Arkhangelsk Governorate
Coordinates: 64°32′N 40°32′E / 64.533°N 40.533°E
| Arkhangelsk Governorate Архангельская губерния | |||||
| Governorate of the Russian Empire, Russian Republic, Soviet Russia | |||||
| |||||
|
Coat of arms | |||||
 | |||||
| Capital | Arkhangelsk | ||||
| History | |||||
| • | Established | 12 December 1796 | |||
| • | Disestablished | 14 January 1929 | |||
| Political subdivisions | nine uyezds | ||||
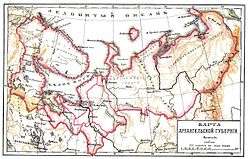
Arkhangelsk Governorate (Russian: Архангельская губерния, Arkhangelskaya guberniya) was an administrative division (a guberniya) of the Russian Empire, which existed from 1796 until 1929. Its seat was in Arkhangelsk. The governorate was located in the north of Russian Empire and bordered Tobolsk Governorate in the south-east, Vologda Governorate in the south, Olonets Governorate in the southwest, Sweden (later Grand Duchy of Finland and later independent Finland) in the west, and Norway in north-west. In the north, the governorate was limited by the White and Barents Seas.
The area of the governorate is currently split between Arkhangelsk and Murmansk Oblasts, the Komi Republic, the Republic of Karelia, and the Nenets Autonomous Okrug.
History
.jpg)
In 1780, Archangelgorod Governorate, with the center in Arkhangelsk, was abolished and transformed to Vologda Viceroyalty. The viceroyalty was subdivided into three oblasts: Vologda, Veliky Ustyug, and Arkhangelsk. On 26 March 1784 Arkhangelsk Oblast was split off and established as Arkhangelsk Viceroyalty. Tsar Paul I on 12 December 1796 issued a decree remaining Arkhangelsk Viceroyalty into Arkhangelsk Governorate. Simultaneously, Olonets Viceroyalty was abolished, and Kemsky Uyezd and about a half of Povenetsky Uyezd were transferred to Arkhangelsk Governorate.[1]
In 1780, Arkhangelsk Oblast (and later on Arkhangelsk Viceroyalty) was subdivided into seven uyezds (the administrative centers, which all had the town status, are given in parentheses),
- Arkhangelsky Uyezd (Arkhangelsk)
- Kholmogorsky Uyezd (Kholmogory)
- Kolsky Uyezd (Kola)
- Mezensky Uyezd (Mezen)
- Onezhsky Uyezd (Onega)
- Pinezhsky Uyezd (Pinega)
- Shenkursky Uyezd (Shenkursk)
Mezen, Onega, and Pinega were incorporated as towns in 1780 just to become the uyezd towns. Kola was incorporated in 1784.
In 1801, the portions of Povenetsky Uyezd were transferred to Olonets Governorate, and Kemsky Uyezd, with the center in Kem, was left in Arkhangelsk Governorate. In 1854, the town of Kola was destroyed during the Crimean War, and Kolsky Uyezd was merged into Kemsky Uyezd. In 1883, Kolsky Uyezd was restored, but in 1899, the uezd ceter was transferred to Aleksandrovsk, and the uyezd renamed into Aleksandrovsky Uyezd. In 1891, Pechorsky Uyezd with the center in Ust-Tsilma was split off from Mezensky Uyezd.
The governorate structure remained in place after the 1917 revolution. In 1917, the governorate thus comprised nine uyezds. On 2 March 1918, Ust-Vashsky Uyezd with the center in Ust-Vashka split off from Mezensky Uyezd (On 6 February 1922 it was abolished and merged back into Mezensky Uyezd). Also in 1918, the western part of Aleksandrovsky Uyezd was transferred to Finland, which became independent, and the rest of the uyezd was incorporated as Murmansk Governorate. In 1920, Kemsky Uyezd was transferred to Karel Labour Commune, which later became the Karelian Socialist Soviet Republic. In 1922, the majorn part of Pechorsky District moved to the newly established Komi-Zyryan Autonomous Oblast. On 15 March 1922 Kholmogorsky Uyezd was renamed into Yemetsky Uyezd, with the transfer of the uyezd town from Kholmogory to Yemetsk.
In the following, administrative changes in the governorate occurred almost on the yearly basis. In 1928, the governorate consisted of five uyezds: Arkhangelsky, Mezensky, Onezhsky, Pechorsky, and Shenkursky.[1]
On 14 January 1929 by the All-Russian Central Executive Committee three governorates (Arkhangelsk, Vologda, and Northern Dvina) and Komi-Zyryan Autonomous Oblast were merged into Northern Krai.
Governors
The administration tasks in the vice-royalty were shared between a governor and a governor general; the governorate had a military governor and a (civil) governor; the military governors were not always appointed. Sometimes a governor general was appointed. The governors of Arkhangelogorod Viceroyalty were[2]
- 1784–1796 Ivan Romanovich Liven (Johann Christophor Lieven), a governor
- 1796–1797 Ivan Ilyich Grevens, a governor
- 1784–1793 Timofey Ivanovich Tutolmin, a governor general;
- 1793–1796 Pyotr Petrovich Konovnitsyn, a governor general;
- 1796 Ivan Romanovich Liven, a governor general.
