Dishevelled
| Dishevelled specific domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Dishevelled | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF02377 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR003351 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC50841 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Dishevelled (Dsh) is a family of proteins involved in canonical and non-canonical Wnt signalling pathways. Dsh is a cytoplasmic phosphoprotein that acts directly downstream of frizzled receptors.[1] It takes its name from its initial discovery in flies, where a mutation in the dishevelled gene was observed to cause improper orientation of body and wing hairs.[2]
Dishevelled plays important roles in both the embryo and the adult, ranging from cellular differentiation and cell polarity to social behavior.[2]
Members
There are three human genes that encode for the dishevelled proteins:[3]
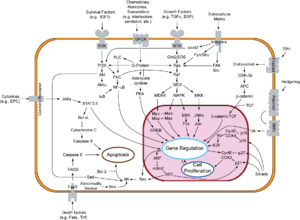
Overview of signal transduction pathways involved in apoptosis.
Example
Alignment of dishevelled-specific domain

References
- ↑ Penton A, Wodarz A, Nusse R (June 2002). "A mutational analysis of dishevelled in Drosophila defines novel domains in the dishevelled protein as well as novel suppressing alleles of axin". Genetics. 161 (2): 747–62. PMC 1462152
 . PMID 12072470.
. PMID 12072470. - 1 2 Wallingford JB, Habas R (October 2005). "The developmental biology of Dishevelled: an enigmatic protein governing cell fate and cell polarity". Development. 132 (20): 4421–36. doi:10.1242/dev.02068. PMID 16192308.
- ↑ Lee YN, Gao Y, Wang HY (February 2008). "Differential mediation of the Wnt canonical pathway by mammalian Dishevelleds-1, -2, and -3". Cell. Signal. 20 (2): 443–52. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.11.005. PMC 2233603
 . PMID 18093802.
. PMID 18093802.
External links
| Look up dishevelled in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- dishevelled proteins at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/9/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.