Alveolar soft part sarcoma
| Alveolar soft part sarcoma | |
|---|---|
|
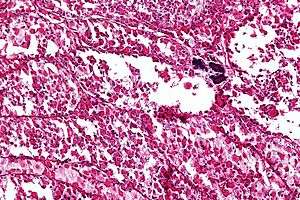
Micrograph of an alveolar soft part sarcoma, showing the characteristic alveolar-like architecture and cells with eccentric nuclei and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm. H&E stain. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| ICD-O | M9581/3 |
| OMIM | 606243 |
| MeSH | D018234 |
Alveolar soft part sarcoma, abbreviated ASPS, is a very rare type of soft-tissue sarcoma, that grows slowly and whose cell of origin is unknown.
It arises mainly in children and young adults. ASPS can migrate (metastasize) into other parts of the body, typically the lungs and the brain.
ASPS is a sarcoma, and that indicates that this cancer initially arises from tissue of embryonic mesenchymal origin. (The fertilized egg divides and redivides forming a sphere. Early in embryogenesis, dimples appear in the poles of the sphere and burrow through the sphere forming an inner passage that will ultimately form the gut. Malignancies arising from cells that were originally part of the outer layer of the sphere and those that were part of the embryonic tunnel are termed carcinomas; malignancies arising from the cells between the outer layer and the inner burrow are termed sarcomas.) Typically, ASPS arises in muscles and deep soft tissue of the thigh or the leg (lower extremities), but can also appear in the upper extremities (hands, neck, and head). While ASPS is a soft tissue sarcoma, it can also spread and grow inside the bones.
The term alveolar comes from the microscopic pattern, visible during the analysis of slides of ASPS under the microscope in histopathology. The tumor cells seem to be arranged in the same pattern as the cells of the small air sacks (alveoli) in the lungs. However, this is just a structural similarity. ASPS was first described and characterized in 1952.[1]
Epidemiology
ASPS is an extremely rare cancer. While sarcomas comprise about 1% of all newly diagnosed cancers, and 15% of all childhood cancers, ASPS comprises less than 1% of sarcomas. According to the American Cancer Society, about 9530 new cases of soft tissue sarcoma will be diagnosed in the USA in 2006. This predicts under 100 new cases of ASPS. Such low numbers of occurrence seriously impede the search for a cure by making it hard to gather any meaningful statistics about the disease. As a result, finding the best treatment option often involves making a lot of educated guesses.
Primary diagnosis
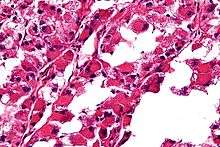
ASPS may exist in the patient’s body for a long time before being diagnosed. It can grow large and push aside surrounding tissues for a long time before causing any discomfort. Therefore, ASPS symptoms may either be a painless swelling, or a soreness caused by compressed nerves or muscles, affecting the range of motion in the area.
Pathology
The definitive diagnosis of ASPS is based on its appearance under the microscope, i.e. its histomorphology, and presence of the characteristic chromosomal translocation.
ASPS' histomorphologic features include an alveolar-like pattern at low magnification and the presence of large cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and eccentric nuclei. Calcifications are commonly present, as may be seen with slow growing neoplasms.
Causes
Chromosomal analysis of ASPS shows the breaking and joining of two chromosomes in the tumor cells. A piece of chromosome X breaks and is joined to chromosome 17.[2] This translocation creates a fusion between two genes named ASPL and TFE3, which results in the formation of an aberrant protein (termed fusion protein) that is not found in normal cells. Two sorts of fusions between chromosome X and chromosome 17 are found in different ASPS tumors: Type one, and type two. Dr. Ladanyi at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, in New York City, has pioneered this work. The first xenograft model of ASPS (for type one) was established in mice by David Vistica at the National Cancer Institute in Frederick, MD in 2009.[3]
Prognosis
Although ASPS displays a relatively indolent course, the ultimate prognosis is poor and is often characterized by late metastases.
Promising clinical trials
- Sunitinib
- Cediranib new trial from England; adult doses have already been established, NCI is currently working on doses for children.
Work out of Huntsman Cancer Institute (HCI) in Utah has demonstrated that ASPS might be driven in part by lactate both being used as a fuel and driving angiogenesis.[4]
ASPS Charities
References
- ↑ Christopherson WM, Foote FW, Stewart FW. "Alveolar soft part sarcomas: structurally characteristic tumors of uncertain histogenesis". Cancer. 1952 (5): 100–111. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(195201)5:1<100::aid-cncr2820050112>3.0.co;2-k.
- ↑ Ladanyi M, Lui MY, Antonescu CR, et al. (January 2001). "The der(17)t(X;17)(p11;q25) of human alveolar soft part sarcoma fuses the TFE3 transcription factor gene to ASPL, a novel gene at 17q25". Oncogene. 20 (1): 48–57. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1204074. PMID 11244503.
- ↑ "Therapeutic vulnerability of an in vivo model of alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS) to antiangiogenic therapy.". J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 31 (8): 561–70. Aug 2009. doi:10.1097/MPH.0b013e3181a6e043. PMC 2784654
 . PMID 19636271.
. PMID 19636271. - ↑ Goodwin ML, Jin H, Straessler K, Smith-Fry K, Zhu JF, Monument MJ, Grossmann A, Randall RL, Capecchi MR, Jones KB. Cancer Cell. 2014 Dec 8;26(6):851-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2014.10.003. Epub 2014 Nov 26. PMID 25453902
- ↑ McFerrin, Jemisha. "Jem's Life ASPS Charity". Jem's Life For ASPS. Retrieved 2014-08-18.
- ↑ Martell, Christie. "Manny Alvarez Foundation". Spear Sarcoma. Retrieved 2016-10-28.
External links
- Torres and Pollock Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma (ASPS) ESUN (December 15, 2010)
- The Alliance Against Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Website dedicated to ASPS patients, information on treatments, etc.
- Cure Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma International An international site with general information, a library, and a discussion group. Organized by patients, and their family and friends