Toyota Matrix
| Toyota Matrix | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Toyota Motor Corporation |
| Also called | Toyota Corolla Matrix |
| Production | 2002–2014 |
| Model years |
|
| Assembly | Cambridge, Ontario, Canada (TMMC) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Sport Compact |
| Body style | 5-door hatchback |
| Layout | Front engine, front wheel drive / all wheel drive |
| Related | |
| Chronology | |
| Successor |
Toyota Corolla iM Toyota C-HR |
The Toyota Matrix, officially referred to as the Toyota Corolla Matrix, is a compact hatchback manufactured by Toyota Motor Manufacturing Canada in Cambridge, Ontario and derived from the Toyota Corolla. Introduced in 2002 as a 2003 model, the Matrix is the result of a joint venture between Toyota and General Motors, with the GM version being the Pontiac Vibe, which was assembled by New United Motor Manufacturing, Inc. (NUMMI) in Fremont, California.[1]
Officially sold in Canada, Mexico, and the United States until being discontinued, the Matrix was positioned as a sporty hatchback counterpart of the North American Corolla and was counted as a variant of it in Toyota's sales figures.[2]
Although identical mechanically, and nearly as much internally, the Matrix and Vibe had different sheetmetal and exterior trim designed by their respective brands. Both vehicles are narrow, tall station wagons styled in a quasi-SUV fashion (called a crossover utility vehicle or "CUV" by Toyota) and marketed to a fairly youthful market segment.[3] This type of car is also commonly referred to as a sport wagon.
First sold in February 2002,[4] the Matrix saw a minor facelift for the 2005 model year, and was redesigned completely in 2009, following the new tenth generation Corolla. Sales of the Matrix were discontinued in the United States in 2013, and in Canada in 2014.
First generation (E130; 2003–2008)
| First generation | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Overview | |
| Production | February 2002 – December 2007 |
| Model years | 2003–2008 |
| Designer | Craig Kember (1999)[5] |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | |
| Transmission | |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 102.4 in (2,601 mm)[6] |
| Length | 171.3 in (4,351 mm)[6] |
| Width | 69.9 in (1,775 mm)[6] |
| Height | 61.0 in (1,549 mm)[6] |
The Matrix was first introduced in the 2003 model year and based on the Toyota Corolla platform.[4] Relatively unchanged in 2004, a facelift for 2005 brought minor revisions to the exterior – mainly revised styling to the front fascia due to complaints of rubbing the ground on the previous incarnation and replacing the red lenses on the taillamps with clear ones.[7][8] Also, the center instrument panel was slightly redesigned and featured a Toyota head unit in place of the previous GM-sourced radio.[8]
Two 1.8 L four-cylinder engines were offered in the Matrix: the 1ZZ-FE used in the Corolla, which originally made 130 horsepower (97 kW) in 2003 through 2005 models, but was reduced to 126 horsepower (94 kW) in 2006,[9] and the performance-oriented 2ZZ-GE taken from the Toyota Celica GT-S,[6] which produced 164 horsepower (122 kW) (previously 180 horsepower (130 kW) in 2003, 173 hp (129 kW) in 2004,[10] and 170 horsepower (130 kW) in 2005).[11] The 2006 drop in power was due to new testing standards, and not a change in the engine's actual performance.[9]
In late 2006, Toyota discontinued use of the 2ZZ-GE engine and dropped the XRS from the Matrix lineup to be temporarily replaced by the M-Theory edition. Like each year of the XRS model, the M-Theory was a limited production run of 2500 cars.[12] All wheel drive was also available from 2003–2006 when coupled to the 1ZZ engine and automatic transmission, but was dropped at the same time as the XRS.[12]
Models
Standard (2003–2008)

