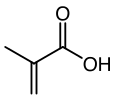
Methacrylic acid
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Methylprop-2-enoic acid | |||
| Other names
Methacrylic acid 2-Methyl-2-propenoic acid α-Methacrylic acid 2-Methylacrylic acid 2-Methylpropenoic acid | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 79-41-4 | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| Abbreviations | MAA | ||
| ChEBI | CHEBI:25219 | ||
| ChemSpider | 3951 | ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.096 | ||
| EC Number | 201-204-4 | ||
| MeSH | C008384 | ||
| PubChem | 4093 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H6O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 86.06 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid or solid | ||
| Odor | Acrid, repulsive[1] | ||
| Density | 1.015 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 14 to 15 °C (57 to 59 °F; 287 to 288 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 161 °C (322 °F; 434 K) | ||
| 9% (25 °C)[1] | |||
| Vapor pressure | 0.7 mmHg (20 °C)[1] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Flash point | 77.2 °C (171.0 °F; 350.3 K) | ||
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |||
| PEL (Permissible) |
none[1] | ||
| REL (Recommended) |
TWA 20 ppm (70 mg/m3) [skin][1] | ||
| IDLH (Immediate danger) |
N.D.[1] | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Methacrylic acid, abbreviated MAA, is an organic compound. This colorless, viscous liquid is a carboxylic acid with an acrid unpleasant odor. It is soluble in warm water and miscible with most organic solvents. Methacrylic acid is produced industrially on a large scale as a precursor to its esters, especially methyl methacrylate (MMA) and poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA). The methacrylates have numerous uses, most notably in the manufacture of polymers with trade names such as Lucite and Plexiglas. MAA occurs naturally in small amounts in the oil of Roman chamomile.
Production and properties
More than 3 million tons of methyl methacrylate (MMA) are produced annually. In one route, acetone cyanohydrin is converted to methacrylamide sulfate using sulfuric acid. That compound is hydrolyzed to methacrylic acid, or it can be converted into methyl methacrylate in one step. In the second route, isobutylene or tert-butanol are oxidized to methacrolein, then methacrylic acid. Methacrolein for this purpose can also be obtained from formaldehyde and ethylene. Isobutyric acid can also be dehydrogenated to methacrylic acid.[2]
Methacrylic acid was first obtained in the form of its ethyl ester by treating phosphorus pentachloride with oxyisobutyric ester (A synonym for beta-hydroxy-butyric acid or 3-hydroxybutyric acid[3]) .[4] It is, however, more readily obtained by boiling citra- or meso-brompyrotartaric acids with alkalis. It crystallizes in prisms. When fused with an alkali, it forms propanoic acid. Sodium amalgam reduces it to isobutyric acid. A polymeric form of methacrylic acid was described in 1880.[5]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0386". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ William Bauer, Jr. "Methacrylic Acid and Derivatives" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a16_441. Article Online Posting Date: June 15, 2000
- ↑ https://www.vocabulary.com/dictionary/oxybutyric%20acid
- ↑ Edward Frankland Annalen, 1865, 136, p. 12
- ↑ F. Engelhorn et al. Ann., 1880, 200, p. 70.