Urushiol-induced contact dermatitis
| Urushiol-induced contact dermatitis | |
|---|---|
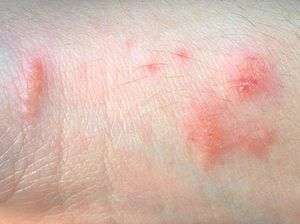 | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| ICD-10 | L23.7 |
| ICD-9-CM | 692.6 |
| DiseasesDB | 32755 |
| eMedicine | emerg/452 |
| MeSH | D011040 |
Urushiol-induced contact dermatitis (also called Toxicodendron dermatitis and Rhus dermatitis) is the medical name given to allergic rashes produced by the oil urushiol, which is contained in various plants, most notably those of the Toxicodendron genus: the Chinese lacquer tree, poison ivy, poison oak, and poison sumac. The name is derived from the Japanese word for the sap of the Chinese lacquer tree, urushi. Other plants in the sumac family (including mango, pistachio, the Burmese lacquer tree, the India marking nut tree, and the shell of the cashew) also contain urushiol,[1] as do unrelated plants such as Ginkgo biloba.
As is the case with all contact dermatitis, urushiol-induced rashes are a Type IV hypersensitivity reaction, also known as delayed-type hypersensitivity. Symptoms include itching, inflammation, oozing, and, in severe cases, a burning sensation.
The American Academy of Dermatology estimates that there are up to 50 million cases of urushiol-induced dermatitis annually in the United States alone, accounting for 10% of all lost-time injuries in the United States Forest Service. Poison oak is a significant problem in the rural Western and Southern United States, while poison ivy is most rampant in the Eastern United States. Dermatitis from poison sumac is less common.
Signs and symptoms
Urushiol causes an eczematous contact dermatitis characterized by redness, swelling, papules, vesicles, blisters, and streaking.[2] People vary greatly in their sensitivity to urushiol. In approximately 15%[3] to 30%[4] of people, urushiol does not trigger an immune system response, while at least 25% of people have a very strong immune response resulting in severe symptoms. Since the skin reaction is an allergic one, people may develop progressively stronger reactions after repeated exposures, or have no immune response on their first exposure but show sensitivity on subsequent exposures.
Approximately 80% to 90% of adults will get a rash if they are exposed to 50 micrograms of purified urushiol. Some people are so sensitive that it only takes a trace of urushiol (two micrograms, or less than one ten-millionth of an ounce) on the skin to initiate an allergic reaction.[5]
The rash takes one to two weeks to run its course and may cause scars, depending on the severity of the exposure. Severe cases involve small (1–2 mm), clear, fluid-filled blisters on the skin. Pus-filled vesicles containing a whitish fluid may indicate an infection. Most poison ivy rashes, without infections, will resolve within 14 days without treatment. Excessive scratching may result in infection, commonly by staphylococcal and streptococcal species; these may require antibiotics.
- Severe allergic reaction to urushiol (poison oak) 4 days after exposure.
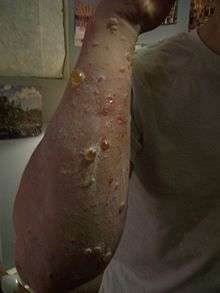 Blistering 48 hours after urushiol contact.
Blistering 48 hours after urushiol contact. Poison ivy rash after 2 days.
Poison ivy rash after 2 days. Poison ivy rash with swelling about 3 days after direct contact.
Poison ivy rash with swelling about 3 days after direct contact.
Cause

Urushiol-induced contact dermatitis is caused by contact with a plant or any other object containing urushiol oil. The oil adheres to almost anything with which it comes in contact, such as towels, blankets, clothing, and landscaping tools. Clothing or other materials that touch the plant and then, before being washed, touch the skin are common causes of exposure.
For people who have never been exposed or are not yet allergic to urushiol, it may take 10 to 21 days for a reaction to occur the first time. Once allergic to urushiol, however, most people break out 48 to 72 hours after contact with the oil. Typically, individuals have been exposed at least once, if not several times, before they develop a rash.[6] The rash typically persists one to two weeks, but in some cases may last up to five weeks.
Urushiol is primarily found in the spaces between cells beneath the outer skin of the plant, so the effects are less severe if the plant tissue remains undamaged on contact. Once the oil and resin are thoroughly washed from the skin, the rash is not contagious. Urushiol does not always spread once it has bonded with the skin, and cannot be transferred once the urushiol has been washed away.
