Wing Chun
 | |
 | |
| Also known as | Wing Cheun, Wing Tsun, Ving Tsun, Wing Tsung |
|---|---|
| Focus | Striking, Trapping |
| Country of origin |
|
| Creator | Ng Mui of the Five Elders |
| Famous practitioners | Sum Nung,[1] Yip Man,[2] Leung Sheung, Bruce Lee,[3]Leung Ting, Kenneth Chung |
| Parenthood | Fujian White Crane |
| Descendant arts | Jeet Kune Do |
| Olympic sport | No |
| Wing Chun | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 詠春 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese | 咏春 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | Spring Chant | ||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Wing Chun (traditional Chinese: 詠春; simplified Chinese: 咏春) is a concept-based Chinese martial art and form of self-defense utilising both striking and grappling while specializing in close range combat.
History
The earliest known mentions of Wing Chun date to the period of Red Boat Opera (late 1800s).
The common legend as told by Yip Man[4] involves the young woman Yim Wing-chun during the period after the destruction by the Qing government of the Southern Shaolin and its associated temples.
Having rebuffed the local warlord's marriage offer, Yim Wing-Chun said she'd reconsider the proposal if he could beat her in a fight. She soon crossed paths with a Buddhist nun named Ng Mui, who was one of the Shaolin Sect survivors, and asked the nun to teach her to fight. According to legend, Ng Mui taught Yim Wing-Chun a new system of martial art that had been inspired by the nun's observations of a confrontation between a Snake and a Crane. This then-still nameless style enabled Yim Wing-Chun to beat the warlord in a one-on-one fight. Yim Wing-Chun thereafter married Leung Bok-Chau and taught him the style, which was later named after her.
Since the system was developed during the Shaolin and Ming resistance to the Qing Dynasty, many legends, including the story of Yim Wing-Chun, were spread regarding the creation of Wing Chun in order to confuse enemies. This is often given as a reason to explain the difficulty in accurately determining the creator or creators of Wing Chun.[5]
Lexicology
Wing Chun is the most common romanization, from the Cantonese pronunciation (simplified Chinese: 咏春; traditional Chinese: 詠春; Cantonese Yale: Wing6 Cheun1; pinyin: Yǒng Chūn; literally: "Spring Chant"). It is also romanized as Ving Tsun or Wing Tsun, and sometimes the characters are substituted with a homonym 永春 (Cantonese Yale: Wing6 Cheun1; literally: "Eternal Spring"). Even though it could be considered a linguistically erroneous romanization at least from English-speaking countries perspective, especially in Finland,[6][7][8] Germany[9][10][11] and Turkey[12] (and as a commonplace term in some other countries such as Austria,[13] Bulgaria,[14] Italy,[15][16][17] Slovakia[18]).
The alternative characters 永春 "eternal spring" are also associated with some other southern Chinese martial arts, including Weng Chun Kung Fu and Yong Chun.[19][20]
| Part of a series on |
| Chinese martial arts (Wushu) |
|---|
 |
|
Styles of Chinese martial arts
|
| Wushu in the world |
|
Historical locations Chen Village (陳家溝) |
| Wushu athletes/practitioners |
|
Legendary figures Bodhidharma (菩提達摩) |
|
Historical individuals Yue Fei (岳飛; 1103—1142) |
|
Modern celebrities Bruce Lee (李小龍 1940—1973) |
| Wushu influence |
|
Related |
Philosophy
One who excels as a warrior does not appear formidable.
One who excels in fighting is never aroused in anger.
One who excels in defeating their enemy does not join issues.
One who excels in employing others humbles themself before them.
This is the virtue of non-contention and matching the sublimity of heaven.[21]
Characteristics
Balance, structure and stance
Some Wing Chun practitioners believe that the person with better body structure will win. A correct Wing Chun stance is like a piece of bamboo, firm but flexible, rooted but yielding. This structure is used to either deflect external forces or redirect them.
Balance is related to structure because a well-balanced body recovers more quickly from stalled attacks and structure is maintained. Wing Chun trains the awareness of one's own body movement derived from muscular, tendon, and articular sources. Performing Wing Chun's forms such as Chum Kiu or the Wooden Dummy form greatly improve proprioception. Wing Chun favours a high, narrow stance with the elbows kept close to the body. Within the stance, arms are positioned across the vitals of the centerline. Shifting or turning within a stance is carried out variantly on the heels, balls, or middle (K1 or Kidney 1 point) of the foot depending on lineage. All attacks and counter-attacks are initiated from this firm, stable base. Wing Chun rarely compromises structure for more powerful attacks because this is believed to create defensive openings which may be exploited.
