Wormser Dom

The St Peter's Dom (German: Wormser Dom) is a church in Worms, southern Germany. The Dom is located on the highest point of the inner city of Worms and is the most important building of the romanesque style in Worms. It is closely associated with Bishop Burchard and the high point of Worms' history in the 12th and 13th centuries. It was the seat of the Catholic Prince-Bishopric of Worms until its extinction in 1800.
It is a basilica with four round towers, two large domes, and a choir at each end. The interior is built in red sandstone. Today, the Wormser Dom is a Catholic parish church, honoured with the title of "Minor Basilica".
Only the ground plan and the lower part of the western towers belong to the original building consecrated in 1110. The remainder was mostly finished by 1181, but the west choir and the vaulting were built in the 13th century, the elaborate south portal was added in the 14th century, and the central dome has been rebuilt.
The ornamentation of the older parts is simple; even the more elaborate later forms show no high development of workmanship. Unique sculptures depicting salvation stories appear above the Gothic-era south doorway. The baptismal font contains five remarkable stone reliefs from the late 15th century. The church's original windows were destroyed by the Oppau explosion on 21. September 1921 and allied bomb raids during 1943 and on 21. February and 18. March 1945; between 1965 and 1995 Mainz artist Alois Plum crafted new windows.
The Dom is 110 m long, and 27 m wide. The transepts, near the west end, extend to 36 m (inner measurements). The height in the nave is 26 m and the interior of the domes are 40 m.

Great events associated with the Dom include the nomination of Leo IX as Pope in 1048, the Concordat of Worms which ended the Investiture controversy in 1122, the marriage of Emperor Frederick II to Isabella of England in 1235 and the Diet of Worms in 1521, during which Martin Luther was condemned as a heretic.
Until the secularisation of the Hochstift and Diocese of Worms, the church was the cathedral of the bishop of Worms. After 1802, St Peter's Dom was reduced to a parish church, but in memory of its earlier importance as the seat of a bishop, it was made a praeposit church by Pope Pius IX in 1862 and a Minor Basilica by Pope Pius XI in 1925. These papal honours, which include privileges for the provost and the church building, are meant to highlight the importance of the church to its surrounding region.
The Dom was built from 1130 to 1181, replacing an early romanesque basilica from the first quarter of the 11th century. According to the most recent research, the building may have began around 1105 with the sanctuary and transept.[1]
The Alte Synagoge (Straßburg) built by Ludwig Levy from 1896-1898 and destroyed in 1940-1941 was modelled on St Peter's Dom.
History
Before the cathedral
-

Dom compared with the Merovingian basilica
-

Dom compared with the Cathedral of Bishop Burchard of Worms
St Peter's Dom is located on the highest hill in the city. Since this hill was safe from flooding, it has been inhabited by people since the third millennium BC. Celtic inhabitants were succeeded by the Germanic tribe of the Vangioni, after whom the area around Worms received the name Wonnegau. They were conquered by the Romans who established a commercial centre and temple area on the hill. The decline of the Roman Empire led to the abandonment of the Roman garrison at Worms in 401. Twelve years later, the Burgundians took over Worms after they were settled within the empire by the Romans with the task of protecting the empire's borders. When they sought to shake off Roman overlordship in 435, they were defeated in battle by the Romans. A year later, the Huns crossed the Rhine and massacred most of the Burgundians.
Church of Brunichildis
After the Battle of the Catalaunian Fields, the Franks came into the Rhine valley and took over Worms by force. At the same time they converted to Christianity. When the Frankish realm was divided into three parts under the Merovingians, Worms belonged to Austrasia. After the rulers of Austrasia and Neustria married each other's sisters, a war broke out, which led to the death of both rulers and one of the sisters. The widow of the Austrasian ruler, Brunichildis lived at Worms around 600 AD. She and her successor, Dagobert I had a church built on top of the foundations of the Roman forum, according to medieval sources. This church was a predecessor of the current building. There is no archaeological evidence for this church. Excavations carried out at the beginning of the twentieth century suggest a larger predecessor build which (given its size) was probably Carolingian. Whether this was an expansion of a Merowingian building or not, is unclear.
Cathedral of Bishop Burchard of Worms

