Water chevrotain
| Water chevrotain | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Taxidermied water chevrotain at the Natural History Museum in London. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Synapsida |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Family: | Tragulidae |
| Genus: | Hyemoschus Gray, 1845 |
| Species: | H. aquaticus |
| Binomial name | |
| Hyemoschus aquaticus Ogilby 1841 | |
 | |
The water chevrotain (Hyemoschus aquaticus), also known as the fanged deer, is a small ruminant found in tropical Africa. It is the largest of the ten species of chevrotains, basal even-toed ungulates which are similar to deer but are barely larger than small dogs.
Description
Unusually for most vertebrates, female water chevrotains are larger than males. On average, they weigh over two kilograms more than the 10 kg males. Their body length is about 85 cm, and their shoulder height is around 35 cm. Water chevrotains have a rich, sleek red-brown coat on top, and the underside of the coat is white. On the body, there is a pattern of white stripes that run horizontally from the shoulder to the tail, with vertical rows of white stripes in the back. The chin, throat and chest are covered in very course hair with a pattern of white V shapes. The back end of the water chevrotain has many powerful muscles and is higher than the shoulders, which makes the body slope downward. The head is held down toward the ground while walking, which allows the water chevrotain to navigate easily through thickets of dense brush. There is a layer of thick, reinforced skin on the dorsal surface, which protects the back from injuries caused by the thick brush. The legs look short and thin compared to the bulky body, and the hooves are similar to a pig’s. The tail is short with a fluffy white underside that resembles a cotton ball.[2]
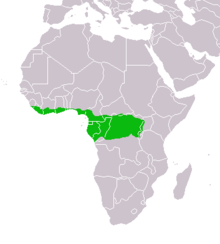
Distribution and habitat
The water chevrotain is endemic to the tropical regions of Africa. While it primarily lives in the coastal regions, the species can be found from Sierra Leone to western Uganda.[3] The water chevrotain can be found in closed canopy moist tropical lowland forest, and within this habitat, they only occupy areas within close range to streams or rivers. The area is rarely inhabited by the species if it is further than 250 m away from water. During the day, chevrotains cannot be found outside of the dense forest; but at night they can be observed in exposed clearings and open river banks.[2]
Behavior
The water chevrotain is exclusively nocturnal, and forages for food in clearings at night. During the day, the water chevrotain hides in the dense cover of the African brush. The resting postures of the species include lying down and sitting up. Because they’re such a solitary species, the interactions between water chevrotains are only antagonistic and reproductive encounters. Males fight other males, mainly over territory. Their fights are typically short, and in them the two competing males run at each other, mouths open. They poke each other with their muzzles and bite. These aggressive fights are thought to be the reason that mature male Water chevrotains normally live no closer than several kilometers apart. The water chevrotain has several different noises that it makes, which include a scream when injured/wounded and an alarm bark. When females fight, they make a high pitched chattering noise, and when pursuing a female, males make a noise through a closed mouth.[2]
Conservation status
It is estimated that the total population of the water chevrotain species is around 278,000. The ICUN Red List has given the status “Least Concern” to the Water chevrotain. Because of its solitary nature, there is very little information about its population in each individual country, but recently there has been evidence that shows the population is declining in some areas.[4]
References
- ↑ IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group (2008). "Hyemoschus aquaticus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2008. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 26 March 2009. Database entry includes a brief justification of why this species is of least concern.
- 1 2 3 "Hyemoschus aquaticus". Ungulates of the World. Retrieved February 2013. Check date values in:
|access-date=(help) - ↑ "Hyemoschus aquaticus". Animal Diversity Web. Retrieved February 2013. Check date values in:
|access-date=(help) - ↑ IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group (2008). "Hyemoschus aquaticus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2012.2. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved February 2013. Check date values in:
|access-date=(help)