Structure is viewed as important, not only for reasons of defense, but also for attack. When the practitioner is effectively "rooted", or aligned so as to be braced against the ground, the force of the hit is believed to be far more devastating. Additionally, the practice of "settling" one's opponent to brace them more effectively against the ground aids in delivering as much force as possible to them.[22][23]
Relaxation
Softness (via relaxation) and performing techniques in a relaxed manner, is fundamental to Wing Chun.
- Tension reduces punching speed and power. Muscles act in pairs in opposition to each other (e.g. biceps and triceps). If the arm is tensed, maximum punching speed cannot be achieved as the biceps will be opposing the extension of the arm. In Wing Chun, the arm should be relaxed before beginning the punching motion.
- Unnecessary muscle tension wastes energy and causes fatigue.
- Tense, stiff arms are less fluid and sensitive during trapping and Chi Sau.
- A tense, stiff limb provides an easy handle for an opponent to push or pull with, whereas a relaxed limb provides an opponent less to work with.
- A relaxed, but focused, limb affords the ability to feel "holes" or weaknesses in the opponent's structure (see Sensitivity section). With the correct forwarding these "holes" grant a path into attacking the opponent.
- Muscular struggle reduces a fight to who is stronger. Minimum brute strength in all movement becomes an equalizer in uneven strength confrontations. This is very much in the spirit of the tale of Ng Mui.
Centerline
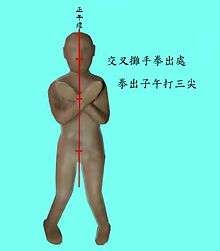
While the existence of a "central axis" concept is unified in Wing Chun, the interpretation of the centerline concept itself is not. Many variations exist, with some lineages defining anywhere from a single "centerline" to multiple lines of interaction and definition. Traditionally the centerline is considered to be the vertical axis from the top of a human's head to the groin. The human body's prime striking targets are considered to be on or near this line, including eyes, nose, throat, solar plexus, stomach, pelvis and groin.
Wing Chun techniques are generally "closed", with the limbs drawn in to protect the central area and also to maintain balance. In most circumstances, the hands do not move beyond the vertical circle that is described by swinging the arms in front, with the hands crossed at the wrists. To reach outside this area, footwork is used. A large emphasis and time investment in training Chi Sau exercise emphasizes positioning to dominate this centerline. The stance and guard all point at or through the center to concentrate physical and mental intent of the entire body to the one target.
Wing Chun practitioners attack within this central area to transmit force more effectively, since it targets the "core center" (or "mother line", another center defined in some lineages and referring to the vertical axis of the human body where the center of gravity lies). For example, striking an opponent's shoulder will twist the body, dispelling some of the force and weakening the strike, as well as compromising the striker's position. Striking closer to the center transmits more force directly into the body.
Punches
Due to the emphasis on the centerline, the straight punch is the most common strike in Wing Chun. However, the principle of simultaneous attack and defense (simplified Chinese: 连消带打; traditional Chinese: 連消帶打; Cantonese Yale: lìhn sīu daai dá; literally: "linking cancel and attack") suggests that all movements in the Siu Nim Tau with a forward execution flow into a strike if no effective resistance is met, without need for recomposure. Other explicit examples of punches can be found in the Chum Kiu and Biu Ji forms, although these punches may appear to be superficially different they are simply the result of the punch beginning from a different origin position while following the same fundamental idea, to punch in a straight line following the shortest distance between the fist and the opponent.
The punch is the most basic and fundamental in Wing Chun and is usually thrown with the elbow down and in front of the body. Depending on the lineage, the fist is held anywhere from vertical to horizontal (palm side up). The contact points also vary from the top two knuckles, to the middle two knuckles, to the bottom three knuckles. Punches do not turn at the wrist as a primal directive is economy of motion and this would create two distinct motions for a single movement.
When executing the punch, one must relax and not use the shoulders or activate the trapezius muscles. The punch comes from the center, Kyun Yau Sam Faat (simplified Chinese: 拳由心发; traditional Chinese: 拳由心發; Cantonese Yale: kyùhn yàuh sām faat; literally: "punch starts from the heart"). The punch is not propelled forward by the elbow, it is projected by simply reaching forward with a closed but relaxed fist as it is a maxim that the body part closest to the intended direction begins the motion.