Berthulf was the first known Bishop of Worms in 614. A new church was laid out, with the dimensions of the current building, under Bishop Burchard of Worms at the beginning of the 11th century. He succeeded in persuading the Salians to abandon their fort in the city, on which he erected the Paulus Stift from 1002/3. The old cathedral was demolished and the construction of the new one occurred simultaneously. It was a cross-shaped basilica with two semicircular choirs, built on an east-west orientation. In 1018, the cathedral was consecrated in the presence of the Emperor, but the western part of the building collapsed only two years later and had to be rebuilt. The church had a flat wooden roof. According to Burchard's biography, the cathedral was magnificently furnished in the 1030s and 1040s. Thus there is mention of columns with golden capitals (which cannot have been the church's main columns). Most likely, Burchard's cathedral was a pier-basilica, since no remains of columns (difficult to acquire in the 11th century anyway) have been found.
Only the foundations of the west towers and the treasury north of the choir, which was probably built at the end of the 11th century, survived subsequent rebuilding.
In 1110, the cathedral was consecrated for the second time. More damage had probably occurred, whose removal was followed by this renewed consecration.
Cathedral of Bishop Burchard II of Worms
The rebuilding in the 12th century resulted, essentially, in the current cathedral. Around 1130, probably because of further damage to the building, Bishop Burchard II began the demolition of the church build by his predecessor Burchard I and the construction of a new church. The whole eastwerk with its towers and cupola were completed by him in the period up to c.1144. The nave and westwerk were erected between 1160 and 1181 by his successors, Conrad I and Conrad II. The latter consecrated it on 2 May 1181.[2] The Dom has features of the late romanesque style, such as being completely vaulted and is decorated in line with Burgundian-Cistercian influence. Several religious buildings of the area are modelled on the Dom's decoration, such that one can speak of a "Worms Style." Additionally, the elevation resembles the Imperial cathedrals in Speyer and Mainz. The gradual progress of the rebuild can be charted with dendrochronology. Lamps were donated for the west choir in 1172 and Bishop Conrad II was buried there in 1192. In former times, the Johanneskirche (Worms) stood on the south side of the cathedral and served as its parish church and baptismal chapel, until it was demolished in 1812.
Renovations of Johannes von Dalberg
About a hundred years after the third consecration, he construction of the Chapel of St Nicholas was begun. A new south portal was built, east of which two more chapels for St Anne and St George were built in the first quarter of the fourteenth century. Since part of the northwest tower collapsed in 1429, it was under reconstruction until 1472. The resulting tower has some late gothic details but strictly adhered to the original shape of the tower, making it an extremely earlier example of conservational restoration. The Aegidius chapel (now the Mary chapel) was built in the east part of the north side-aisle in 1480/1485.
Towards the end of the century, under Bishop Johann von Dalberg the original romanesque cloisters (west of the Chapel of St Nicholas) were renovated, resulting in five monumental late gothic reliefs on the life of Jesus which are now located in the north side-aisle of the Dom: Tree of Jesse (1488),[3] Annunciation (1487), birth of Christ (1515), entombment (c.1490) and the resurrection (c.1490). A sixth relief depicting the crucifixion was probably lost in the destruction of 1689. In the Andreasstift (Worms) there are four large round keystones about 88 cm (35 in) in diameter decorated with coats of arms, which derive from the cloisters and were donated by Bishop Ruprecht of Regensberg, and the Domherrs Philipp von Flersheim, Erpho von Gemmingen and Wilhelm von Stockheim. Another cloister keystone belonging to the Archbishop of Cologne and Domscholaster Hermann IV of Hesse is now located above the entrance to the Abbey church of Neuburg Abbey in Heidelberg.[4] The foundation stone of the cloisters from the year 1484, which had been thought lost, was found during cleaning in the Dom's lapidarium at the end of February 2014.[5]
Protestant Reformation to French Revolution
The importance of the diocese and the Dom at Worms derives from the Diet of Worms in 1521. Shortly after the diet, some Worms congregations converted to the teachings of Martin Luther. In 1556, all parishes in the Palatinate followed suit.
During the Thirty Years War, Swedish troops held the city from 1632 to 1635 and the cathedral was used for Protestant services.
In the Nine Years War, Heidelberg, Mannheim, Speyer and Worms were devastated at the command of King Louis XIV. Churches were plundered and, though the attempt to blow up the Dom failed, it was heavily damaged by fire. Bishop Franz Ludwig von Pfalz-Neuberg had the cathedral restored in 1698. Some baroque elements date to this time, like the windows of the silver chamber and the high altar of Balthasar Neumann.

