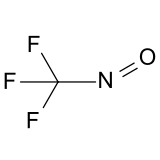
Trifluoronitrosomethane
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Trifluoronitrosomethane | |
| Other names
Trifluoro-nitrosomethane Trifluoro-nitroso-methane Nitrosotrifluoromethane | |
| Identifiers | |
| 334-99-6 | |
| ChemSpider | 60949 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.804 |
| PubChem | 67630 |
| |
| Properties | |
| CF3NO | |
| Molar mass | 99.012 g/mol |
| Appearance | Deep blue gas |
| Melting point | −196.6 °C (−321.9 °F; 76.5 K) |
| Boiling point | −85 °C (−121 °F; 188 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | highly toxic and reactive |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Trifluoronitrosomethane (commonly abbreviated TFNM) is a highly reactive and toxic halomethane. Its distinctive deep blue colour is unusual for a gas.
History
Trifluoronitrosomethane was synthesized for the first time in 1936 by Otto Ruff and Manfred Giese at the University of Wrocław.[1] It was created through the fluorination of silver cyanide in the presence of silver nitrate and silver oxide.
Production
Trifluoronitrosomethane can be produced from the reaction of trifluoroiodomethane and nitric oxide under a UV light with a yield of up to 90% in normal pressure. The reaction results in the creation of mercury.[2][3][4]
References
- ↑ O. Ruff und M. Giese: Das Trifluor-nitroso-methan, CF3NO (III.) In: Ber dtsch Chem Ges 69, 1936, S. 684–689. doi:10.1002/cber.19360690411
- ↑ A. Senning: N-, 0-, AND S-trihalomethyl compounds. In: Chemical Reviews 65, 1964, S. 385–412.
- ↑ C. W. Taylor u. a.: The Preparation of Polyfluoronitrosoalkanes from Nitrosyl Polyfluoroacylates. In: The Journal of organic chemistry 27, 1962, S. 1064–1066. doi:10.1021/jo01050a523
- ↑ J. D. Park u. a.: Preparation of Perfluoronitrosoalkanes. Reaction of Trifluoroacetic Anhydride with Nitrosyl Chloride. In: The Journal of organic chemistry 27, 1962, S. 1642. doi:10.1021/jo01051a519
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/17/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.