Web of trust
In cryptography, a web of trust is a concept used in PGP, GnuPG, and other OpenPGP-compatible systems to establish the authenticity of the binding between a public key and its owner. Its decentralized trust model is an alternative to the centralized trust model of a public key infrastructure (PKI), which relies exclusively on a certificate authority (or a hierarchy of such). As with computer networks, there are many independent webs of trust, and any user (through their identity certificate) can be a part of, and a link between, multiple webs.
The web of trust concept was first put forth by PGP creator Phil Zimmermann in 1992 in the manual for PGP version 2.0:
As time goes on, you will accumulate keys from other people that you may want to designate as trusted introducers. Everyone else will each choose their own trusted introducers. And everyone will gradually accumulate and distribute with their key a collection of certifying signatures from other people, with the expectation that anyone receiving it will trust at least one or two of the signatures. This will cause the emergence of a decentralized fault-tolerant web of confidence for all public keys.
Operation of a web of trust
All OpenPGP-compliant implementations include a certificate vetting scheme to assist with this; its operation has been termed a web of trust. OpenPGP identity certificates (which include public key(s) and owner information) can be digitally signed by other users who, by that act, endorse the association of that public key with the person or entity listed in the certificate. This is commonly done at key signing parties.
OpenPGP-compliant implementations also include a vote counting scheme which can be used to determine which public key – owner association a user will trust while using PGP. For instance, if three partially trusted endorsers have vouched for a certificate (and so its included public key – owner binding), OR if one fully trusted endorser has done so, the association between owner and public key in that certificate will be trusted to be correct. The parameters are user-adjustable (e.g., no partials at all, or perhaps 6 partials) and can be completely bypassed if desired.
The scheme is flexible, unlike most public key infrastructure designs, and leaves trust decision(s) in the hands of individual users. It is not perfect and requires both caution and intelligent supervision by users. Essentially all PKI designs are less flexible and require users to follow the trust endorsement of the PKI generated, certificate authority (CA)-signed, certificates.
Simplified explanation
There are two keys pertaining to a person: a public key which is shared openly and a private key that's withheld by the owner. The owner's private key will decrypt any information encrypted with its public key. In the web of trust, each user has a ring with a group of people's public keys.
Users encrypt their information with the recipient's public key, and only the owner's private key will decrypt it. Each user then digitally signs the information with their private key, so when they verify it with their own public key, they can confirm that it is the person in question. Doing this will ensure that the information came from the specific user and has not been tampered with, and only the intended recipient can read the information (because only they know their private key).
Contrast with typical PKI
In contrast, a typical X.509 PKI permits each certificate to be signed only by a single party: a certificate authority (CA). The CA's certificate may itself be signed by a different CA, all the way up to a 'self-signed' root certificate. Root certificates must be available to those who use a lower level CA certificate and so are typically distributed widely. They are for instance, distributed with such applications as browsers and email clients. In this way SSL/TLS-protected Web pages, email messages, etc. can be authenticated without requiring users to manually install root certificates. Applications commonly include over one hundred root certificates from dozens of PKIs, thus by default bestowing trust throughout the hierarchy of certificates which lead back to them.
Web of trust problems
The OpenPGP web of trust is essentially unaffected by such things as company failures, and has continued to function with little change. However, a related problem does occur. Users, whether individuals or organizations, who lose track of a private key can no longer decrypt messages sent to them produced using the matching public key found in an OpenPGP certificate. Early PGP certificates did not include expiry dates, and those certificates had unlimited lives. Users had to prepare a signed cancellation certificate against the time when the matching private key was lost or compromised. One very prominent cryptographer is still getting messages encrypted using a public key for which they long ago lost track of the private key.[1] They can't do much with those messages except discard them after notifying the sender that they were unreadable and requesting resending with a public key for which they still have the matching private key. Later PGP, and all OpenPGP compliant certificates include expiry dates which automatically preclude such troubles (eventually) when used sensibly. This problem can also be easily avoided by the use of "designated revokers", which were introduced in the early 1990s. A key owner may designate a third party that has permission to revoke the key owner's key (in case the key owner loses their own private key and thus loses the ability to revoke their own public key).
