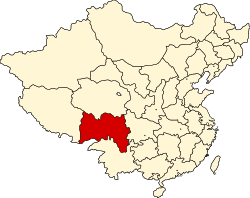
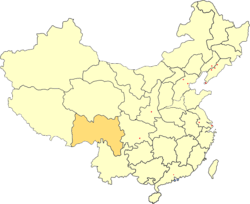
Xikang
| Xikang Province 西康省 | |||||
| | |||||
| |||||
 | |||||
| Capital | Kangding (1912-1931) Ba'an (1931-1935) Ya'an (1935-1936) Kangding (1935-1949) Xichang (1949-1950) | ||||
| Historical era | 20th Century | ||||
| • | Established | 1939 | |||
| • | Fall of Xichang | 27 March 1950 | |||
| • | Disestablished | 1950 | |||
| Area | |||||
| • | Estimate | 451,521 km2 (174,333 sq mi) | |||
| Population | |||||
| • | Estimate | 1,748,458 | |||
| Density | 3.9 /km2 (10 /sq mi) | ||||
| Today part of | | ||||
| Xikang Province 西康省 | |||||
| | |||||
| |||||
 | |||||
| Capital | Kangding (1950-1951) Ya'an (1951-1955) | ||||
| Historical era | 20th Century | ||||
| • | Established | 1950 | |||
| • | Disestablished | 1955 | |||
| Area | |||||
| • | 1953 | 451,521 km2 (174,333 sq mi) | |||
| Population | |||||
| • | 1953 | 3,381,064 | |||
| Density | 7.5 /km2 (19.4 /sq mi) | ||||
| Today part of | | ||||
Xikang or Sikang (Chinese: 西康省; pinyin: Xīkāng Shěng) was a province of the Republic of China comprising most of the Kham region of traditional Tibet, where the Khampa, a subgroup of the Tibetan people, live. The eastern part of the province was inhabited by a number of different ethnic groups, such as Han Chinese, Yi, Qiang people and Tibetan, while the western part of the province was inhabited by Tibetans. Xikang, then known as Chuanbian (川邊), was a special administrative region of the Republic of China until 1939, when it became an official province. The provincial capital was Kangding from 1939 to 1951 and Ya'an from 1951 to 1955. The province had a population of some 3.4 million in 1954.[1]
History
Following the Wuchang Uprising in October 1911 which led to the downfall of the Qing dynasty, this region was established as the Chuanbian Special Administrative District (川邊特別行政區) by the newly founded Republic of China.
In June 1930 this region was invaded by the army of Tibet, precipitating the Sino-Tibetan War. With the district locked in internal struggles, no reinforcements were sent to support the Sichuanese troops stationed here. As a result, the Tibetan army captured, without encountering much resistance, Garze and Xinlong Counties. When a negotiated ceasefire failed, Tibetan forces expanded the war attempting to capture parts of southern Qinghai province. In March 1932 their force invaded Qinghai but was defeated by the local Hui warlord Ma Bufang in July, routing the Tibetan army and driving it back to this district.
The Hui army captured counties that had fallen into the hands of the Tibetan army since 1919. Their victories threatened the supply lines to the Tibetan forces in Garze and Xinlong. As a result, part of the Tibetan army was forced to withdraw.
In 1932 Liu Wenhui in cooperation with the Qinghai army, sent out a brigade to attack the Tibetan troops in Garze and Xinlong, eventually occupying them, Dêgê and other counties east of the Jinshajiang River. The 1934 Khamba Rebellion led by the Pandatsang family broke out against the Tibetan government in Lhasa. The Khampa revolutionary leader Pandatsang Rapga was involved.
In January 1939, the Chuanbian Special Administrative District officially became a province of the Republic, the Sikang Province. Kesang Tsering was sent by the Chinese to Batang to take control of Sikang, where he formed a local government. He was sent there for the purpose of propagating the Three Principles of the People to the Khampa.[2]
In 1950, following the defeat of the Kuomintang by the Communists in the Chinese Civil War, Xikang was split along the Yangtze into Sikang to the east and a separate Chamdo Territory (昌都地区) to the west. Chamdo was merged into Tibet Autonomous Region in 1965. The rest of Sikang was merged into Sichuan in 1955.
Administrative divisions
1939-1950
| Name | Administrative Seat | Traditional Chinese | Subdivisions | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Administrative Circuit | Kangding County | 第一行政督察區 | 4 counties, 1 bureau | Later the Xikang Province Tibetan Autonomous Region |
| Second Administrative Circuit | Yingjing County | 第二行政督察區 | 7 counties | Later the Ya'an Division |
| Third Administrative Circuit | Xichang County | 第三行政督察區 | 9 counties, 3 bureaus | Later the XIchang Division |
| Fourth Administrative Circuit | Garzê County | 第四行政督察區 | 15 counties | Later the Xikang Province Tibetan Autonomous Region |
| Fifth Administrative Circuit | — | 第五行政督察區 | 13 counties | Chamdo Region; de facto controlled by Tibet |
1950–1955
| Name | Administrative Seat | Simplified Chinese | Hanyu Pinyin | Subdivisions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ya'an | Ya'an | 雅安市 | Yǎ'ān shì | none |
| Ya'an Division | Ya'an County | 雅安专区 | Yǎ'ān Zhuānqū | 9 counties |
| Xichang Division | Xichang County | 西昌专区 | Xīchāng Zhuānqū | 12 counties |
| Xikang Province Tibetan Autonomous Region | Kangding County | 西康省藏族自治区 | Xīkāng Shěng Zàngzú Zìzhìqū | 20 counties, 2 bureaus |
| Liangshan Yi Autonomous Region | Zhaojue County | 凉山彝族自治区 | Liángshān Yízú Zìzhìqū | 7 counties |
List of Governors
Kuomintang (Nationalist) Communist Party of China
Chairperson of the Provincial Government
| № | Portrait | Name (Birth–Death) |
Term of Office | Political Party | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |
Liu Wenhui 劉文輝 Liú Wénhuī (1895–1936) |
1 January 1939 | 9 December 1949 | Kuomintang |
| Defected to the Communists. | |||||
| 2 |  |
Ho Kuo-kuang 賀國光 Hè Guóguāng (1885–1969) |
25 December 1949 | March 1950 | Kuomintang |
| Fled to Taiwan via Haikou after fall of Xichang. | |||||
Xikang CPC Party Committee Secretary
| № | Portrait | Name (Birth–Death) |
Term of Office | Political Party | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Liao Zhigao 廖志高 Liào Zhìgāo (1913–2000) |
1950 | 1955 | Communist Party of China | |
| Province abolished. | |||||
Xikang People's Government Chairperson (Governor after January 1955)
| № | Portrait | Name (Birth–Death) |
Term of Office | Political Party | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Liao Zhigao 廖志高 Liào Zhìgāo (1913–2000) |
26 April 1950 | September 1955 | Communist Party of China | |
| Province abolished. | |||||
See also
- Map showing the locations of provinces of the ROC
- Kham
References
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on August 5, 2009. Retrieved November 17, 2009.
- ↑ Hsiao-ting Lin (2010). Modern China's ethnic frontiers: a journey to the west. Volume 67 of Routledge studies in the modern history of Asia (illustrated ed.). Taylor & Francis. p. 27. ISBN 0-415-58264-4. Retrieved 2011-12-27.
area and spreading Sun Yat-sen's Three People's Principle among the Tibetan and Khampa minorities, Kesang Tsering set up a field headquarters in Batang (Pa'an). There he appointed his own Xikang provincial government staff and issued an