Ashkelon–Beersheba railway
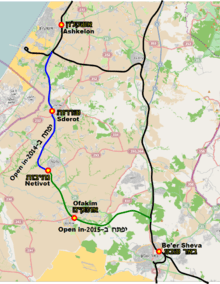
and stations.
The Ashkelon–Beersheba railway is a railway line linking Ashkelon and Beersheba operated by Israel Railways.[1] It spans approximately 60 km of double track in the northern Negev region of southern Israel and provides rail service to the cities of Sderot, Netivot and Ofakim. The line links Beersheba, Sderot, Netivot, and Ofakim to Ashkelon and Tel Aviv.
Route and construction timeline
|
|
The line is composed of three sections:
- A reconstruction and double-tracking of a part of the historic Ashkelon–Gaza coastal railway between Ashkelon and Yad Mordechai, parts of which were previously dismantled since the early 1970s.
- A brand new railway between Yad Mordechai and Goral junction on the Railway to Beersheba. This section contains the new Sderot, Netivot and Ofakim stations.
- An existing section of the Railway to Beersheba between Goral and Beersheba. The connection between the new railway heading from Ofakim to the Railway to Beersheba is achieved using a flying junction at Goral. This section is intended to be triple-tracked in a future follow-up project, with some bridges along the route already having been widened to accommodate three tracks.
The line includes three new road bridges, 18 rail bridges, four grade separations and 11 bridge or tunnel passages for farming equipment.
Construction progress
The line was constructed in stages with the Sderot station opening first, followed by the Netivot station. Construction of the railway to Beersheba was completed in August 2015, except for the Ofakim station. Service to Beersheba started on September 17, 2015 after a dedication ceremony by Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu.[2][3][4] The Ofakim station was opened on December 31, 2015.[5]
Services
The railway serves a new intercity line between Beersheba and Tel Aviv through the communities of the northern Negev, as well as stopping in existing railway stations in Ashkelon, Ashdod, Yavne, and Rishon LeZion.
The railway is also expected to serve freight trains, supplementing the current freight service via the railway to Beersheba and the Heletz railway.
External links
References
- ↑ "Ashkelon-Beersheba Railway". Israel Railways website (in Hebrew). Israel Railways. Retrieved 1 August 2012.
- ↑ "Israeli Railways Passenger Traffic Up 6%". Globes. Retrieved 26 August 2015.
- ↑ "PM Netanyahu dedicates new Ashkelon Beer Sheva railway line". Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Israeli Government. Retrieved 18 September 2015.
- ↑ "New data:More and More Israelis Traveling By Train" (in Hebrew). Globes. Retrieved 26 August 2015.
- ↑ "Next stop: Ofakim" (in Hebrew). Arutz Sheva. Retrieved 11 January 2016.