Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy
| Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy | |
|---|---|
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | neurology |
| ICD-10 | G71.0 |
| ICD-9-CM | 359.1 |
| OMIM | 159000 159001 607801 603511 602067 608423 609115 253600 253601 253700 608099 604286 601287 601954 254110 607155 608807 609308 611307 611588 607439 606822 |
| DiseasesDB | 32189 |
| MedlinePlus | 000711 |
| eMedicine | neuro/189 |
| MeSH | D049288 |
| GeneReviews | |
Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD) or Erb's muscular dystrophy [1] is a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of rare muscular dystrophies.[2] It is characterised by progressive muscle wasting which affects predominantly hip and shoulder muscles.LGMD has an autosomal pattern of inheritance and currently has no known cure.[3]
Signs and symptoms
The symptoms of an individual with Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD) generally has difficulty walking, going both up and down stairs and raising from a chair. Difficulty bending over and falling on a regular basis are also common. Difficulty lifting certain objects is also a common presentation of LGMD as well as difficulty holding your arms out or above your head. Eventually the ability to walk/run deteriorates.[4][5]
Further presentations an individual with LGMD might have are:
 |
PVC (a type of palpitation) recording
An audio clip recording of a PVC symptom, made with a cardiac event monitor. |
| Problems playing this file? See media help. | |
- Pseudohypertrophy[4]
- Muscle hypertrophy[6]
- Respiratory muscle problems[6]
- Low back discomfort[4]
- Palpitation[4]
- Distal muscle problems[6]
- Facial muscle weakness[4]
- Weak shoulder muscle [4]
The disease inevitably gets worse over time, although progression is more rapid in some patients than others. Eventually the disease can affect other muscles such as the ones located in the face. The disease commonly leads to dependence on a wheelchair within years of symptom onset, but there is high inter-patient variability, with some patients maintaining mobility.[3][4]
The muscle weakness is generally symmetric, proximal, and slowly progressive. In most cases, pain is not present with LGMD, and mental function is not affected. LGMD can begin in childhood, adolescence, young adulthood or even later, the age of onset is usually between 10 and 30. Both genders are affected equally, when limb-girdle muscular dystrophy begins in childhood the progression appears to be faster and the disease more disabling. When the disorder begins in adolescence or adulthood the disease is generally not as severe and progresses more slowly.There is no sensory neuropathy or autonomic or visceral dysfunction at presentation.
Genetics
In terms of the genetics of LGMD is an inherited disorder, though it may be inherited as a dominant or recessive genetic defect. The result of the defect is that the muscles cannot properly form certain proteins needed for normal muscle function. Several different proteins can be affected, and the specific protein that is absent or defective identifies the specific type of muscular dystrophy. Among the proteins affected in LGMD are α, β, γ and δ sarcoglycans. The sarcoglycanopathies could be possibly amenable to gene therapy.[7]
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy can be done via muscle biopsy, which will show the presence of muscular dystrophy, and genetic testing is used to determine which type of muscular dystrophy a patient has. Immunohistochemical dystrophin tests can indicate a decrease in dystrophin detected in sarcoglycanopathies. In terms of sarcoglycan deficiency there can be variance (if α-sarcoglycan and γ-sarcoglycan are not present then there's a mutation in LGMD2D).[5]
The 2014 Evidence-based guideline summary: Diagnosis and treatment of limb-girdle and distal dystrophies indicates that individuals suspected of having the inherited disorder should have genetic testing. Other tests/analysis are:[5][8]
- High CK levels(x10-150 times normal)
- MRI can indicate different types of LGMD.
- EMG can confirm the myopathic characteristic of the disease.