Although simple skin exposure is most common, ingestion of urushiol can lead to serious, systemic reactions. Burning plant material is commonly said to create urushiol-laden smoke that causes a systemic reaction, as well as a rash in the throat and eyes. Firefighters often get rashes and eye inflammation from smoke-related contact.[7] A high-temperature bonfire may incinerate urushiol before it can cause harm, while a smoldering fire may vaporize the volatile oil and spread it as white smoke. However, some sources dispute the danger of burning urushiol-containing plant material.[8]
Mechanism
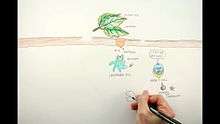
Urushiols are oxidized in-vivo, generating a quinone form of the molecules.[9] The toxic effect is indirect, mediated by an induced immune response. The oxidized urushiols acts as haptens, chemically reacting with, binding to, and changing the shape of integral membrane proteins on exposed skin cells. One protein recognized in this process is CD28.[10]
Affected proteins interfere with the immune system's ability to recognize these cells as normal parts of the body, causing a T-cell-mediated immune response.[11] This response is directed at the complex of urushiol derivatives (namely, pentadecacatechol) bound in the skin proteins, attacking the cells as if they were foreign bodies.
Treatments
Treatment consists of two phases: stopping the urushiol contact that is causing the reaction (this must be done within minutes)[12] and, later, reducing the pain and/or itching.[5][13]
Primary treatment involves washing exposed skin thoroughly with soap, water, and friction as soon as possible after exposure is discovered. Soap or detergent is necessary because urushiol is an oil; friction, with a washcloth or something similar, is necessary because urushiol adheres strongly to the skin.[14] Commercial removal preparations, which are available in areas where poison ivy grows, usually contain surfactants, such as the nonionic detergent Triton X-100, to solubilize urushiol; some products also contain abrasives.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration recommends applying a wet compress or soaking the affected area in cool water; topical corticosteroids (available over-the-counter) or oral corticosteroids (available by prescription); and topical skin protectants, such as zinc acetate, zinc carbonate, zinc oxide, and calamine. Baking soda or colloidal oatmeal can relieve minor irritation and itching. Aluminum acetate, sometimes known as Burow's solution, can also ease the rash.[15]
Showers or compresses using hot (but not scalding) water can relieve itching for up to several hours, though this "also taxes the skin's integrity, opening pores and generally making it more vulnerable", and is only useful for secondary treatment (not for cleaning urushiol from the skin, which should be done with cold water).[16] People who have had a prior systemic reaction may be able to prevent subsequent exposure from turning systemic by avoiding heat and excitation of the circulatory system and applying moderate cold to any infected skin with biting pain.
Antihistamine and hydrocortisone creams, or oral antihistamines in severe cases, can alleviate the symptoms of a developed rash. Nonprescription oral diphenhydramine (U.S. trade name Benadryl) is the most commonly suggested antihistamine. Topical formulations containing diphenhydramine are also available but may further irritate the skin.
In cases of extreme symptoms, steroids such as prednisone or triamcinolone are sometimes administered to attenuate the immune response and prevent long-term skin damage, especially if the eyes are involved. Prednisone is the most commonly prescribed systemic treatment but can cause serious adrenal suppression, so it must be taken carefully and tapered off slowly.[17] If bacterial secondary infection of affected areas occurs, antibiotics may also be necessary.
Scrubbing with plain soap and cold water will remove urushiol from skin if it is done within a few minutes of exposure.[12] Many home remedies and commercial products (e.g., Tecnu, Zanfel) also claim to prevent urushiol rashes after exposure. A study that compared Tecnu ($1.25/oz.) with Goop Hand Cleaner or Dial Ultra Dishwashing Soap ($0.07/oz.) found that differences among the three—in the range of 56-70% improvement over no treatment—were nonsignificant (P>0.05), but that improvement over no treatment was significant at the same level of confidence.[18]
Further observations:
- Ordinary laundering with laundry detergent will remove urushiol from most clothing[19] but not from leather or suede.
- The fluid from the resulting blisters does not spread urushiol to others.[20][21]
- Blisters should be left unbroken during healing.[22]
- Poison ivy and poison oak are still harmful when the leaves have fallen off, as the toxic residue is persistent, and exposure to any parts of plants containing urushiol can cause a rash at any time of the year.[12]
- Ice, cold water, cooling lotions, and cold air do not help cure poison ivy rashes, but cooling can reduce inflammation and soothe the itch.[19]
- Results for jewelweed as a natural agent for treatment are conflicting, but the latest studies indicate that it "failed to decrease symptoms of poison ivy dermatitis" [1980] and had "no prophylactic effect" [1997].[23]
Prevention
A rarely cited double-blind study in 1982 reported that a course of oral urushiol usually hyposensitized subjects.[24]
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Urushiol-induced contact dermatitis. |
References
- ↑ Lepoittevin, J.-P., Benezra, C., Asakawa, Y. 1989. Allergic contact dermatitis to Ginkgo biloba L.: retationship with urushiol. Arch. Dermatol. Res., 281: 227-230.