The renovation of the Dom was nullified by French Revolutionary troops. At the end of 1792, Speyer, Worms, Mainz and Frankfurt were sacked by revolutionary troops. The Dom served as a stable and a tavern. Between 1818 and 1830 the cloisters were demolished and the stones from it were auctioned off.
Renovation 1886-1935
A full renovation of St Peter's Dom only began in 1886. Because of structural weaknesses and damage suffered in the fire of 1689, the west choir had to be completely rebuilt. Great importance was placed on reusing as much of the original stone as possible. In the outer wall this was taken so far that today all but a small portion of the old stones are in their original locations. On the inside wall, large flat stones had to be used and faithfully reconstructed. The sharply bent dosseret over the central rosette window was not rebuilt since it was blamed for the structural issues. Today the dosserets run perpendicular to the edge of the rosette and frame it clearly. The general renovations, which also included renovation of the chapel of St Nicholas, the reconstruction of the whole floor and the addition of an entirely new crypt for the tombs of the Salians under the high choir, were only completed in 1935.
In the course of the renovation work, in 1920 the Dom building master Philipp Brand was standing on the scaffolding when a dachshund leapt at him and attempted to bite him on the leg. He stepped to the side and as a result escaped from a falling stone which had broken loose above him. In the upper left of the south portal, at the edge of the window in the left corner is a statue of the dachshund - Philipp Brand had this installed as a small memorial.
In the allied bombing on 21 February and 18 March 1945, the Dom was damaged by a bomb, which did not affect the interior. The roof burnt but the vaults remained intact.
Architecture
The Dom is a pier-basilica with two choirs and a transept. A central tower is located on the crossing, another over the western choir. Both choirs are flanked by two round staircase towers. The nave is vaulted in various ways: the central aisle has rib vaulting, while the side aisles have groin vaults. The apse of the west choir takes the form of an octagon and is decorated with various rosette windows
Glass windows
As a result of the Oppau explosion on 21 September 1921, nothing remains of the Medieval glass windows.[6]
The contemporary glass of the Dom is quite varied. As well as simple clear or milky glass in the transepts, are complicated pictoral windows, especially in the chapels, like the coloured glass windows of Heinz Hindorf in the Chapel of Mary, which depict scenes from Mary's life and the Fourteen Holy Helpers (1986-1988), and the Geschichtsfenster (1992) in the Chapel of St George, which depict the history of the diocese of Worms in 20 scenes, from the first known bishop, Victor, in 345 to the destruction of the city in the Second World War. An unusual political statement is found in the depiction of the Biblis Nuclear Power Plant as the Tower of Babel in a series of examples of human sinfulness.[7]
Burials
Sarcophagi in the Crypt
Four Salian princes were buried in the altar space of the Frankish church and were then built over. Another five followed by 1046. These are the ancestors and relatives of Emperor Conrad II:
- Conrad the Red, Duke of Lorraine (Great-grandfather) † 955,
- Judith, Duchess of Carinthia (Grandmother) † 991,
- Henry, Count of Wormsgau (Father) † 990/991,
- Judith (Sister) † 998,
- Conrad I, Duke of Carinthia (Uncle) † 1011
- Matilda (wife of the preceding) † 1031/32,
- Queen Matilda † 1034, consort of Henry I of France and daughter of Conrad II (transferred to Worms in 1046),
- Conrad II, Duke of Carinthia (Cousin, son of Conrad I) † 1039,
- Bischop Azecho, Successor of Bischop Burchard, † 1044.
These sarcophagi have been located in a specially built crypt since the beginning of the 20th century.
Since the floor level of the transept and the east choir is over six metres above ground level, one must assume that there was a crypt below it.
Graves

There are a number of grave monuments, gravestones and grave plates in the Dom, including:
- Reinbold Beyer von Boppard († 1364), Dom-custos in Worms, brother of Bishop Dietrich Bayer von Boppard († 1384)
- Dietrich von Bettendorf (1518–1580), Dom deacon and Bishop of Worms
- Wilhelm von Efferen (1563–1616), Bishop of Worms
- Eberhard von Heppenheim genannt vom Saal († 1559), Domherr, nephew of Dom-deacon of Speyer, Johannes von Heppenheim genannt vom Saal († 1555)
- Franz Rudolph von Hettersdorf (1675–1729), Dom-capitular und donor of the Nicholas altar
- Johann Adam von Hoheneck († 1731), Dom deacon of Worms
- Johann Franz Jakob Anton von Hoheneck (1686–1758), Dom capitular of Worms, Dom deacon of Mainz
- Landolf von Hoheneck († 1247), Bischop of Worms, posthumous epitaph from 1756
- Franz Carl Friedrich von Hohenfeld (1696–1757), Dom deacon
- Christoph Jodok von Ketteler (1661–1735), Dom capitular
- Philipp von Rodenstein (1564–1604), Bishop of Worms
- Georg von Schönenberg (1530–1595), Bishop of Worms, donated the George altar for his tomb
(outside in the former cloisters)
- Burchard II, also Bucco or Buggo († 1149), Bishop of Worms and builder of the Ostwerk of the Dom.
Chapel of St Nicholas

