Tendō, Yamagata
| Tendō 天童市 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| City | |||
|
Tendō skyline | |||
| |||
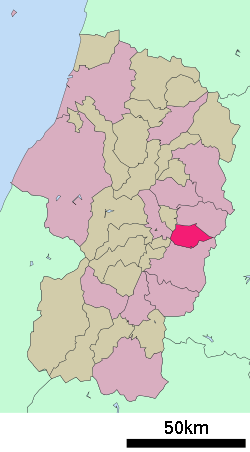 Location of Tendō in Yamagata Prefecture | |||
 Tendō
| |||
| Coordinates: 38°21′44.2″N 140°22′40.6″E / 38.362278°N 140.377944°ECoordinates: 38°21′44.2″N 140°22′40.6″E / 38.362278°N 140.377944°E | |||
| Country | Japan | ||
| Region | Tōhoku | ||
| Prefecture | Yamagata Prefecture | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 113.01 km2 (43.63 sq mi) | ||
| Population (October 2015) | |||
| • Total | 61,781 | ||
| • Density | 547/km2 (1,420/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | Japan Standard Time (UTC+9) | ||
| City symbols | |||
| • Tree | Maple | ||
| • Flower | Azalea | ||
| • Bird | Meadow bunting | ||
| Phone number | 023-654-1111 | ||
| Address | 1-1-1 Oinomori, Tendō-shi, Yamagata-ken 994-8510 | ||
| Website | Official website | ||

Tendō (天童市 Tendō-shi) is a city located in Yamagata Prefecture in the Tohoku region of northern Japan.
As of October 2015, the city had an estimated population of 61,781 and a population density of 547 persons per km2. The total area was 113.01 square kilometres (43.63 square miles).[1]
Geography
Tendō is located in the east-central portion of the Yamagata Basin, bordered by the Ōu Mountains to the east.
Neighboring municipalities
Climate
Tendō has a humid continental climate (Köppen climate classification Dfa) with very warm summers and cool winters. Precipitation is plentiful throughout the year, although the months from February to June have somewhat less rainfall.
History
During the Edo period, the area of present-day Tendō was part of Tendō Domain, a 20,000 koku feudal domain under the Tokugawa shogunate controlled by the Oda clan, who ruled from 1831-1871.[2]
After the start of the Meiji period, the area organized as Tendō Village under Higashimurayama District, Yamagata Prefecture in 1878. It was elevated to town status on April 27, 1892 and became a city on October 1, 1958.
Economy
The economy of Tendō is based on seasonal tourism, agriculture and wood products. The city is traditionally known for its production of the wooden pieces used in Japanese chess (shogi). The city also has numerous onsen hot springs within its borders.
Education
- Uyō-Gakuen College
- Tendō has twelve elementary schools, six middle schools and two high schools.
Transportation
Railway
Highways
International relations
Twin towns — Sister cities
 - Marostica, Italy,[3] since April 22, 1993.
- Marostica, Italy,[3] since April 22, 1993. – Blenheim, New Zealand,[3] since July 7, 1989
– Blenheim, New Zealand,[3] since July 7, 1989 – Wafangdian, China,[3] since May 27, 2002
– Wafangdian, China,[3] since May 27, 2002
Notable people
- Kenta Kurihara, professional baseball player
- Chiyako Sato, musician
References
- ↑ Official website
- ↑ Baedeker. (2012). Japan, p. 561; Hotta, Anne and Yoko Ishiguro. (1986). A guide to Japanese hot springs, p. 192.
- 1 2 3 "International Exchange". List of Affiliation Partners within Prefectures. Council of Local Authorities for International Relations (CLAIR). Retrieved 21 November 2015.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tendō, Yamagata. |
- Official website (Japanese)
-
 Tendo travel guide from Wikivoyage
Tendo travel guide from Wikivoyage