Wing Chun primarily encourages utilizing the whole upper body from the waist to maximize power, this is often referred to as "coiling", which increases impact and minimizes "telegraphing" strikes, and is motivated by observations of the snake.
Punches that do not utilize maximum body mass such as punches thrown in quick succession in a "straight blast" or "chain punching" are executed correctly, when used primarily for disorienting and off-balancing the opponent. Criticisms of favoring weak punches are a misunderstanding of their intended purpose.
Wing Chun favors the vertical punch for several reasons:
- Directness. The punch is not "loaded" by pulling the elbow behind the body. The punch travels straight towards the target from the guard position (hands are held in front of the chest).
- Protection. The elbow is kept low to cover the front midsection of the body. It is more difficult for an opponent to execute an elbow lock/break when the elbow occupies this position. This aids in generating power by use of the entire body structure rather than only the arm to strike. Also with the elbow down, it offers less opening for the body to be attacked while the forearm and punch intercept space towards the head and upper body.
- Strength and Impact. Wing Chun practitioners believe that because the elbow is behind the fist during the strike, it is thereby supported by the strength of the entire body rather than just a swinging fist, and therefore has more impact. A common analogy is a baseball bat being swung at someone's head (a round-house punch), as opposed to the butt end of the bat being thrust forward into the opponent's face (wing chun punch), which would cause far more damage than a glancing hit and is not as easy to evade. Many skilled practitioners pride themselves on being able to generate "short power" or large amount of power in a short space. A common demonstration of this is the "one-inch punch", a punch that starts only an inch away from the target yet delivers an explosive amount of force. This is a principle example of a coiled strike in which multiple abdominal muscles can contribute to the punching power while being imperceptible to the attacker. It is a common misconception that "one-inch punches" utilize a snapping of the wrist.
- Alignment & Structure. Because of Wing Chun's usage of stance, the vertical punch is thus more suitable. The limb directly in front of the chest, elbow down, vertical nature of the punch coupled with a snap twisting of the waist requires a practitioner's body to naturally untwist or release before the rebound of the punch. This effectively demonstrates an understanding of the equal and opposite force reactions attributed to Newtonian Physics. This is a desirable trait to a Wing Chun practitioner because it promotes the use of the entire body structure to generate power and prevents wrist injury or being pushed away by the high degree of forward power being reflected.
Kicks
Kicks can be explicitly found in the Chum Kiu and Muk Jong forms, though some have made interpretations of small leg movements in the Siu Nim Tau and Biu Ji to contain information on kicking as well. Depending on lineage, a beginner is often introduced to basic kicking before learning the appropriate form. Traditionally, kicks are kept below the waist. This is characteristic of southern Chinese martial arts, in contrast to northern systems which utilize many high kicks.
Kicks in Wing Chun are mostly directed at the lower half of the body. Wing Chun kicks are designed to knock an opponent off balance, break their leg, or to bring an opponent on their knees.
Variations on a front kick are performed striking with the heel. The body may be square and the knee and foot are vertical on contact (Chum Kiu), or a pivot may be involved with the foot and knee on a plane at an angle (Muk Jong). At short distances this can become a knee. A roundhouse kick is performed striking with the shin in a similar manner to the Muay Thai version with most of the power coming from the body pivot. This kick is usually used as a finisher at closer range, targeting anywhere between the ribs and the back of the knee, this kick can also become a knee at close range. Other kicks include a stamping kick (Muk Jong) for very close range and a sweep performed with the heel in a circular fashion.
Every kick is both an attack and defence, with legs being used to check incoming kicks or to take the initiative in striking through before a more circular kick can land. Kicks are delivered in one movement directly from the stance without chambering/cocking.
Types of Kicks include:
Front Kick, Side Kick, Roundhouse Kick (usually delivered to the ribs or thigh), Shovel Kick (A kick that targets the knee/shin), Spinning Back Kick, Sweep.
Elbows and Knees
Wing Chun relies heavily on elbow strikes at close range. Common targets for elbows include the chest, chin, head, and face. Elbow strikes are delivered in a manner similar to Muay Thai, using the whole body and turning of the hips to generate power.
Elbow strikes include: Rising elbow (6 to 12) Horizontal elbow Kneeling elbow (12 to 6) Reversing elbow Spinning elbow strikes
Knees are delivered also, usually in a clinching position, but some Sifus also teach entering with flying knee strikes to bridge the distance.