- Electrocardiography (cardiac arrhythmias in LGMD1B can occur)
Types
The "LGMD1" family is autosomal dominant, and the "LGMD2" family is autosomal recessive.[3] Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy is explained in terms of gene, locus,OMIM and type as follows:
| Family | Inheritance | Type | OMIM | Gene | Locus | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LGMD1 | autosomal dominant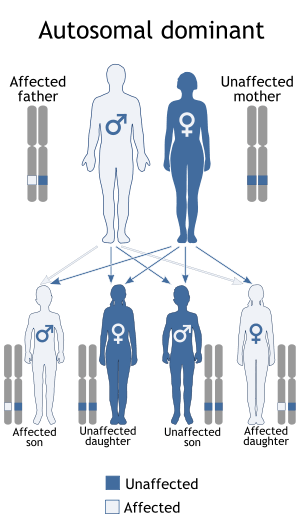 138pixels | LGMD1A | 159000 | TTID | ||
| LGMD1B | 159001 | LMNA | ||||
| LGMD1C | 607801 | CAV3 | ||||
| LGMD1D | 603511 | DNAJB6 | ||||
| LGMD1E | 601419 | DES | ||||
| LGMD1F | 608423 | TNPO3 | 7q32.1–q32.2 | |||
| LGMD1G | 609115 | HNRPDL | 4q21 | |||
| LGMD1H | 613530 | 3p25.1–p23 | ||||
| LGMD2 | autosomal recessive 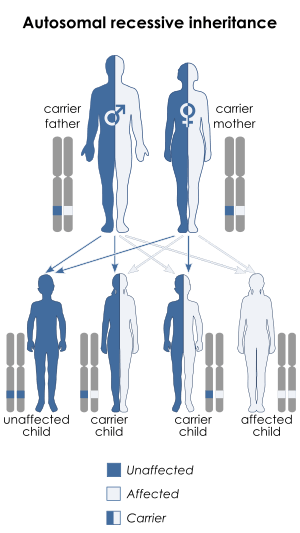 | LGMD2A | 253600 | CAPN3 | ||
| LGMD2B | 253601 | DYSF | ||||
| LGMD2C | 253700 | SGCG | ||||
| LGMD2D | 608099 | SGCA | ||||
| LGMD2E | 604286 | SGCB | ||||
| LGMD2F | 601287 | SGCD | ||||
| LGMD2G | 601954 | TCAP | ||||
| LGMD2H | 254110 | TRIM32 | ||||
| LGMD2I | 607155 | FKRP | ||||
| LGMD2J | 608807 | TTN | ||||
| LGMD2K | 609308 | POMT1 | ||||
| LGMD2L | 611307 | ANO5 | ||||
| LGMD2M | 611588 | FKTN | ||||
| LGMD2N | 607439 | POMT2 | ||||
| LGMD2O | 606822 | POMGNT1 | ||||
| LGMD2Q | 613723 | PLEC1 |
Treatment

Treatment for limb-girdle muscular dystrophy can take the form of exercise and physical therapy which are advised to maintain as much muscle strength and joint flexibility as possible, there are few studies corroborating the effectiveness of exercise. Physical therapy and exercise may prevent the rapid progression of the disease rather than halt or reverse it.[9] Calipers,as an example, may be used to maintain mobility and quality of life. Careful attention to lung and heart health is required, corticosteroids in LGMD 2C-F individuals, shows some improvement [6] Additionally individuals can follow management that follows:[8]
- Occupational therapy
- Respiratory therapy
- Speech therapy
- Neutralizing antibody to myostatin should not be pursued
In terms of the prognosis of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy in its mildest form, affected individuals have near-normal muscle strength and function.LGMD isn't typically a fatal disease,though it may eventually weaken the heart and respiratory muscles, leading to illness or death due to secondary disorders. The frequency of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy ranges from 1 in 14,500 (in some instances 1 in 123,000)[2][3]
Research
There is a variety of research under way targeted at various forms of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy. Among the methods thought to hold promise for treatment include gene transfer therapy,[10] which works by inserting in cells of defective genes with a healthy gene.[11]
According to a review by Bengtsson et al. some success with AAV-mediated gene therapies (for different disorders) have increased interest in researchers, with CRISPR/Cas9 and exon-skipping helping these therapeutic goals along. Limb-girdle muscular dystrophies has many different types which are due to different gene mutations. LGMD2D is caused by a mutation in the α-sarcoglycan gene.Future treatment could be had by gene therapy through recombinant adeno-associated vectors.[12]
Conversely, according to a review by Straub, et al. there are several research issues that need to be targeted, the rareness of the disease, our poor understanding of the mechanism of LGMD2, and absence of patient cohorts, consequently biomarkers for individuals with LGMD2 are lacking. The review goes on to state that animal models for LGMD2 have been used to analyse therapeutic medications. Also adding that while prednisone has been used and has had positive effects on affected LGMD2 individuals there is still no evidence of its effectiveness in trials that are placebo-controlled[13]
References
- ↑ Newfoundland, FRCP William Pryse-Phillips MD, FRCP(C) Faculty of Medicine Health Sciences Centre Memorial University of Newfoundland St John's (2009-05-06). Companion to Clinical Neurology. Oxford University Press, USA. p. 579. ISBN 9780199710041.