A non-technical, social difficulty with a Web of Trust like the one built into PGP/OpenPGP type systems is that every web of trust without a central controller (e.g., a CA) depends on other users for trust. Those with new certificates (i.e., produced in the process of generating a new key pair) will not likely be readily trusted by other users' systems, that is by those they have not personally met, until they find enough endorsements for the new certificate. This is because many other Web of Trust users will have their certificate vetting set to require one or more fully trusted endorsers of an otherwise unknown certificate (or perhaps several partial endorsers) before using the public key in that certificate to prepare messages, believe signatures, etc.
Despite the wide use of OpenPGP compliant systems and easy availability of on-line multiple key servers, it is possible in practice to be unable to readily find someone (or several people) to endorse a new certificate (e.g., by comparing physical identification to key owner information and then digitally signing the new certificate). Users in remote areas or undeveloped ones, for instance, may find other users scarce. And, if the other's certificate is also new (and with no or few endorsements from others), then its signature on any new certificate can offer only marginal benefit toward becoming trusted by still other parties' systems and so able to securely exchange messages with them. Key signing parties are a relatively popular mechanism to resolve this problem of finding other users who can install one's certificate in existing webs of trust by endorsing it. Websites also exist to facilitate the location of other OpenPGP users to arrange keysignings. The Gossamer Spider Web of Trust also makes key verification easier by linking OpenPGP users via a hierarchical style web of trust where end users can benefit by coincidental or determined trust of someone who is endorsed as an introducer, or by explicitly trusting GSWoT's top-level key minimally as a level 2 introducer (the top-level key endorses level 1 introducers).
The possibility of finding chains of certificates is often justified by the "small world phenomenon": given two individuals, it is often possible to find a short chain of people between them such that each person in the chain knows the preceding and following links. However, such a chain is not necessarily useful: the person encrypting an email or verifying a signature not only has to find a chain of signatures from their private key to their correspondent's, but also to trust each person of the chain to be honest and competent about signing keys (that is, they have to judge whether these people are likely to honestly follow the guidelines about verifying the identity of people before signing keys). This is a much stronger constraint.
Another obstacle is, there are also various costs and timing involve for both side to physically (attend a Key signing party, or) meet with someone physically to verify ID against a person's key: planning, scheduling or early-appointment, travel, lodging, food, etc. A software user may have to verify hundreds of software components from hundreds of original developers or WOT based specific-users in trust-chain, to establish trust level for each software components. Millions or billions of software users cannot just practically or physically travel and meet with hundreds of other specific-users from WOT or with hundreds of original developer or author, located in different parts of the world.
When original developer's or author's or file-releaser's key is collected from a public keyserver, then there are various ways (and vulnerabilities) exist to mis-guide users or deliver incorrect data, as public keyserver is also a type of third-party, a 3rd-party middle-man. When original author or developer also publishes or shares their updated original public-key (or file-signing pub-key) in their own keyserver under their own domain webserver, inside their own premise: own-home or own-home-office or own-office, and forces HKPS encrypted connection usage for public-key delivery, only then users can get correct and trusted key. For details, see "WOT Assisting Solutions" section in below.
Strong set
The strong set refers to the largest collection of strongly connected PGP keys.[2] This forms the basis for the global web of trust. Any two keys in the strong set have a path between them; while islands of sets of keys that only sign each other in a disconnected group can and do exist, only one member of that group needs to exchange signatures with the strong set for that group to also become a part of the strong set.[3] The strong set had a size of about 55000 Keys at the beginning of the year 2015.[4]
Mean shortest distance
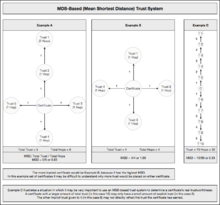
In statistical analysis of the PGP/GnuPG/OpenPGP Web of trust the mean shortest distance (MSD) is one measurement of how "trusted" a given PGP key is within the strongly connected set of PGP keys that make up the Web of trust.