Uncommitted techniques
Wing Chun techniques are uncommitted. This means that if the technique fails to connect, the practitioner's position or balance is less affected. If the attack fails, the practitioner is able to "flow" easily into a follow-up attack. All Wing Chun techniques permit this. Any punches or kicks can be strung together to form a "chain" of attacks. According to Wing Chun theory, these attacks, in contrast to one big attack, break down the opponent gradually causing internal damage. Chained vertical punches are a common Wing Chun identifier.
Trapping skills and sensitivity
The Wing Chun practitioner develops reflexes within the searching of unsecured defenses through use of sensitivity. Training through Chi Sau with a training partner, one practices the trapping of hands. When an opponent is "trapped", he or she becomes immobile.
Chinese philosophy:
| “ |
Greet what arrives, escort what leaves and rush upon loss of contact (來留去送,甩手直衝) |
” | |
| — Yip Man | |||
Close range
Wing Chun teaches practitioners to advance quickly and strike at close range. While the Wing Chun forward kick can be considered a long range technique, many Wing Chun practitioners practice "entry techniques"—getting past an opponent's kicks and punches to bring them within range of Wing Chun's close range repertoire. This means that theoretically, if the correct techniques are applied, a shorter person with a shorter range can defeat a larger person by getting inside their range and attacking them close to their body.
Curriculum
Forms and San Sik
Forms are meditative, solitary exercises which develop self-awareness, balance, relaxation and sensitivity. Forms also train the practitioner in the fundamental movement and the correct force generation of Wing Chun.
San Sik (Chinese: 散式; Cantonese Yale: Sáan Sīk; pinyin: Sǎn Shì; literally: "Casual Style") are compact in structure. They can be loosely grouped into three broad categories:
1. Focus on building body structure through basic punching, standing, turning, and stepping drills.
2. Fundamental arm cycles and changes, firmly ingraining the cardinal tools for interception and adaptation.
3. Sensitivity training and combination techniques.
It is from the forms and san sik that all Wing Chun techniques are derived. Depending on lineage, the focus, content and intent of each form can have distinct differences which can therefore have far reaching implications. This also means that there are a few different ideas concerning what constitutes progression in the curriculum from form to form, so only a general description of overlap between different schools of thought is possible here.
What's commonly seen are six Wing Chun forms:[24] three empty hand forms, one "wooden dummy" form, and two weapons forms.
Empty hand
| 小念頭 | Siu Nim Tau (simplified Chinese: 小念头; traditional Chinese: 小念頭; Cantonese Yale: Síu Nihm Tàuh; pinyin: Xiǎo Niàn Tóu; literally: "little idea") | The first, and most important form in Wing Chun, Siu Nim Tau, is the foundation or "seed" of the art from which all succeeding forms and techniques depend.[25] Fundamental rules of balance and body structure are developed here. Using a car analogy: for some branches this would provide the chassis,[26] for others this is the engine.[27] It serves basically as the alphabet for the system. Some branches view the symmetrical stance as the fundamental fighting stance, while others see it as more a training stance used in developing technique.[28] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 尋橋 | Chum Kiu (simplified Chinese: 寻桥; traditional Chinese: 尋橋; Cantonese Yale: Chàhm Kìu; pinyin: Xún Qiáo; literally: "seeking bridge") | The second form, Chum Kiu, focuses on coordinated movement of bodymass and entry techniques to "bridge the gap" between practitioner and opponent and move in to disrupt their structure and balance.[29][30] Close-range attacks using the elbows and knees are also developed here. It also teaches methods of recovering position and centerline when in a compromised position where Siu Nim Tau structure has been lost. For some branches bodyweight in striking is a central theme, whether it be from pivoting (rotational) or stepping (translational). Likewise for some branches, this form provides the engine to the car. For branches who use the "sinking bridge" interpretation, the form takes on more emphasis of an "uprooting" context adding multi-dimensional movement and spiraling to the already developed engine. | |