- 1 2 https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/limb-girdle-muscular-dystrophy
- 1 2 3 4 Pegoraro, Elena; Hoffman, Eric P. (1993-01-01). Pagon, Roberta A.; Adam, Margaret P.; Ardinger, Holly H.; Wallace, Stephanie E.; Amemiya, Anne; Bean, Lora JH; Bird, Thomas D.; Fong, Chin-To; Mefford, Heather C., eds. Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophy Overview. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle. PMID 20301582.update 2012
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 MedlinePlus Encyclopedia Limb-girdle muscular dystrophies
- 1 2 3 http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1170911-overview
- 1 2 3 4 http://patient.info/doctor/limb-girdle-muscular-dystrophy
- ↑ Reference, Genetics Home. "limb-girdle muscular dystrophy". Genetics Home Reference. Retrieved 2016-04-22.
- 1 2 Narayanaswami, Pushpa; Weiss, Michael; Selcen, Duygu; David, William; Raynor, Elizabeth; Carter, Gregory; Wicklund, Matthew; Barohn, Richard J.; Ensrud, Erik (2014-10-14). "Evidence-based guideline summary: Diagnosis and treatment of limb-girdle and distal dystrophies". Neurology. 83 (16): 1453–1463. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000000892. ISSN 0028-3878. PMC 4206155
 . PMID 25313375.
. PMID 25313375. - ↑ Medicine and Rehabilitation for Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophy Treatment & Management ~treatmentPhysical Medicine and Rehabilitation for Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophy Treatment & Management at eMedicine
- ↑ Liaison, Melanie Martinez, Office of Communications and Public. "Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophy". www.niams.nih.gov. Retrieved 2016-04-22.
- ↑ Reference, Genetics Home. "How does gene therapy work?". Genetics Home Reference. Retrieved 2016-04-23.
- ↑ Bengtsson, Niclas E.; Seto, Jane T.; Hall, John K.; Chamberlain, Jeffrey S.; Odom, Guy L. (2016-04-15). "Progress and prospects of gene therapy clinical trials for the muscular dystrophies". Human Molecular Genetics. 25 (R1): R9–R17. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddv420. ISSN 0964-6906. PMC 4802376
 . PMID 26450518.
. PMID 26450518. - ↑ Straub, Volker; Bertoli, Marta (2016-02-01). "Where do we stand in trial readiness for autosomal recessive limb girdle muscular dystrophies?". Neuromuscular Disorders. 26 (2): 111–125. doi:10.1016/j.nmd.2015.11.012. – via ScienceDirect (Subscription may be required or content may be available in libraries.)
Further reading
- Cotta, Ana; Carvalho, Elmano; da-Cunha-Júnior, Antonio Lopes; Paim, Júlia Filardi; Navarro, Monica M.; Valicek, Jaquelin; Menezes, Miriam Melo; Nunes, Simone Vilela; Xavier Neto, Rafael. "Common recessive limb girdle muscular dystrophies differential diagnosis: why and how?". Arquivos de Neuro-Psiquiatria. 72 (9): 721–734. doi:10.1590/0004-282X20140110. ISSN 0004-282X.
- Liu, Jian; Harper, Scott Q. (2012-08-01). "RNAi-based Gene Therapy for Dominant Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophies". Current gene therapy. 12 (4): 307–314. doi:10.2174/156652312802083585. ISSN 1566-5232. PMC 4120526
 . PMID 22856606.
. PMID 22856606. - ANGELINI, CORRADO; TASCA, ELISABETTA; NASCIMBENI, ANNA CHIARA; FANIN, MARINA (2014-12-01). "Muscle fatigue, nNOS and muscle fiber atrophy in limb girdle muscular dystrophy". Acta Myologica. 33 (3): 119–126. ISSN 1128-2460. PMC 4369848
 . PMID 25873780.
. PMID 25873780.