In the course of the third period of construction, an early romanesque chapel in honour of St Nicholas of Myra was built, which was consecrated in 1058. Its consecration inscription and the tympanon of the former entrance to the Dom, with one of the oldest known depictions of St Nicholas, are preserved.[8][9] It was apparently used to store a relic of the Saint, which had been brought by Empress Theophanu from Byzantium, at the time of her marriage to Otto II in 972.
The current chapel of St Nicholas was built on the same location between 1280 and 1315 in the Gothic style, with two aisles, immediately west of the man portal on the south side aisle of the Dom. At this time, when St Nicholas was still buried in Myra, his cult spread through the west and he was revered as patron of various groups and helper in many matters. This could explain the unusual size and sumptuousness of the chapel. The Jesuit and Bollandist, Daniel Papebroch (1628–1714) saw the original Worms relic of St Nicholas in 1660. He described it as a "finger bone" of the saint, which at that time was stored in the Dom sacristry, but had previously been displayed in his own chapel. He states also that the Worms relic was always immersed in oil, just as the relic of St Nicholas in Bari is to this day.[10] Papebroch also mentions a still-extant sumptuous consecration offering from Queen Constance of Sicily († 1198) to Saint Nicholas.[11] The old relic o Nicholas was lost in the destruction during the Nine Years War. At the end of the twentieth century, a new one was acquired, which is kept once more in the chapel of Nicholas, in a modern reliquary.
The chapel was originally part of the cloisters which were located immediately to the west and was hidden by them for half its length. When the remains of the cloisters were finally cleared away in 1830, the structure of the chapel fell out of balance so that they finally had to completely dismantle it in 1920/27, like the west choir a few years earlier, install new foundations and rebuild it anew. On this same occasion, they also attempted to correct the proportions of the chapel which had become ungainly after the removal of the cloisters, by extending it to the west by a half vault. The current (southern) entranceway to the chapel derives from modern times, but its tympanon comes from the portal which formerly led from the cloisters into the chapel.
The furnishings of the chapel of St Nicholas consist today of pieces which were all originally intended for other contexts. The gothic carved altar comes from Southern Germany and was only acquired a few decades ago. The late Gothic Baptismal font was originally located in the Johanneskirche, which was demolished in the 19th century, the almost life size Gothic depiction of three young women was in a nearby abbey.[12] The intense blue-red windows immerse the chapel in an almost mystic twilight. In the highly elevated roof of the chapel, the collection of architectural decorations and casts of them are housed, while the cellar houses the central heating of the Dom. The chapel now serves as the baptismal chapel of the Dom and is used for weekday services. Thus it has appropriated the functions of the old Johanneskirche.
High altar
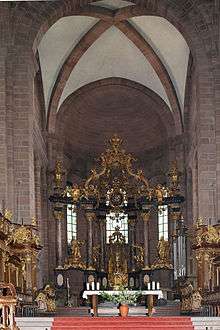
Franz Ludwig von Pfalz-Neuburg, Prince-elector of Mainz and Prince-Bishop of Worms, left enough money in his will to have a new high altar built. His successor, Prince-Bishop Franz Georg von Schönborn, asked his brother Friedrich, the Bishop of Würzburg to provide the builder Johann Balthasar Neumann for the project. The latter produced the new high altar made of gilt wood and multicoloured marble.
Organs
Main organ (Klais 1985)

Klais Orgelbau built a swallow's nest organ with three manuals and 34 registers in 1985, which was slightly reorganised and re-toned in 2007. The machine has a mechanical playing action, the tracker action is electronic.
Choir organ (Oberlinger 1996)

In addition, there is also a choir organ with mechanical playing and tracker action in the style of the choir organs of Aristide Cavaillé-Coll, which was built in 1996 by Oberlinger. The special feature of this organ's design is that it is extremely compact for its disposition and at the same time, as a result of a pipe construction specially developed by Oberlinger it can be moved about 50 cm (20 in) away from the wall. This compact structure was necessary so that view of the sumptuous high altar from the nave wouldn't be obscured by the organ. A special construction of the air intake was required to achieve this small size. The design was accomplished by organ master and architect Wolfgang Oberlinger in close partnership with the diocese's architects and conservators. The organ was arranged by Oberlinger's Windesheim workshop in collaboration with the organist Daniel Roth. The instrument was intoned by Jean-Pierre Swiderski, a noted expert on the designs of Aristide Cavaillé-Coll.
Bells
Before the destruction of Worms in 1689 during the Nine Years War, six bells hung in the four towers of the church. In 1728, the Dom received a new six part peal. In the course of the Secularisation at the end of the 18th century, these bells were confiscated. When the Dom became a parish church, four bells were hung in the southeast tower, with the strike tone sequence h0–dis1–fis1–gis1.[13] They were destroyed by aerial bombing at the end of the Second World War.[14]