- ↑ DermAtlas -1892628434
- ↑ Wilson, Stephanie. "Howstuffworks "How Poison Ivy Works"". Science.howstuffworks.com. Retrieved 2010-06-04.
- ↑ Michael Rohde. "Contact-Poisonous Plants of the World". Mic-ro.com. Retrieved 2010-06-04.
- 1 2 "Poison Oak". Waynesword.palomar.edu. 2011-01-16. Retrieved 2015-10-06.
- ↑ Ray, Thomas MD, Professor Emeritus of Dermatology. "Poison Ivy: The Most Common of Allergens". University of Iowa Health Care. Retrieved 30 October 2015.
- ↑ "FIREFIGHTERS BATTLE HIDDEN DANGERS THIS WILDFIRE SEASON: POISON OAK, IVY AND SUMAC PLANTS TOP CAUSE OF DISABILITY, SICK TIME". Fireengineering.com. Retrieved 2015-10-06.
- ↑ Dietrich Frohne; Hans Jurgen Pfander (1984). A Colour Atlas of Poisonous Plants: A Handbook for Pharmacists, Doctors, Toxicologists, and Biologists. Wolfe Publishing Ltd. p. 291 pp. ISBN 0-7234-0839-4.
- ↑ "Modulation of fatty acid oxidation alters contact hypersensitivity to urushiols: role of aliphatic chain beta-oxidation in processing and activation of urushiols". J Invest Dermatol. 108 (1): 57–61. Jan 1997. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12285632.
- ↑ Kalish, RS; Wood, JA (Mar 1997). "Induction of hapten-specific tolerance of human CD8+ urushiol (poison ivy)-reactive T lymphocytes". J Invest Dermatol. 108 (3): 253–7. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12286447.
- ↑ C.Michael Hogan (2008) Western poison-oak: Toxicodendron diversilobum, GlobalTwitcher, ed. Nicklas Stromberg "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2009-07-21. Retrieved 2010-04-21.
- 1 2 3 Bill Einsig, Bill (2002), Poison Ivy Myth: Science, Environment and Ecology Flash for Educators (No. 341), in Keystone Outdoors Magazine (May 11), excerpted by the Penn State Integrated Pest Management, accessed 7 October 2015.
- ↑ "Soothing Remedies for Poison Ivy and Poison Oak". Googobits.com. 2005-08-04. Retrieved 2010-06-04.
- ↑ "How to never have a serious poison ivy rash again" on YouTube
- ↑ Archived July 16, 2010, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Hauser, Susan Carol; William L. Epstein (2008). A Field Guide to Poison Ivy, Poison Oak, and Poison Sumac. Globe Pequot. p. 60. ISBN 978-0-7627-4741-2. Retrieved 2010-11-21.
- ↑ "Poison Ivy, Oak, and Sumac". Surviveoutdoors.com. Retrieved 2010-06-04.
- ↑ Stibich, A. S., Yagan, M., Sharma, V., Herndon, B. and Montgomery, C. (2001). "Cost-effective post-exposure prevention of poison ivy dermatitis". International Journal of Dermatology. 39 (7): 515–518. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2000.00003.x. PMID 10940115.
- 1 2 "Aetna InteliHealth: Featuring Harvard Medical School's Consumer Health Information". Intelihealth.com. Archived from the original on February 11, 2012. Retrieved 6 October 2015.
- ↑ "Poison ivy, oak, and sumac". American Academy of Dermatology.
- ↑ "Outsmarting Poison Ivy and Other Poisonous Plants". U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
- ↑ "Poison Ivy, Oak and Sumac". OutDoorPlaces.com. Retrieved 22 September 2010.
- ↑ Shenefelt, Philip D. (2011). "Herbal Treatment for Dermatologic Disorders". Herbal Medicine: Biomolecular and Clinical Aspects (2nd ed.). Boca Raton, Florida, USA: CRC Press. Retrieved October 5, 2015.
- ↑ Epstein, W. L.; Byers, V. S.; Frankart, W. (1982-09-01). "Induction of antigen specific hyposensitization to poison oak in sensitized adults". Archives of Dermatology. 118 (9): 630–633. doi:10.1001/archderm.118.9.630. ISSN 0003-987X. PMID 06180687.