Drew Streib wrote the following in his explanation of keyring analysis:[5]
There are a variety of metrics one could apply to this set, but I've chosen initially to measure the "mean shortest distance" (MSD) to each key. Since every key is reachable from every other in the strong set, it is possible to find out the shortest distance (number of hops) to any given key from any other key. Averaging these distances gives the MSD to that key from every other key in the strong set.It is desirable to have as short as possible an MSD to your key, as that means that on average, people can reach your key quickly through signatures, and thus your key is relatively more trusted than a key with a higher MSD.
NOTE: This does not mean that you should universally trust keys with a low MSD. This is merely a relative measurement for statistical purposes.
The MSD has the property of being no more than 1 higher than your lowest signature. In the worst case, every key in the strong set could reach you by getting to that key, plus 1 hop to get to you. It also encourages the joining of keys that are separated by great distances in the graph, as it will make you a highway of sorts for shortest paths between keys in those groups. In the end, it encourages an overall tightening of the world graph, shortening distances between key owners.
MSD has become a common metric for analysis of sets of PGP keys. Very often you will see the MSD being calculated for a given subset of keys and compared with the global MSD which generally refers to the keys ranking within one of the larger key analyses of the global Web of trust.
WOT assisting solutions
Physically meeting with original developer or author, is always the best way to obtain and distribute and verify and trust PGP/GPG Keys with highest trust level, and will remain as the best level of best trustworthy way. Publishing of GPG/PGP full Key or full Key fingerprint on/with widely known (physical/paper-material based) book, by the original author/developer, is the 2nd best form of sharing trustworthy key with and for users.
However, it is not practical for millions of users who want to communicate securely or millions of software users, who need to meet with hundreds of (communication recipient users or need to meet with hundreds of) software developers, whose software or PGP/GPG Key they want to verify and trust and ultimately use in their computer. Therefore, one or more trusted third-party authority (TTPA) type of entity or group need to be available and used by users, and such entity/group need to be capable of providing trusted-verification or trusted-delegation service for millions of users around the world, at any time.
Practically, to verify any downloaded or received content or data or email or file's authenticity, a user need to verify their downloaded main content or data/email or file's PGP/GPG signature code/file (ASC, SIG), so users would need to use original developer-owner's or author-owner's trustworthy public-key, or would need to use trustworthy file-signing key trusted-by original developer or author or original-releaser. And to really trust a specific PGP/GPG key, users would need to physically meet with very specific and original author or developer, or users would need to physically meet with the original-releaser of file-signing key's original-owner, or, users would need to find another alternative trustworthy user, who is in trusted-chain of WOT (aka, who is trusted by that very specific original author or developer) and then physically meet with that person, to verify their real ID with his/her PGP/GPG key (and also provide your own ID and key to the other user, so that both side can sign/certify and trust each other's PGP/GPG key). Whether a software is popular or not, software users are usually located around the world in different locations. It is physically not possible for a original author or developer or file-releaser to provide key or trust or ID verification services to millions of users. Neither it is practical for software users to physically meet with every software or every software-library or every piece of code's developer or author or releaser, which they will use or need to use in their computer. Even with multiple trusted people/person (by original-author) in trusted-chain from WOT, its still not physically or practically possible for every developer or author to meet with every other users, and its also not possible for every users to meet with hundreds of developers whose software they will be using or working on.
