Oregon Caves Historic District
|
Oregon Caves Historic District | |
|
Oregon Caves Chateau | |
  | |
| Location | Oregon Caves National Monument |
|---|---|
| Nearest city | Cave Junction, Oregon |
| Coordinates | 42°05′45″N 123°24′17″W / 42.09583°N 123.40472°WCoordinates: 42°05′45″N 123°24′17″W / 42.09583°N 123.40472°W |
| Area | Approx. 11 acres (4.5 ha)[1][2] |
| Built | 1926–1942 |
| Architect | Gust Lium and Francis Lange |
| Architectural style | National Park Service Rustic |
| NRHP Reference # |
92000058 (original) 11001028 (increase) |
| Significant dates | |
| Added to NRHP | February 25, 1992[3] |
| Boundary increase | January 12, 2012[3] |
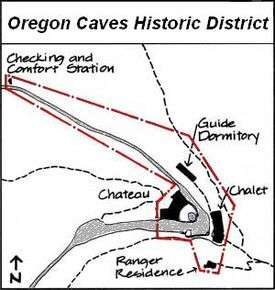
Oregon Caves Historic District covers 60 acres (240,000 m2) in the main visitor area of Oregon Caves National Monument in southern Oregon. The district includes four primary buildings plus two other structures. Because of the unique rustic architecture of these National Park Service buildings and the surrounding park landscape, the area was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1992.
History
Elijah Davidson discovered the Oregon Caves in 1874 while bear hunting near Sand Mountain (now renamed Mount Elijah after Davidson). While Native Americans may have known of the caves prior to Davidson’s discovery, no evidence of earlier exploration or use has been found. Thus, Davidson is credited with being the first person to enter the caves.[4]
In 1907, Joaquin Miller visited the caves. After his visit, he wrote an article that highlighted the cave’s unique beauty. The article gave the caves nationwide exposure. Under authority of the Antiquities Act of 1906, Federal Government ordered a site survey, which was completed in 1908. As a result, of the survey and continued advocacy from Miller and others prominent citizens, the Oregon Caves were designated as a National Monument by President William Howard Taft in 1909.[5][6]
The United States Forest Service was given responsibility for the Oregon Caves National Monument in 1909. Due to the caves remote location the first permanent road to the site was not completed until 1922. In 1934, oversight of the monument passed to the National Park Service. Over the next nine years, the Park Service worked with the Civilian Conservation Corps to develop and landscape the Oregon Caves site to attain the look of a "rustic alpine village" nestled in a mountain canyon. The Park Service’s naturalistic design principles dictated the use of indigenous materials and rustic stone work. Every element was careful set in place to highlight the rugged character of the canyon. Cedar-bark sheathing was used as a unifying design element on all the buildings.[7] While some changes have been made to the original structures, the buildings still retain their unique rustic character which is enhanced by the surrounding park landscape. In 1992, 60 acres (240,000 m2) of the Oregon Caves National Monument was listed as a historic district on the National Register of Historic Places.[8]
Structures
The buildings in the Oregon Caves Historic District illustrate the National Park Service rustic-style architecture. The historic structures remain generally intact with only a few minor exceptions necessary for general site rehabilitation due to landslide, flood damage, and safety codes.[7] The Oregon Caves Historic District has four primary buildings plus two other structures. The primary buildings are the Chalet, built in 1924 and reconstructed in 1942; the Oregon Caves Chateau built in 1934; the Guide Dormitory, built in 1927 with major additions in 1940 and 1972; and the Ranger Residence, built in 1936. The most noteworthy of these is the Chateau, which is individually listed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP # 87001346).[6]
Five of the six structures within the historic district, the four primary buildings and an original Checking and Comfort Station, are considered contributing structures with common, distinctive features. All the buildings were built between 1926 and 1942 with rough-cut, Port Orford cedar-bark sheathing, wood-shingled roofs, and rustic stone work.[6]

- The original Oregon Caves Chalet was built in 1924. It was the first permanent building constructed at the site. The Chalet was completely reconstructed in 1942. This project not only rebuilt the original structure, but also added a third floor and a prominent gabled breezeway entrance. The new structure was covered by the same cedar-bark sheathing use on the other monument buildings. Today, the Chalet retains its original features except the stone steps in front were replaced with concrete steps for safety reasons. The first floor is currently a visitor center, and the upper two floors of the Chalet still serve as a dormitory for seasonal guides.[6][7][9]
- In 1929, a builder from Grants Pass, Oregon named Gust Lium announced plans to construct the large lodge facility to service visitors to the monument. The Oregon Caves Chateau was completed in 1934. Built on a slope, the Chateau is a complex structure, six-stories high with ten sides. It was originally used as the National Park Service headquarters as well as a visitor lodge. Today, the Chateau still provides overnight lodging and guest services for monument visitors. It also houses a coffee shop, a restaurant, and a gift shop. Part of Cave Creek actually passes through the building, appearing as a water feature in the dining room. The original wooden verandas were replaced with steel fire escapes in 1958; nevertheless, the Chateau is considered one of the national park systems best preserved rustic lodges.[6][7][9]
