Los Alamitos Circle
| Los Alamitos Circle | |
|---|---|
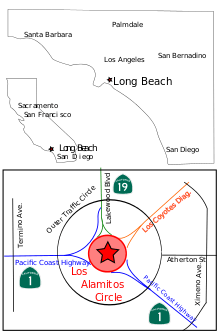 Map showing location of the Long Beach Traffic Circle in State of California, Southern California, and including nearby roads and interconnect with the Pacific Coast Highway. | |
| Location | |
| Long Beach, California | |
| Coordinates: | 33°47′24″N 118°08′33″W / 33.79°N 118.1425°WCoordinates: 33°47′24″N 118°08′33″W / 33.79°N 118.1425°W |
| Roads at junction: |
Los Coyotes Diagonal |
| Construction | |
| Type: | Roundabout |
The Los Alamitos Traffic Circle, informally known as the Long Beach Traffic Circle (or just the Traffic Circle, as there are no other high volume traffic circles in Southern California), is a roundabout at the intersection of Lakewood Boulevard (State Route 19), Pacific Coast Highway (State Route 1/former US Highway 101 Alternate) and Los Coyotes Diagonal in Long Beach, California. The intersection was originally constructed as a traffic circle in 1930 and reconstructed as a modern roundabout in 1993.
History
In 1930, German engineer Werner Ruchti was contracted to design the traffic circle, which was to be based on European models. Construction was expedited in order to accommodate the increased vehicle traffic that was expected with the 1932 Summer Olympics, held in Los Angeles, as many of the aquatic and rowing events were to be held in Long Beach.[1]
The Los Alamitos Traffic Circle was one of the first of its kind to be constructed in the United States, and prior to their truncation, was also an end point of US 6 (which connects Provincetown, Massachusetts some 3,227 miles (5,193 km) to the east) and US 91.[2]
Reclassification
In 1993, the circle was converted from an old-style traffic circle to a modern roundabout by the California Department of Transportation (Caltrans). This was the first such conversion in the United States. Yield signs replaced Stop signs, giving drivers inside the circle the right of way, which increased traffic flow efficiency. PCH (the main thoroughfare) was given an additional entry lane at both north and south bound routes.[3] Also added were widened feeder lanes,[4] and dedicated lanes for traffic traveling only 90 of the 360 degrees of the circle - the equivalent of a right turn at a traditional American traffic light. After the conversion, both the total auto accident and the injury rate significantly dropped, making the circle one of the safest statistically in the nation. The aforementioned modifications ran a cost of $350,000.[3]
The Los Alamitos Traffic Circle was very similar to the 1932 Garces Memorial Circle located in Bakersfield, though the Bakersfield circle has not undergone modernization to roundabout standards.
Present day
Today the circle handles over 60,000 vehicles a day, mostly commuters from Orange County in the south heading to jobs in the South Bay area of Los Angeles County. The roadway is now owned by the State of California but managed by the City of Long Beach in cooperation with the California Department of Transportation (Caltrans). The city provides landscaping and traffic code enforcement, while the state provides road maintenance.
In addition to the main traffic circle, there is also an Outer Traffic Circle that is concentric with the main roundabout. The artery Atherton Street ends at the Outer Traffic Circle and does not continue toward the main roundabout
Notes
- ↑ Grobaty, Tim (September 12, 2011). "The Traffic Circle's roundabout history". Press-Telegram. Retrieved February 14, 2013.
- ↑ "California Highways,Routes 89 through 96". www.cahighways.org. Retrieved 2008-06-14.
- 1 2 "What a brilliant, lousy idea looks like". www.latimes.com. Retrieved February 15, 2015.
- ↑ "Tim Grobaty: The Traffic Circle's roundabout history". www.presstelegram.com. Retrieved February 15, 2015.
References
- "Drivers experience fewer crashes at L.B. Traffic Circle," Ruth Estrada, Online Forty-Niner (California State University, Long Beach newspaper).
- "Converting Old Traffic Circles to Modern Roundabouts: Michigan State University Case Study," Timothy J. Gates, E.I.T. and Robert E. Maki, D.P.A., P.E., Michigan State University, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering.
- "The Grand Army of the Republic (Memorial) Highway," Article 1, 3/03, US Route 6 Tourist Association, http://www.route6tour.com/history.htm .
- "Ourston Roundabout Engineering - Los Alamitos Circle," http://www.ourston.com/company/projects/los-alamitos.html