A few solutions are: original author/developer need to first set a trust-level to sign/certify their own file-signing key. Then updated public-keys and updated file-signing public-keys must also have to be published and distributed (or made accessible) to users, via online secure and encrypted mediums, so that any user from any location in world, can get the correct and trusted public-key. To make sure that each users are getting the correct and trusted public-keys and signed-code/file, original dev/author or original-releaser must publish their updated public-keys on their own Keyserver and force HKPS encrypted connection usage, or publish their updated and full public-keys (and signed-code/file) on their own HTTPS encrypted webpage, under their own webserver, from their own primary domain, (not-from sub-domains which are located in external-servers, not-from any mirror, not-from any external/shared forum/wiki etc website servers, not-from any public or external/shared cloud or hosting service servers), and is located/kept securely in their own premises: own-home, own-home-office, or own-office. In that way, those small pieces of original keys/code, will travel intact and will remain unmodified during transit and will reach destination without being eavesdropped or modified, into user's side.
When original public-keys/signed-codes are shown in original dev's or author's own webserver or keyserver, over encrypted connection or encrypted webpage, then any other files, data or content can be transferred over any type of non-encrypted connection, like: HTTP/FTP, etc, and from any sub-domain server or from any mirror or from any shared cloud/hosting servers, because, non-encrypted connection based downloaded items/data/files can be authenticated later, by using the original public-keys/signed-codes, which were obtained from the original author's/developer's own server over secured, encrypted, and trusted connection/channels.
Using encrypted connection to transfer keys/sign-code, allow software users to delegate their trust with a PKI TTPA (trusted third party authority), like public CA (Certificate Authority), to help in providing trusted connection in between the original developer/author's webserver and millions of users' computers, at any time.
When the original author/developer's domain-name and webserver is signed by DNSSEC, and when used SSL/TLS public certificate is declared/shown in TLSA/DANE DNSSec DNS resource-record, (and when SSL/TLS Certs in the trust chain are pinned and used via HPKP technique by web servers), then a web-server's webpage or data can also be verified via another PKI TTPA: DNSSEC and DNS namespace maintainer ICANN, other than a public CA. DNSSEC is an another form of PGP/GPG WOT but for name-servers, it creates trusted-chain for name-servers first (instead of people/person), then people/person's PGP/GPG Keys can also be added into a server's DNSSEC DNS records. So any users who want to communicate securely or any software users, can effectively get/receive their data/key/code/webpage etc verified via two (aka, dual/double) trusted PKI TTPAs/Channels at same time: ICANN (DNSSEC) and CA (SSL/TLS Certificate). So PGP/GPG key/signed-code data can be trusted, because of usage-of or application-of such solutions and techniques: HKPS, HKPS+DNSSEC+DANE, HTTPS, HTTPS+HPKP or HTTPS+HPKP+DNSSEC+DANE.
If a vast number of user's group create their own new DLV based DNSSEC registry, and if users use that new DLV (along with ICANN-DNSSEC) root-key in their own local DNSSEC-based DNS Resolver/Server, and if domain-owners also use it for additional signing of their own domain-names, then there can be a new third TTPA. In such case, any PGP/GPG Key/signed-code data or a webpage or web data can be three/triple-channel verified.
See also
- Virtual community
- CAcert signs OpenPGP keys if you are checked through a web of trust, they also issue free X.509 certificates.
- Thawte stopped signing OpenPGP keys many years ago and now only issues X.509 certificates.
- Friend-to-friend (F2F) computer network.
- Ripple (payment protocol)
References
- ↑ Ferguson, Niels & Schneier, Bruce (2003). Practical Cryptography. Wiley. p. 333. ISBN 978-0471223573.
- ↑ Penning, Henk. "on the apache.org web of trust". Archived from the original on 13 December 2013. Retrieved 13 December 2013.
- ↑ Streib, M. Drew. "Explanation of this Keyring Analysis". Archived from the original on 3 February 2009. Retrieved 13 December 2013.
- ↑ Penning, Henk P. "analysis of the strong set in the PGP web of trust". Retrieved 8 January 2015.
- ↑ Streib, M. Drew. "Explanation of this Keyring Analysis". Archived from the original on 3 February 2009. Retrieved 13 December 2013.
Further reading
Ferguson, Niels; Bruce Schneier (2003). Practical Cryptography. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-22357-3.
External links
- An explanation of the PGP Web of Trust
- analysis of the strong set in the PGP web of trust - regularly updated