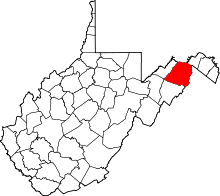
Hampshire County Courthouse (West Virginia)
|
Hampshire County Courthouse | |
|
Hampshire County Courthouse shortly after its construction, 1920s | |
  | |
| Location | 66 N. High St., Romney, West Virginia |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 39°20′32″N 78°45′22″W / 39.34222°N 78.75611°WCoordinates: 39°20′32″N 78°45′22″W / 39.34222°N 78.75611°W |
| Area | less than one acre |
| Built | 1922 |
| Architect | Holmboe & Pogue[1] |
| Architectural style | Neoclassical Revival |
| MPS | County Courthouses of West Virginia MPS |
| NRHP Reference # | 05001006[2] |
| Added to NRHP | September 7, 2005 |
The Hampshire County Courthouse is a Neoclassical edifice in the center of downtown Romney, county seat of Hampshire County, West Virginia. The present building was constructed in 1922 to replace the previous 1833 Neoclassical courthouse that had been destroyed by fire in 1921. The original bell from the 1833 courthouse hangs in the domed bell tower.[3]
Civil War history
During the Civil War, John Baker White was the Clerk of Court for the courthouse.
No court proceedings convened in Hampshire County between 1861 and 1864[4][5] and the county's courthouse was utilized as a stable by Union soldiers stationed in Romney during the war.[6][7]
Upon learning of this, White was again concerned for the safety of the county's records and proceeded to load land registration records ledger books onto wagons[6][7] and had them transported to Winchester for safekeeping.[6][7] White selected for transport only the bound volumes of records which included "deed books, wills, and settlements of estates" and kept the unbound paper records in the courthouse, thus separating them so that the entirety of the county's records could not be destroyed by Union forces.[6][7] White likely chose to transport the bound volumes of records, as the loose paper records would have been more cumbersome to keep together.[7]
In 1863, when Winchester was no longer a safe location for the storage of Hampshire County's records and they again risked destruction by Union Army forces,[6][7] White's son Captain Christian Streit White took responsibility for the records and transferred them to Front Royal.[7][8] When Front Royal became endangered by advancing Union Army forces, Captain White had the records moved to Luray Caverns where they remained for several months.[5][7][8] In the Fall of 1864, the county's record books were rescued by Captain White and his company as Union Army troops were in the process of destroying them.[7][8] Captain White's company loaded about 150 record books into a wagon and they were taken to North Carolina where they remained safely for the duration of the war.[5][7][8] Hampshire County's land records survived and were returned to the courthouse following the conclusion of the American Civil War,[5] likely by a soldier returning to the area from North Carolina.[8] Had White not separated the records and sent the bound volumes away for safekeeping, Hampshire County would have lost all its records during the course of the war, as those that remained in the courthouse were destroyed.[6]
Miscellany
The original cast iron fence that surrounded the 1833 courthouse was removed during reconstruction of the present courthouse and relocated to the Hiett Graveyard on North River between the communities of North River Mills and Pleasant Dale.[9]
Gallery
-

1833 Courthouse
-
View of Romney with the 1922 Courthouse visible on the right
References
- ↑ American Contractor 18 June 1921: 69. Chicago.
- ↑ National Park Service (2010-07-09). "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service.
- ↑ "Historic Buildings and Sites". Hampshire County Convention and Visitors Bureau website. Hampshire County Convention and Visitors Bureau. 2007-09-30.
- ↑ Maxwell 1897, p. 278.
- 1 2 3 4 Munske 2004, p. 40.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Maxwell 1897, p. 370.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 "Guide to the (West) Virginia Court Documents Collection", Marietta College Library, Marietta College, retrieved June 19, 2013
- 1 2 3 4 5 Maxwell 1897, p. 371.
- ↑ "HIETT (Jonathan) Graveyard". Wayne McGahuey Hampshire County Cemetery Project. HistoricHampshire.org. 2007-09-30.
See also
- List of historic sites in Hampshire County, West Virginia
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Hampshire County, West Virginia