- The Guide Dormitory was constructed in 1927. It is located north of the Chateau and northwest of the Chalet. The dormitory is a wood frame structure with peaked dormers above the second story windows. Additions made in 1940 and 1972 nearly tripled the buildings footprint; however, the original portion of the building is the oldest structure in the historic district.[6]
- Construction of the Ranger Residence was begun in late 1935 and completed in early 1936. The structure was built on a steep slope south and upslope from the Chalet. The building was designed by Francis Lange, resident landscape architect at Crater Lake National Park. It is a one-story structure with a living room, combined kitchen-dining room, and two bedrooms. In 1974, the building was converted to office space.[6]
- The Checking and Comfort Station was built in 1941. It is a wood frame building with cedar-bark sheathing near the monument’s day-use parking area. Rustic stone masonry was added to the north side of the building in the 1960s. The building was made handicapped accessible in 1979. Today, the facility is used as a visitor contact center and restrooms.[6]
- *Chateau courtyard
 *Chalet Breezeway
*Chalet Breezeway *Trail to Guide Dorm
*Trail to Guide Dorm *Ranger Residence
*Ranger Residence
In addition to the existing structures in the historic district, there were seven rustic duplex-cabins built on a step slope south of the Chalet behind the Ranger Residence. These cabins were constructed in 1926, as rental units for park guests. After 1935, some were also used as ranger residences. Each cabin was slightly different due to unique site topography. However, all of the cabins had cedar-bark sheathing and gabled roofs that matched the features of the nearby Chateau and Chalet. The cabins were removed in 1988.[6]
Setting
The Oregon Caves National Monument is located on Mount Elijah in the Siskiyou Mountains. It is sited on 480 acres (1.9 km2) in upper Cave Creek Canyon with elevations ranging from 3,800 feet (1,200 m) to 5,450 feet (1,660 m) above sea level. Cave Creek originates inside the Oregon Caves emerges near the Chateau. The creek flows westward through a steep canyon out of the monument.[6]
The natural environment surrounding the Oregon Caves Historic District has not changes significantly since the historic structures were built. The overall site design and landscaping successfully blended the historic structures into the natural setting. The Chalet and Chateau are located on the canyon bench near the cave entrance with the Ranger Residence and Guide Dormitory sited along opposite sides of the canyon. A plaza area is located between the Chalet and Chateau. The Plaza landscaping and stone masonry walls provide shade and rustic accent that highlight the historic district’s primary buildings. In addition, the surrounding forest is dense and hides the service road, adding to the district’s rustic feeling.[7]
Access
The Oregon Cave Historic District is within the boundaries of the Oregon Caves National Monument. The monument is located in the Siskiyou Mountains of southwest Oregon, seven miles (11 km) north of the Oregon-California border. It is 20 miles (32 km) east of Cave Junction, Oregon on Oregon Highway 46 which terminates at the monument’s day-use parking lot.[6]
The weather in the Oregon Caves area is generally moderate. However, storms can occur without warning and are sometimes very intense. In addition, fog is common in the winter and early spring. The average rainfall is approximately 50 inches (1.3 m) per year, and the average annual snowfall is 160 inches (4.1 m). During the winter, the access highway is often closed temporarily during heavy snow storms.[6]
See also
References
- ↑ Mark, Stephen R. (June 1991), National Register of Historic Places Registration Form: Oregon Caves Historic District (PDF), retrieved May 19, 2014.
- ↑ Glanville, Abby (February 2010), National Register of Historic Places Registration Form: Oregon Caves Historic District (Boundary Increase) (PDF), retrieved May 19, 2014.
- 1 2 Oregon Parks and Recreation Department, Oregon Historic Sites Database, retrieved May 19, 2014.
- ↑ "Elijah Davidson's story by Tom Siewert", National Park Service, United States Department of Interior, 4 November 2006.
- ↑ "History and Culture", National Park Service, United States Department of Interior, 8 November 2007.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Gilbert, Cathy and Marsha Tolon, "Cultural Landscape Inventory of Oregon Caves National Monument", Cultural Landscape Report, National Park Service, United States Department of Interior, Seattle, Washington, Winter 1992.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Statement of Significance", Oregon Caves Culture Landscape Report, National Park Service, United States Department of Interior, 5 February 2002.
- ↑ "Oregon Caves Historic District", National Register of Historic Places, www.nationalregisterofhistoricalplaces.com, 4 May 2008.
- 1 2 "Oregon Caves Historic District: A Cultural Legacy", National Park Service, United States Department of Interior, 19 August 2007.
External links
 Media related to Oregon Caves Historic District at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Oregon Caves Historic District at Wikimedia Commons- Oregon Caves National Monument
- National Park Service