Warsaw Uprising Monument
| Pomnik Powstania Warszawskiego | |
 | |
| Coordinates | 52°14′58″N 21°0′21″E / 52.24944°N 21.00583°ECoordinates: 52°14′58″N 21°0′21″E / 52.24944°N 21.00583°E |
|---|---|
| Location | Warsaw, Poland |
| Designer | Wincenty Kućma, Jacek Budyn |
| Height | 10 metres (33 ft) |
| Completion date | 1 August 1989 |
| Dedicated to | Warsaw Uprising insurgents |
Warsaw Uprising Monument (Polish: Pomnik Powstania Warszawskiego) is a monument in Warsaw, Poland, dedicated to the Warsaw Uprising of 1944. Unveiled in 1989, it was sculpted by Wincenty Kućma and the architect was Jacek Budyn. It is located on the southern side of Krasiński Square.
The monument has been described as "the most important monument of post-war Warsaw."[1] Gazeta Wyborcza reported in 2012 that it is one of the most visited landmarks for foreign tourists.[2]
History
.jpg)
The Warsaw Uprising, which broke out on 1 August 1944 and lasted until 2 October 1944, was one of the most important and devastating events in the history of Warsaw and Poland. Up to 90% of Warsaw's buildings were destroyed during the hostilities and the systematic destruction of the city carried out by the Germans after the uprising.[3]
However, it was also an event that the communist authorities of the post-war People's Republic of Poland found highly controversial, as it was organised by the Polish resistance movement which had fought for Poland's independence during World War 2 - principally the Home Army, the remnants of which were brutally suppressed by the post-war Stalinist regime. In addition, Joseph Stalin had purposefully stopped the Soviet advance through Polish territory just short of Warsaw immediately after the outbreak of the uprising, and not only refused to aid the insurgents, but also refused to allow planes of the western allies to land and refuel on Soviet-held territory, to ensure that only very limited supplies could be delivered to Warsaw from the outside.[1][3][4] As a result, the uprising was brutally crushed by the Germans over a period of 63 days while the Soviets watched on (even after finally resuming their offensive and capturing the right bank the River Vistula in mid-September 1944). After the uprising the Germans expelled the entire population from the city and spent the whole of October, November and December 1944 looting Warsaw and destroying whatever was still standing, while the Soviets continued to do nothing to intervene (they finally entered the ruins of the abandoned city in January 1945 after waiting for the Germans to leave).
As a result of these "controversies", the significance of the uprising was downplayed for many years after the Second World War, while the Home Army and wartime Polish government were condemned by communist propaganda. These political factors made official memorialisation of the Warsaw Uprising impossible for decades, and subsequent debates about the form and location of the monument further delayed the project.[1][3]
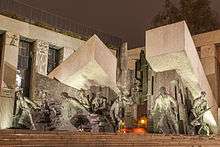
Poland's communist government finally gave permission to construct the monument on 12 April 1988.[1] It was unveiled on 1 August 1989, the 45th anniversary of the Uprising.[3][5] The monument was designed by sculptor Wincenty Kućma and architect Jacek Budyn.[1][5]
Description
The monument is located on the southern side of Krasiński Square.[1] In 1999 the building of the Supreme Court of Poland was constructed in the area directly behind it.[1]
The monument is made from bronze and is about 10 metres (33 ft) tall.[1] It is composed of two parts, located within a short distance of each other. The larger, elevated element shows a group of insurgents actively engaged in combat, running from the artistic vision of a collapsing building, represented by a more abstract composition.[3][5][6] The smaller element shows insurgents descending into a manhole – a reference to the use of Warsaw's sewer system by the insurgents to move across German-held territory during the uprising, and specifically to the evacuation of 5300 resistance fighters from Warsaw's Old Town to the city centre at the beginning of September 1944 - a five-hour journey which started from Krasiński Square (there is a small plaque across the road from the monument at the intersection of Długa and Miodowa streets above the two manholes that were actually used).
The realistic style of the monument has been favourably compared to a still from a movie, or a historical painting by Jan Matejko,[3] but also criticised for its socrealist style.[1][3] There have also been critical voices saying that the monument is "defeatist", and that it was a gesture of reconciliation by the passing communist government that came many years too late.[3] A 2013 analysis suggests that the monument is in need of renovation, particularly due to deterioration caused by atmospheric pollutants.[5]
According to the authors, it is a part of a memorial triptych, the other two parts of which are the Monument to the Defenders of the Polish Post Office (pl) in Gdańsk and the Monument to the Fallen in Defense of the Homeland (pl) in Częstochowa.[7]
| Panoramic Views of the Monument | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
See also
- Warsaw Uprising
- Home Army
- Polish resistance movement in World War II
- Warsaw Uprising Museum
- Warsaw Insurgents Cemetery
- Cultural representations of the Warsaw Uprising#Monuments to the Insurgents in Warsaw
- Little Insurgent Monument
- Monument to Victims of the Wola Massacre
- Monument to the Ghetto Heroes (with which the Warsaw Uprising Monument is often confused)
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Warszawa - Pomnik Bohaterów Powstania Warszawskiego - sztuka.net
- ↑ Warszawa. Pomnik Powstania Warszawskiego
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Wincenty Kućma i Jacek Budyn, Pomnik Powstania Warszawskiego | Culture
- ↑ Kristin Kopp; Joanna Nizynska (8 May 2012). Germany, Poland and Postmemorial Relations: In Search of a Livable Past. Palgrave Macmillan. pp. 149–152. ISBN 978-1-137-05205-6.
- 1 2 3 4 Pomnik Powstania Warszawskiego: krótki opis formalny oraz program prac konserwatorskich przy brązowvch fragmentach monumentu wynikaiach ze stanu ich zachowania
- ↑ Titus Ensink; Christoph Sauer (27 November 2003). The Art of Commemoration: Fifty years after the Warsaw Uprising. John Benjamins Publishing Company. pp. 11–. ISBN 978-90-272-9603-0.
- ↑ "185 elementów, w sumie 20 ton. Kto pamięta, jak powstał Pomnik Poległym w Obronie Ojczyzny?"
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Warsaw Uprising Monument. |
- (Polish) Pomnik Powstania Warszawskiego
Further reading
- (Polish) Zdzisław Życieński,O Pomnik Powstania Warszawskiego, Biuletyn IPN, nr 8-9/2007
- Marian Pyzel (1 January 1992). Bitwa o pomnik Powstania Warszawskiego 1944 (in Polish). Joanna Pyzel.

