EGTA (chemical)
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
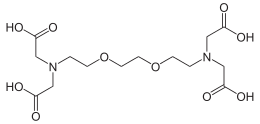
| IUPAC name
Ethylene glycol-bis(2-aminoethylether)-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid | |
| Other names
Triethylene glycol diamine tetraacetic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 67-42-5 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:30740 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL240390 |
| ChemSpider | 5972 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.592 |
| KEGG | D00569 |
| PubChem | 6207 |
| UNII | 526U7A2651 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H24N2O10 | |
| Molar mass | 380.35 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 241 °C (466 °F; 514 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
EGTA (ethylene glycol-bis(β-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid) is an aminopolycarboxylic acid, a chelating agent. It is a colourless solid that is related to the better known EDTA. Compared to EDTA, it has a lower affinity for magnesium, making it more selective for calcium ions. It is useful in buffer solutions that resemble the environment in living cells[1] where calcium ions are usually at least a thousandfold less concentrated than magnesium.
The pKa for binding of calcium ions by tetrabasic EGTA is 11.00, but the protonated forms do not significantly contribute to binding, so at pH 7, the apparent pKa becomes 6.91. See Qin et al. for an example of a pKa calculation.[2]
EGTA has also been used experimentally for the treatment of animals with cerium poisoning and for the separation of thorium from the mineral monazite. EGTA is used as a compound in elution buffer in the protein purification technique known as tandem affinity purification, in which recombinant fusion proteins are bound to calmodulin beads and eluted out by adding EGTA.
EGTA is often employed in dentistry and endodontics for the removal of the smear layer.
See also
References
- ↑ Bett, Glenna C. L.; Rasmusson, Randall L. (2002). "1. Computer Models of Ion Channels". In Cabo, Candido; Rosenbaum, David S. Quantitative Cardiac Electrophysiology. Marcel Dekker. p. 48. ISBN 0-8247-0774-5.
- ↑ Ning Qin; Riccardo Olcese; Michael Bransby; Tony Lin; Lutz Birnbaumer (March 1999). "Ca2+-induced inhibition of the cardiac Ca2+ channel depends on calmodulin". PNAS. 96 (5): 2435–2438. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.5.2435. PMC 26802
 . PMID 10051660. Retrieved 2007-10-22.
. PMID 10051660. Retrieved 2007-10-22.