| 鏢指 | Biu Ji (simplified Chinese: 镖指; traditional Chinese: 鏢指; Cantonese Yale: Bīu Jí; pinyin: Biāo Zhǐ; literally: "darting fingers") | The third form, Biu Ji, is composed of extreme short-range and extreme long-range techniques, low kicks and sweeps, and "emergency techniques" to counter-attack when structure and centerline have been seriously compromised, such as when the practitioner is seriously injured.[31] As well as pivoting and stepping, developed in Chum Kiu, a third degree of freedom involving more upper body and stretching is developed for more power. Such movements include very close range elbow strikes and finger thrusts to the throat. For some branches this is the turbo-charger of the car. For others it can be seen as a "pit stop" kit that should never come in to play, recovering your "engine" when it has been lost. Still other branches view this form as imparting deadly "killing" and maiming techniques that should never be used if you can help it. A common wing chun saying is "Biu Ji doesn't go out the door." Some interpret this to mean the form should be kept secret, others interpret it as meaning it should never be used if you can help it. |
Wooden dummy
| 木人樁 | Muk Yan Jong (simplified Chinese: 木人桩; traditional Chinese: 木人樁; Cantonese Yale: Muhk Yàhn Jōng; pinyin: Mùrénzhuāng; literally: "wooden dummy") | The Muk Yan Jong form is performed against a "wooden dummy", a thick wooden post with three arms and a leg mounted on a slightly springy frame representing a stationary human opponent. Although representative of a human opponent, the dummy is not a physical representation of a human, but an energetic one. Wooden dummy practice aims to refine a practitioner's understanding of angles, positions, and footwork, and to develop full body power. It is here that the open hand forms are pieced together and understood as a whole. | .jpg) The Hong Kong wall mounted version of the Wooden Dummy |
|---|
|[32]Star Dummy is also a Wing Chun training tool. It consists of three poles that are embedded into the ground such as to be strong enough for kicking each an arms span apart in a triangle. The form consists of Wing Chun kicking patterns: front kick, front kick with foot pointed out using broad area of foot and knee rotation to outside, and side kick.
Forms
Both the Wai Yan (Weng Chun) and Nguyễn Tế-Công branches use different curricula of empty hand forms. The Tam Yeung and Fung Sang lineages both trace their origins to Leung Jan's retirement to his native village of Gu Lao, where he taught a curriculum of San Sik.
The Siu Lim Tau of Wing Chun is one long form that includes movements that are comparative to a combination of Siu Lim Tau, Chum Kiu, and Biu Ji of other families. The other major forms of the style are Cheui Da (simplified Chinese: 随打; traditional Chinese: 隨打; Cantonese Yale: Chèuih Dá; literally: "Chase Strike"), Jeui Da (Chinese: 追打; Cantonese Yale: Jēui Dá; literally: "Chase Strike"), Fa Kyun (Chinese: 花拳; Cantonese Yale: Fā Kyùhn; literally: "Variegated Fist"), Jin Jeung (Chinese: 箭掌; Cantonese Yale: Jin Jéung; literally: "Arrow Palm"), Jin Kyun (Chinese: 箭拳; Cantonese Yale: Jin Kyùhn; literally: "Arrow Fist"), Jeui Kyun (Chinese: 醉拳; Cantonese Yale: Jeui Kyùhn; literally: "Drunken Fist"), Sap Saam Sau (Chinese: 十三手; Cantonese Yale: Sahp Sāam Sáu; literally: "Thirteen Hands"), and Chi Sau Lung (simplified Chinese: 黐手拢; traditional Chinese: 黐手攏; Cantonese Yale: Chī Sáu Lùhng; literally: "Sticking Hands Set").
Also, a few family styles of Wing-Chun (especially those coming from the Hung Syun Hei Baan (Chinese: 紅船戲班; Chinese: 红船戏班; Cantonese Yale: HùhngSyùhn Heibāan; literally: "Red Boat Theatrical Troupe") have a combination advanced form called Saam Baai Fat (Chinese: 三拜佛; Cantonese Yale: Sāam Baai Faht; literally: "Three Bows to Buddha") which includes many flow/leak techniques from all of the first 'standard' 7 forms.
Weapons
Once correct force generation in the open-handed forms is achieved, the student is ready to progress to weapons. With the open hand forms delivering force to the end of the finger tips, the idea is to be able to extend that force further to the end of a weapon as an extension of the body, using the same principles. Also, these weapons forms can be used as an exercise to strengthen the forearms and wrists even further.