The governors of Arkhangelsk Governorate were[2]
- 1797 Dmitry Fyodorovich Glinka;
- 1797–1798 Nikolay Isayevich Akhverdov;
- 1798–1799 Nazariy Stepanovich Muravyov;
- 1799–1802 Ivan Fyodorovich Mezentsev;
- 1802 Alexey Matveyevich Okulov;
- 1802–1803 Pyotr Fyodorovich Martyanov, acting governor;
- 1803–1804 Alexandr Matveyevich Veryovkin;
- 1804–1805 Pyotr Fyodorovich Martyanov, acting governor;
- 1805–1807 Kazimir Ash;
- 1807–1823 Andrey Yakovlevich Perfilyev;
- 1823–1824 Nikolay Sergeyevich Tukhachevsky;
- 1824–1827 Yakov Fyodorovich Ganskau;
- 1827–1829 Ivan Yakovlevich Bukharin;
- 1829–1831 Vladimir Sergeyevich Filimonov;
- 1831–1837 Ilya Ivanovich Ogaryov;
- 1837 Viktor Yakovlevich Roslavets;
- 1837 Nikolay Ivanovich Khmelnitsky;
- 1837–1839 Alexander Nikolayevich Muravyov, formerly sentenced as a decembrist;
- 1839–1842 Platon Viktorovich Stepanov;
- 1842–1843 Mikhail Fyodorovich Nozhin, acting governor;
- 1843–1856 Vilem (Vikentiy) Frantsevich Fribers;
- 1856–1863 Nikolay Ivanovich Arandarenko;
- 1863–1866 Nikolay Martynovich Garting;
- 1866 Alexey Gavrilovich Kaznacheyev;
- 1866–1869 Sergey Pavlovich Gagarin;
- 1869–1870 Nikolay Alexandrovich Kachalov;
- 1871–1880 Nikolay Pavlovich Ignatyev;
- 1880–1881 Modest Mavrikiyevich Koniar;
- 1881–1882 Nikolay Mikhaylovich Baranov;
- 1882–1883 Pyotr Alexeyevich Poltoratsky;
- 1883 Nikolay Pavlovich Shchepkin;
- 1883–1885 Konstantin Ivanovich Pashchenko;
- 1885–1893 Nikolay Dmitrievich Golitsyn, later the last Imperial Prime Minister of Russia;
- 1893–1901 Alexander Platonovich Engelgardt;
- 1901–1904 Nikolay Aleksandrovich Rimsky-Korsakov;
- 1904–1905 Nikolay Georgievich fon Byunting (von Bünting);
- 1905–1907 Nikolay Nikolayevich Kachalov;
- 1907–1911 Ivan Vasilyevich Sosnovsky;
- 1911–1917 Sergey Dmitriyevich Bibikov.
After February 1917, the highest authority in the governorate belonged to the Comissar of the Governorate, and after November 1917 – to the Governorate Executive Committee (with the exception of the period of the Civil War in Russia, when Arkhangelsk was occupied by the Entente troops). The governors were not appointed any more.
The military governors of Arkhangelsk Governorate were[2]
- 1797–1798 Ivan Romanovich Liven;
- 1798 Boris Borisovich Letstsano (Lezzano);
- 1798 Dmitry Ivanovich Lobanov-Rostovsky;
- 1798–1799 Dmitry Petrovich Volkonsky;
- 1799–1801 Karl Andreyevich Liven;
- 1802–1803 Sergey Andreyevich Bekleshov;
- 1803–1807 Ivan Petrovich Ferster;
- 1807–1811 Martin Petrovich Dezin;
- 1811–1813 Alexey Grigoryevich Spiridov;
- 1813–1820 Alexey Fedotovich Klokachyov;
- 1842–1850 Alexander Ivanovich Traverse;
- 1850–1854 Roman Platonovich Boil;
- 1854–1857 Stepan Petrovich Khrushchov;
- 1857–1859 Bogdan Alexandrovich Glazenap;
- 1907 Dmitry Davidovich Grigoryev.
The following governors general were appointed,[2]
- 1820–1823 Alexey Fedotovich Klokachyov;
- 1823–1830 Stepan Ivanovich Minitsky;
- 1836–1842 Iosif Ivanovich Sulima;
- 1862–? Konstantin Ivanovich Istomin;
- 1915 Arkady Mikhaylovich Valuyev, acting governor general.
Demography
Language
- By the Imperial census of 1897.[3]
| Language | Number | percentage (%) | males | females |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Russian | 294 865 | 85.1 | 139 174 | 155 691 |
| Zyrian | 23 259 | 6.7 | 11 058 | 12 201 |
| Karelian | 19 522 | 5.6 | 8737 | 10785 |
| Samoyedic | 3 874 | 1.1 | 2 030 | 1 844 |
| Lappish | 1 742 | 0.5 | 870 | 872 |
| Finnish | 1 276 | 0.4 | 645 | 631 |
| Polish | 456 | 0.0 | 350 | 106 |
| German | 309 | 0.0 | 118 | 191 |
| Belarusian | 256 | 0.0 | 133 | 123 |
| Yiddish | 253 | 0.0 | 156 | 97 |
| Norwegian and Danish | 226 | 0.0 | 125 | 101 |
| Romani | 147 | 0.0 | 84 | 63 |
| Lithuanian | 81 | 0.0 | 80 | 1 |
| Ukrainian | 51 | 0.0 | 45 | 6 |
| Estonian | 76 | 0.0 | 70 | 6 |
| Other | 143 | 0.0 | 109 | 34 |
| Total | 346 536 | 100.0 | 163 784 | 182 752 |
References
- 1 2 "Административно-территориальное деление Архангельской губернии в XVIII-XX вв." (in Russian). Архивы России. 2000. Archived from the original on 24 July 2011. Retrieved 25 August 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 Архангельская область (in Russian). narod.ru. Retrieved 25 August 2011.
- ↑ Language Statistics of 1897 (Russian)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Arkhangelsk Governorate. |
.png)