Dwarf shrew
| Dwarf shrew | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Eulipotyphla |
| Family: | Soricidae |
| Genus: | Sorex |
| Species: | S. nanus |
| Binomial name | |
| Sorex nanus Merriam, 1895 | |
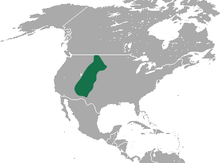 | |
| Dwarf shrew range | |
The dwarf shrew (Sorex nanus) is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is endemic to Arizona, Colorado, Montana, Nebraska, New Mexico, South Dakota, Utah and Wyoming in the United States.[1]
The type locality is Estes Park (Larimer County), Colorado, USA.
Description
As described by their common name, the dwarf shrew is a very small species of shrew, usually weighing 1.8 to 3.2 g. They change their pelage (fur) based on the season to aid in hiding from predators. In summer their pelage is brown to olive brown on the dorsal side, their backs. This color extends down their sides and merges with the smoke gray fur on their stomachs. Their tails are bi-colored, a mixture of dark fur on top and beige fur underneath. During the winter their pelage turns lighter and grayer, especially on their backs, again so they can blend into their surroundings. [1]
Phylogeny
The phylogeny of the dwarf shrew is very controversial. Given the sheer number of species in the genus Sorex it is very difficult to tell all of them apart. There is a phylogeny proposed, and widely accepted now, in which S. vagrans gave rise to S. nanus along with S. longirostris and S. ornatus. This same theory provides evidence that Sorex nanus along with Sorex tenellus diverged more recently than their relatives because they are morphologically indistinguishable from each other except for very small size differences. [3]
Distribution and Habitat
The dwarf shrew lives primarily in mountain habitats, although they will descend as low as 1400 to 1500 m in the mountain ranges where they reside, the foothills of the Great Basin ranges and the Rocky Mountains. The ecological distribution of dwarf shrews isn’t fully known. They have mostly been reported from rocky habitats in the alpine tundra and subalpine coniferous forests. It does seem that the dwarf shrew is more tolerant of dry situations than its other shrew relatives. [1] Dwarf shrews are also found in dry brushy slopes in Colorado around 1,670 m, in sagebrush-grassland in Montana at 1,036-1,128 m, and even at 750 m in Black Hills, South Dakota. This further adds to the mystery of their distribution. [5] Dwarf shrew fossils have been found in late Pleistocene deposits in Hermit’s Cave, New Mexico and Moonshiner and Middle Butte caves in Idaho. [2] In the past mammalogists considered the dwarf shrew to be a rare species. From 1895 to 1966 there were only reports of 18 sightings of the dwarf shrew but a study on a frog in 1966 led to the capture of 24 dwarf shrews using pitfall traps. [1] Another reason that they were thought to be a rare species is that they have a very fragmented distribution throughout southwestern North America and they are easily confused with their closely related shrew family. [4]
References
- 1 2 Hammerson, G. (2008). "Sorex nanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2009.2. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 8 February 2010.
- Don E. Wilson & DeeAnn M. Reeder (editors). 2005. Sorex (Otisorex) nanus. Mammal Species of the World. A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed), Johns Hopkins University Press, 2,142 pp. (Available from Johns Hopkins University Press, 1-800-537-5487 or (410) 516-6900, or at http://www.press.jhu.edu).
[1] Hoffmann, R., & Owen, J. (1980). Sorex tenellus and Sorex nanus. American Society of Mammalogists, 131, 1-4. Retrieved March 12, 2015, from http://www.science.smith.edu/msi/
[2] Emslie, S. (2002). Fossil Shrews (Insectivore Soricidae) from the Late Pleistocene of Colorado. Southwestern Association of Naturalists, 47(1), 62-69. Retrieved March 12, 2015, from JSTOR.
[3] George, S. (1988). Systematics, Historical Biogeography, and Evolution of the Genus Sorex. Journal of Mammalogy, 69(3), 443-461. Retrieved March 12, 2015, from JSTOR.
[4] Hafner, D., & Stahlecker, D. (2002). Distribution of Merriam's Shrew (Sorex merriami) and the Dwarf Shrew (Sorex nanus) and New Records for New Mexico. The Southwestern Naturalist, 47(1), 134-137. Retrieved March 12, 2015, from JSTOR.
[5] Mullican, T., & Carraway, L. (1990). Shrew Remains from Moonshiner and Middle Butte Caves, Idaho. Journal of Mammalogy, 71(3), 351-356. Retrieved March 12, 2015, from JSTOR.