| 八斬刀 | Baat Jaam Dou (simplified Chinese: 八斩刀; traditional Chinese: 八斬刀; Cantonese Yale: Baat Jáam Dōu; pinyin: Bā Zhǎn Dāo; literally: "Eight Slashing Knives"), also known as Yee Jee Seung Do (simplified Chinese: 二字双刀; traditional Chinese: 二字雙刀; Cantonese Yale: Yih Jih Sēung Dōu; pinyin: èr zì shuāng dāo; literally: "Parallel Shape Double Knives"). | A form involving a pair of large "Butterfly Knives", slightly smaller than short swords (Dao). Historically the knives were also referred to as Dit Ming Do ("Life-Taking Knives"). | Modern Hybrid Blade Style Wing Chun Butterfly Swords |
|---|---|---|---|
| 六點半棍 | Luk Dim Bun Gwan (simplified Chinese: 六点半棍; traditional Chinese: 六點半棍; Cantonese Yale: Luhk Dím Bun Gwan; pinyin: Liù Diǎn Bàn Gùn; literally: "Six and A Half Point Pole") | "Long Pole"— a tapered wooden pole ranging anywhere from 8 to 13 feet in length. Also referred to as "Dragon Pole" by some branches. For some branches that use "Six and A Half Point Pole", their 7 principles of Luk Dim Boon Gwun(Tai-uprooting, lan-to expand, dim-shock, kit-deflect, got-cut down, wan-circle, lau-flowing) are used throughout the unarmed combat as well. The name six and a half point pole comes from these 7 principles, with the last principle:Lau, or Flowing counting as half a point. |  Leung Ting demonstrating the Long Pole |
The Yuen Kay Shan / Sum Nung branch also historically trained throwing darts (Biu). According to Sum Nung, his skill with them was not comparable enough to Yuen Kay Shan's for him to include them in the current curriculum.
Chi Sau
Chi Sau (Chinese: 黐手; Cantonese Yale: Chī Sáu; pinyin: Chī Shǒu; literally: "sticking hands") is a term for the principle and drills used for the development of automatic reflexes upon contact and the idea of "sticking" to the opponent (also known as "sensitivity training"). In reality, the intention is not to "stick" to your opponent at all costs, but rather to protect your centerline while simultaneously attacking your opponent's centerline.[33] In Wing Chun, this is practiced by two practitioners maintaining contact with each other's forearms while executing techniques, thereby training each other to sense changes in body mechanics, pressure, momentum and "feel". The increased sensitivity gained from this drill helps a practitioner attack and counter an opponent's movements precisely, quickly, and with appropriate techniques.
Chi Sau additionally refers to methods of rolling hands drills (Chinese: 碌手; Cantonese Yale: Lūk Sáu; literally: "rolling hands"). Luk Sau participants push and "roll" their forearms against each other in a single circle while trying to remain in relaxed form. The aim is to feel force, test resistance, and find defensive gaps. Other branches have a version of this practice where each arm rolls in small, separate circles. Luk Sau is most notably taught within the Pan Nam branch of Wing Chun where both the larger rolling drills as well as the smaller, separate-hand circle drills are taught.
In some lineages (such as the Yip Man and Jiu Wan branches), Chi Sau drills begin with one-armed sets called Daan Chi Sau (Chinese: 单黐手; Cantonese Yale: Dāan Chī Sáu; literally: "Single Sticking Hand"), which help the novice student to get the feel of the exercise; each practitioner uses one hand from the same side as they face each other. Chi Sau is a sensitivity drill to train and obtain specific responses and should not be confused with actual sparring or fighting though it can be practiced or expressed in a combat form.
Chi Geuk
Chi Geuk (simplified Chinese: 黐脚; traditional Chinese: 黐腳; Cantonese Yale: Chī Geuk; pinyin: Chī Jiǎo; literally: "sticking legs") is the lower-body equivalent of the upper body's Chi Sau training, aimed on developing awareness in the lower body and obtaining relaxation of the legs.
Muk Waan
Muk Waan (simplified Chinese: 木环; traditional Chinese: 木環; Cantonese Yale: Muhk Wàahn; pinyin: Mù Huán; literally: "Wooden Ring"), or Juk Waan (simplified Chinese: 竹环; traditional Chinese: 竹環; Cantonese Yale: Jūk Wàahn; pinyin: Zhú Huán; literally: "Bamboo Ring") is another, somewhat rare training-tool in some families of Wing Chun. An approximately 10 inch to 14 inch ring made of bamboo or rattan (some schools use a metal ring), the Juk Wan is used for training the wrists and forearms, and to instruct the student in "flow" from technique to technique. Some schools set up a form for this technique, while other schools train techniques and strategies without a formulated pattern.
