingtests.co.nz/resources/speed-limits-in-new-zealand/
- ↑ http://www.aftenposten.no/nyheter/iriks/Farten-settes-opp-pa-begge-sider-av-Oslofjorden-7575406.html
- ↑ http://www.panama-offshore-services.com/driving_a_vehicle_in_panama.htm
- ↑ http://www.adcidl.com/Driving-in-Papua-New-Guinea.com
- ↑ "Speed Limits, Road Classifications and Breakdown Recovery". Angloinfo Qatar. Angloinfo. Retrieved 2016-06-16.
- 1 2 3 "Traffic Code in Russia". consultantplus. Retrieved 2013-05-28.
- ↑ "V obci sa bude jazdit 50, pokuty budú vyššie". SME.sk. Retrieved 2009-11-16.
- ↑ "Sadzobník pokút 2016: Koľko zaplatíme za dopravné priestupky". SME.sk. Retrieved 2016-02-16.
- ↑ "At what Speed is it Legal for Speeding Fines to be Issued?". Retrieved 2016-09-04.
- ↑ http://caravanistan.com/transport/driving/
- ↑ http://www.adcidl.com/Driving-in-Turkmenistan.html
- ↑ http://www.worldtravelguide.net/uganda/getting-around
- ↑ http://www.newvision.co.ug/news/641971-city-drivers-get-new-speed-limits.html
- ↑ http://www.cps.gov.uk/legal/p_to_r/road_traffic_offences_guidance_on_fixed_penalty_notices/#speed
- ↑ Enter your Company or Top-Level Office (2010-08-23). "Metropolitan Police Department: Speeding Laws, Fines and Safety Tips". Mpdc.dc.gov. Retrieved 2011-11-26.
- ↑ http://www.tryuruguay.com/road-rules-in-uruguay.html
- ↑ http://www.vanuaturentalcars.com/info.html
- ↑ https://books.google.com/books?id=FBllKxtYnNkC&pg=PA110&lpg=PA110&dq=speed+limits+in+NEW+CALEDONIA&source=bl&ots=4kX4Rgikh7&sig=PSO5Y__yFr_UvCnx8YSW3ZLpT1k&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0CFYQ6AEwB2oVChMI1sL36qH3yAIVhj0aCh1oAAVC#v=onepage&q=speed%20limits%20in%20NEW%20CALEDONIA&f=false