Today, three bells hang in the southeast tower, made of a special metal called "Briloner Sonderbronze" (a tin-free copper-silicon alloy).[15]
| No. |
Name |
Year |
Forger |
Weight (kg) |
Ø (cm) |
Nominal (16tel) |
Inscription |
| 1 | Peter and Paul | 1949 | Albert Junker, Brilon | 2218 | 185 | c1 −4 | Petrus und Paulus – beschützt die Stadt Worms (Peter and Paul: Protect the City of Worms) |
| 2 | Mary | 1949 | Albert Junker, Brilon | 1114 | 126 | e1 −2 | Maria – Dein Hilf wir all begehren. (Mary: We all desire your help) |
| 3 | Brother Conrad | 1949 | Albert Junker, Brilon | 653 | 106 | g1 −1 | Hl. Bruder Konrad – bitte für uns. Gestiftet von Karl Kübel und Ehefrau. (Holy Brother Conrad: Please (pray) for us. Donated by Karl Kübel and wife) |
| Details of the future bells | |||||||
| 1 | 2700 | 165 | h0 | ||||
| 3 | 1600 | 140 | d1 | ||||
| 6 | 500 | 95 | a1 | ||||
| 7 | '400 | 85 | h1 | ||||
| 8 | 250 | 73 | d2 | ||||
For the great church jubilee in 2018, the peal of the church is to be expanded with five bells. The current bells will remain but will receive new clappers. A new bell will be cast with the deepest strike tone h0 and the other bells will have the strike tones d1, a1, h1, d2.[16]
St Peter's Dom in the Nibelungen Saga
An episode in the Nibelungenlied takes place at the portal of the Dom. The rival queens Brünhilde and Kriemhild disputed over which of their husbands (Siegfried or Gunther) has the higher rank, and therefore, which of them should enter the Dom first. This is a key episode which leads to Siegfried's death and the destruction of the Nibelungs.[17]
The portal in question was on the north side of the Dom and was considerably more elaborate before it was destroyed in 1689.
In connection with this episode, the Nibelungenfestspiele have taken place on an outdoor stage in front of the Dom since 2002.
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to St. Peter's Cathedral (Worms). |
- ↑ Kurt F. de Swaaf: Wormser Dom: Historiker entreißen den Steinen ihr Geheimnis (www.spiegel.de) 19. August 2009
- ↑ Webportal Wormser Dom
- ↑ Webseite zum Wurzel-Jesse-Relief im Wormser Dom
- ↑ Webseite mit Foto des von Erzbischof Hermann von Hessen gestifteten Schlusssteines
- ↑ wormser-zeitung.de: "Anno domini 1484..." – Grundstein des Wormser Doms gefunden. Wormser Zeitung, 28. Februar 2014, Sandra Dörr (2. März 2014)
- ↑ http://www.worms.de/de/kultur/stadtgeschichte/wussten-sie-es/liste_dom_gebaeude/2006-11_domfenster-zerstoerung.php
- ↑ Information des Wormser Dombauvereins
- ↑ Webseite mit Foto der Weiheinschrift von 1058
- ↑ Webseite zum romanischen Tympanon an der Nikolauskapelle
- ↑ Udo Kindermann: Kunstdenkmäler zwischen Antwerpen und Trient: Beschreibungen und Bewertungen des Jesuiten Daniel Papebroch aus dem Jahre 1660. Erstedition, Übersetzung und Kommentar, Böhlau Verlag, Köln, 2002, S. 93, ISBN 3-412-16701-0
- ↑ Webseite zum Weihegeschenk der Königin Konstanze
- ↑ Webseite zum Wormser Dreijungfrauenstein
- ↑ Motette (Hg.): Glocken-Landschaft Bistum Mainz, Motette-Verlag, Düsseldorf 2005, p. 34.
- ↑ Information on the historic bells
- ↑ Vollgeläut on YouTube.
- ↑ Information on the new bells
- ↑ Das Nibelungenlied
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "article name needed". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
Coordinates: 49°37′49″N 8°21′35″E / 49.63028°N 8.35972°E
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "article name needed". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
Coordinates: 49°37′49″N 8°21′35″E / 49.63028°N 8.35972°E