Sash System
Although historically uncommon during the era of Yip Man and Prior, there has been a trend of many schools and lineages adopting their own sash ranking system. Examples are as follows:
William Cheung Lineage: White, Light Blue, Blue, Dark Blue, Light Brown, Dark Brown, Black, Grey, Green, Gold, Gold plus one logo, Gold plus two logos, Gold plus three logos, Gold plus four logos, Gold plus 5 logos, Red Sash
Sunny Tang Lineage: No Sash, Red, Green, Blue, Black
Austin Goh Lineage: Yellow, Green, Blue, Red, Brown, Black
Southern martial arts
Wing Chun, together with Hung Gar and Choi Lei Fut, is named as one of "The Three Great Martial Art Schools of the South", which originated and became popular in Southern China.
Global spread
Wing Chun is practiced globally in over 64 countries.[34] It is the world's most popular form of Southern Kung Fu.[35]
In popular culture
Donnie Yen has caused impact in the martial arts world through his various films. Donnie Yen played the role of Wing Chun Grandmaster Ip Man in the 2008 movie Ip Man, which was a box office success; and its sequels Ip Man 2 and Ip Man 3.[36]
Notable practitioners

- Anderson Silva, one of the most successful MMA fighters of all time.
- Brandon Lee trained in Wing Chun as well as Jeet Kune Do, Muay Thai, & Shaolin Kung-Fu.
- Bruce Lee (Chinese: 李小龍/李小龙) learned from Sifu Yip Man & Wong Shun Leung[37][38][39][40]
- Donnie Yen (Chinese: 甄子丹) learned from Sifu Ip Chun
- Ip Chun Eldest son of Ip Man and inheritor of the legacy of Wing Chun-style kung fu[41]
- Jackie Chan (Chinese: 成龍/成龙) learned from Sifu Leung Ting[42]
- Jeff Thompson (England) learned from Sifu Wong Shun Leung[43][44]
- Michelle Yeoh (Chinese: 楊紫琼)
- Nicholas Tse (Chinese: 謝霆鋒/谢霆锋) learned from Phillip Ng[45]
- Ray Sefo
- Robert Downey Jr., Hollywood actor[46]
- Sammo Hung (Chinese: 洪金寶/洪金宝)
- Ti Lung (Chinese: 狄龍/狄龙)
- Yuen Biao (Chinese: 元彪)
- Nicolas Cage trains in Wing Chun as well as Jeet Kune Do, Karate, & Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu.
Branches
See also
References
- ↑ Complete Wing Chun: The Definitive Guide to Wing Chun's History and Traditions – Robert Chu, René Ritchie, Y. Wu – Google Books. Books.google.com (1998-06-15). Retrieved on 2012-01-14.
- ↑ Complete Wing Chun: The Definitive Guide to Wing Chun's History and Traditions – Robert Chu, René Ritchie, Y. Wu – Google Books. Books.google.com (1998-06-15). Retrieved on 2012-01-14.
- ↑ Wing Chun Kung Fu: Traditional Chinese King Fu for Self-Defense and Health – Ip Chun, Michael Tse – Google Books. Books.google.com. Retrieved on 2012-01-14.
- ↑ "Translation of Ip Man's account of Wing Chun's History". Kwokwingchun.com. Retrieved 2013-02-10.
- ↑ The Secret History of Wing Chun: The Truth Revealed, – By Benny Meng and Alfredo Delbrocco
- ↑ "Historiaa - Wing Tsung Kung Fu Finland". Wing Tsung Kung Fu Finland. Retrieved 2016-02-28.
- ↑ "Mitä on Wing Tsung? - Wing Tsung Kuopio". Wing Tsung Kuopio. Retrieved 2016-02-28.
- ↑ "Wing Tsung Vantaa". Wing Tsung Vantaa. Retrieved 2016-02-28.
- ↑ ":: Wing- Tsung.de ::". www.wing-tsung.de. Retrieved 2016-02-28.
- ↑ "WTAA - WTAA". www.iwtaa.de. Retrieved 2016-02-28.
- ↑ München, Dai-Sifu Reimers - Kampfsportschule. "Kampfkunstschulen Dai-Sifu Reimers | WT Schule". www.wingtsung.info. Retrieved 2016-02-28.
- ↑ WTAA-TR. "WTAA Federasyonu 土耳其詠春阿塔曼拳術總會". www.wtaa-tr.org. Retrieved 2016-02-28.
- ↑ "wingtsung kampfkunst marcus neuner selbstverteidigung". WingTsung (in German). Retrieved 2016-02-28.
- ↑ "Винг Чун Кунг Фу и Ескрима - WMAA - България -". Винг Чун Кунг Фу и Ескрима - WMAA - България (in Bulgarian). Retrieved 2016-02-28.
- ↑ "Palestra Shodan - Wing Tsung". www.shodan.it. Retrieved 2016-02-28.
- ↑ "Wing Tsung Kung-Fu". emas-roma.com. Retrieved 2016-02-28.
- ↑ "Wing Tsung Escrima Sanremo". www.wingtsungescrima.com. Retrieved 2016-02-28.
- ↑ "Wing Tsung". www.wingtsung.sk. Retrieved 2016-02-28.
- ↑ "Weng Chun Kung Fu". Weng-chun.com. Retrieved 2013-02-10.
- ↑ "Yong Chun White Crane Kung Fu". Yongchunbaihechuen.com. Retrieved 2013-02-10.
- ↑ "The Way of the Warrior". Howard Reid and Michael Croucher. ISBN 0712600795
- ↑ "Rediscovering the Roots of Wing Chun". Kung Fu Magazine. Retrieved 2010-02-06.
- ↑ "Integrative Wing Chun". Kung Fu Magazine. Retrieved 2010-02-06.
- ↑ "Six Forms of Wing Chun". Wingchunlife.com. Retrieved 2013-02-10.
- ↑ Michel Boulet. "The Simple Basics of a Complex Art". the Wing Chun Archive. Retrieved 2013-02-10.
- ↑ Jim Fung (2009-02-23). "Wing Chun Stance". Wingchun.com.au. Retrieved 2013-02-10.
- ↑ Tsui Sheung Tin. "The Hidden Power of Siu Nim Tau". Tstvingtsun.bc.ca. Retrieved 2013-02-10.
- ↑ martialarts2 Archived February 3, 2010, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "The Forms of Wing Chun Kuen Kung Fu | Reading Academy Wing Chun & Kali". Teamwingchun.co.uk. Retrieved 2013-02-10.
- ↑ "Ving Tsun Martial Arts Studio – Training". Tstvingtsun.bc.ca. Retrieved 2013-02-10.
- ↑ City Wing Chun – Training Notes Archived April 15, 2009, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Grand Master Philip Holder
- ↑ "Chi Sau: What's Behind Sticky Hand Training". Wingchunlife.com. Retrieved 2013-02-10.
- ↑ "Orange County Wing Chun FAQ's". Ocwingchun.com. 2004-02-26. Retrieved 2013-02-10.
- ↑ "Kung Fu Magazine's Description of Wing Chun". Ezine.kungfumagazine.com. Retrieved 2013-02-10.
- ↑ "2008 Chinese Box Office records". Boxofficemojo.com. Retrieved 2013-02-10.
- ↑ "BRUCE LEE AND HIS FRIENDSHIP WITH WONG SHUN LEUNG".
- ↑ "Who Taught Bruce Lee?".
- ↑ "Wong meet Bruce Lee".
- ↑ "Wong Shun Leung – The Logic Behind Wing Chun".
- ↑ Boehler, Patrick (27 August 2014). "Chinese kung fu masters battle over inheritance of Yip Man's Wing Chun legacy". South China Morning Post (Online). South China Morning Post Publishers Ltd. Retrieved 10 September 2016.
- ↑ "Jackie Chan Wing Chun Practitioner".
- ↑ "Sifu Li Heng Chang Official Website (Chinese: 李恆昌)".
- ↑ "重温《功夫》看星爷打咏春拳".
- ↑ "壹盤生意叛逆詠春派搶攻上位 - 明星八掛大分享".
- ↑ Sarah Kurchak (February 8, 2016). "How Wing Chun Helped Robert Downey Jr. Battle Addiction". Fightland.
34. "Wing Chun Gung Fu : The Explosive Art of Close Range Combat" by Randy Williams
Sources
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Wing Chun. |
- Chu, Robert; Ritchie, Rene; & Wu, Muthu Veeran (india). (1998). Complete Wing Chun: The Definitive Guide to Wing Chun's History and Traditions. Boston: Tuttle Publishing. ISBN 0-8048-3141-6.
- Leung Ting (1978). Wing Tsun Kuen. Hong Kong: Leung's Publications. ISBN 962-7284-01-7.
- Ritchie, Rene, "Wing Chun Concepts".