Starting out at US$14,670 in 2003, the no-frills base model came with few options. While it did have standard air conditioning, it left out features like color-keyed mirrors and door handles, blacked out window frames and power mirrors. One option the base model could be had with was AWD for an additional $1,465 (although the actual increase was $2,445, since AWD only came with an automatic transmission). Adding AWD brought the car's curb weight of 2,679 lb (1,215 kg) up to 2,943 lb (1,335 kg) and decreased power by 7 hp (5 kW) and 7 lb·ft (9 N·m).[13][14] In 2004, the price of a base model remained unchanged, but by the last year of production, 2008, it had risen to $15,510.[15]
XR (2003–2008)
The Matrix's XR mid-grade trim level added features like color-matched mirrors and door handles, a leather-wrapped steering wheel, and a panic button on the key fob. Options available with the XR trim included a sunroof, body kit, and 16-inch (410 mm) alloy wheels. A 2003 XR started at US$16,180 and 2,701 lb (1,225 kg), but when equipped with AWD cost at least $18,445 (only $305 less than an XRS) and weighed in at 2,965 lb (1,345 kg).[14] Like the base model, the XR's AWD engine was detuned. Again, the car's price for its sophomore year stayed the same, but in the four years after that, it rose to $16,990.[16]
XRS (2003–2006)

For US$18,750-, the top-of-the-line model came standard with four-wheel disc brakes and six speakers. Also included on all XRS models were anti-lock brakes with Electronic Brakeforce Distribution, 16-inch alloy wheels, and cruise control. In 2003, 17-inch wheels could be had, but only on cars without a sunroof. An option combining 17-inch (430 mm) wheels and a sunroof became available the second year of production. In 2005, an XRS started out at $18,850, and for its last year, it sold for at least $19,250.[17]
The XRS trim included an engine upgrade to Toyota's higher-performance 2ZZ-GE engine. Displacing 1,796 cc (1.796 L; 109.6 cu in), or 109.6 cubic inches, it produced 180 hp (134 kW) and 130 lb·ft (176 N·m) – a then-rare 100 horsepower-per-liter. While its 11.5:1 compression ratio was a large factor in its performance, the engine could change to a second cam profile at higher RPMs through Toyota's VVTL-i and was designed for operation up to 8500 RPM. The engine's high compression necessitates "premium" gasoline (91 octane or above in the (R+M)/2 scale). With the exception of an available automatic in 2003, a six-speed manual transmission was the only gearbox offered in the XRS.[6] A Transitional Low Emission Vehicle (TLEV) its first year of production,[18] the 2ZZ was retrofitted in 2004 with a smog pump and reclassified as an Ultra Low Emission Vehicle (ULEV).[19]
The Matrix was able to come to a full stop from 60 mph (97 km/h) in only 114 feet (35 m).[6] On a skidpad, the car achieved .83 g, only .03 g less than the Celica GTS, during testing by Motor Trend and Sport Compact Car.[20][21] Due to being front wheel drive, the XRS has a weight distribution of 59/41 (front/rear), which may result in understeer when driven hard. It weighs in at a relatively light 2,800 lb (1,300 kg).[6][22]
M-Theory (2007)
Not a trim level, the M-Theory edition was a 2007-only[23] appearance package with an exclusive "Speedway Blue" color. For US$1,500, a customer got 17-inch Caldina wheels, a chrome exhaust tip, a numbered plaque (1 of 2500), four wheel disc brakes, and a spoiler. To improve handling, a "sport tuned suspension" and strut tower brace were included.[24]
Interior


One of the Matrix's unique design features is its interior, particularly the rear 60/40 seats and cargo area. Made with rigid plastic backs, the rear seats fold flat, creating a 53.2 cu ft (1.51 m3) cargo area. In a practicality test, Motor Trend was able to haul more cargo in the Matrix than in a Subaru WRX wagon with 61.1 cu ft (1.73 m3) of space.[6] In addition to the eight tie-downs in the back for attaching the included cargo nets and tonneau cover, the seats and rear floor have integrated rails for installing extra tie-downs.[6][20]
Up front, the passenger seat also folds flat, accommodating long items like surf boards or allowing drivers to use the tray in its back to hold items like a laptop computer. An electronic device can be charged with the 115 volt/100 watt power inverter(US models only).[25] The first year of production (2003), the instrument cluster was completely red.[4] However, the next year, Toyota made the numbers white while keeping the rest of the gauges red.[7] When the car was updated in 2005, a digital clock was added to the radio bezel.[8]
Crash testing
NHTSA crash test ratings (2003):[26]
- Frontal Crash Test – Driver:





- Frontal Crash Test – Passenger:





- Side Impact Rating –





- Side Impact Rating – Rear:




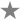
- Rollover Rating:





Recalls
In May 2008, Toyota issued a recall for 2003 and 2004 model year Corollas and Matrixes. The recall notice cites two bolts in each of the front doors as potentially causing the window to come off the track and break. This recall only applies to models equipped with power windows.[27] General Motors issued a recall for the same problem on 2003 and 2004 Pontiac Vibes with power windows at the same time.[28]
On August 26, 2010, Toyota issued a recall for 2005 to 2008 model year Corollas and Matrixes, equipped with the 1ZZ-FE engine and two-wheel drive. The recall notices states that an improperly manufactured Engine Control Module (ECM) can develop a crack in its circuitry, potentially causing the "Check Engine" light to illuminate, harsh shifting, and stalling and/or failure of the engine to start.[29]
Second generation (E140; 2009–2014)
| Second generation | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Overview | |
| Production | January 2008–2014 |
| Model years |
|
| Assembly | Cambridge, Ontario, Canada (TMMC) |
| Designer |
Hirofumi Fukui (2005) Yoshiyasu Neuchi and Shigetoshi Kozai (2011 facelift: 2009) |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | |
| Transmission | |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 102.4 in (2,601 mm)[30] |
| Length | |
| Width | 69.5 in (1,765 mm)[30] |
| Height |
|
Initially rumored by Toyota and auto news media as a Matrix replacement named the Blade,[31] the second generation Matrix was unveiled on October 31, 2007, at the Specialty Equipment Market Association (SEMA) show in Las Vegas, and was first available at dealerships in February 2008, as a 2009 model.[32] The Matrix' Pontiac Vibe sibling was also upgraded, but production of that model ended after 2009 when the entire Pontiac brand was retired.
In the United States, three trim grades (Standard [base], S, and XRS) are offered,[30] as well as two inline-four engines: a 1,797 cc (1.797 L; 109.7 cu in) 2ZR-FE for the base model (chassis code ZRE142) and a 2,362 cc (2.362 L; 144.1 cu in) 2AZ-FE for the S and XRS grades. The former is offered with either a five-speed manual or four-speed automatic transmission, while the larger engine is equipped with either a manual or automatic five-speed transmission.[30] In addition, the S grade can be equipped with a four-speed automatic and all-wheel drive.[33]

Canadian buyers are offered four trim levels: a 1.8 L-powered base model and the XR, AWD, and XRS models with a 2.4 liter engine.[34][35]
This Toyota Matrix generation marks it the first time it is sold in Mexico. The Toyota Matrix comes only in two trim levels to Mexico: Base and XR.
For the 2011 model year, the Matrix received redesigned exterior and interior elements, including front and rear fascias, wheels, and seat fabrics.[36]
Models

Beginning in 2008, Toyota began offering different trim levels in the United States and Canada. The XR trim became exclusive for Canada, and the S model was released only in the U.S., while AWD remained available in both markets after 2009. All vehicles have an independent front suspension with MacPherson struts,[30] but only XRS models and cars equipped with all-wheel drive and 158 horsepower, feature an independent rear suspension using double wishbones instead of a semi-independent torsion beam.[30][37] The 2009 models have less interior space than the preceding years, with a total of 48.9 cu ft (1.38 m3) compared to the original 53.2 cu ft (1.51 m3).[30]
The XRS grade was dropped from the U.S. lineup for the 2011 model year.
Safety
All models come standard with side torso airbags, side curtain airbags, anti-lock braking and electronic brakeforce distribution.[38] For the 2010 model the previously optional Vehicle Stability Control and traction control systems became standard.[39]
Toyota's Smart Stop Technology was added to the Matrix for the 2011 model year.
The Matrix is rated "Good" in both frontal and side Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) crash tests.[40][41]
NHTSA crash test ratings (2009):[42]
- Frontal Crash Test – Driver:





- Frontal Crash Test – Passenger:





- Side Impact Rating – Driver:





- Side Impact Rating – Passenger:





- Rollover Rating:





Recalls
The 2009 to 2010 model year Toyota Matrix (and its Pontiac Vibe relative) are subject to the 2009–2011 Toyota vehicle recalls regarding floor mat and accelerator pedal replacement.[43]
On October 10, 2012, Toyota issued a recall for 2009 model year Corolla and Matrix, along with 10 other models. The recall notices states that improperly lubricated driver's side power window master switch may develop a “notchy” or sticky feel, and that improper aftermarket lubrication may present a fire hazard. The repair involves lubricating the switch assembly with a special fluorine grease.[44]
Discontinuation
On August 5, 2013, Toyota announced that it would end production of the Matrix for the US market after the 2013 model year due to declining sales, and that there were no plans to replace it with another vehicle.[45] The Canadian market continued for the 2014 model year, with those assembled in Cambridge, Ontario by Toyota Motor Manufacturing Canada. The Matrix was then discontinued in Canada and was not offered for the 2015 model year.[46] Toyota continued to sell a range of compact hatchbacks in North America through its Scion brand. On September 1, 2016, "the Scion brand transitioned to Toyota."[47] For the 2017 model year, the Toyota C-HR will be the successor of the Matrix, along with the Scion xD.
References
- ↑ "What We Make – Voltz". New United Motor Manufacturing, Inc. Archived from the original on 2008-05-12. Retrieved 2008-10-13.
- ↑ "Sales". Automotive News magazine. Retrieved 2009-04-28.
- ↑ Huffman, John. "A sleek "CUV" with youthful imagination - 2003 Toyota Matrix". The Car Connection. Retrieved 2008-04-26.
- 1 2 3 Jacquot, Josh (April 2009). "2003 Toyota Matrix XRS Road Test Review". Sport Compact Car. Retrieved 2013-08-07.
- ↑ Hakim, Danny (2002-06-02). "Private Sector; A Hip Toyota, by His Design". The New York Times. Retrieved 2016-09-16.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Walton, Chris (March 2002). "The Next Band Wagons". Motor Trend: 82–90. Retrieved 2008-07-18.
- 1 2 "2004 Toyota Matrix Photo Archive". Edmunds.com. Retrieved 2008-10-21.
- 1 2 3 "2005 Toyota Matrix Photo Archive". Edmunds.com. Retrieved 2008-10-21.
- 1 2 "2006 Toyota Matrix Complete Review". New Car Test Drive, Inc. Retrieved 2008-10-22.
- ↑ "2004 Toyota Matrix – Specs". New-cars.com. Retrieved 2008-10-22.
- ↑ "2005 Toyota Matrix New Car Buyer's Guide". Car.com. Retrieved 2008-10-22.
- 1 2 Peters, Eric. "2007 Toyota Matrix Review". The Car Connection. Retrieved 2008-07-24.
- ↑ "2003 Toyota Matrix Complete Review". New Car Test Drive, Inc. Retrieved 2008-10-12.
- 1 2 "2003 Toyota Matrix Front-wheel Drive Hatchback vs All-wheel Drive Hatchback". Autoblog.com.
- ↑ "2004 - 2008 Toyota Matrix". Autoblog.com.
- ↑ "2004–2008 Toyota Matrix XR". Autoblog.com.
- ↑ "2005-2006 Toyota Matrix XRS". Autoblog.com.
- ↑ "2003 Toyota Matrix XRS". Fueleconomy.gov. Retrieved 2008-10-12.
- ↑ "2004 Toyota Matrix XRS". Fueleconomy.gov. Retrieved 2008-10-12.
- 1 2 Bedard, Patrick (June 2002). "Chrysler PT Cruiser vs. Ford Focus, Pontiac Vibe, Mazda Protegé5, Suzuki Aerio, Toyota Matrix". Car and Driver. Retrieved 2008-10-12.
- ↑ Huffman, John Pearley (November 2000). "Toyota Thunder: TRD Celica GT-S – Road Test". Car and Driver. Retrieved 2008-10-12.
- ↑ "2003 Toyota Matrix - Compare Trims". Autoblog.com.
- ↑ "2008 Toyota Matrix". gaywheels.com. Retrieved 2008-10-12.
- ↑ "Toyota Matrix M-Theory Package Announced". autoblog.com. Retrieved 2008-10-12.
- ↑ "Toyota Matrix a 'crossover' of youthful practicality". Jsonline.com. Retrieved 2008-10-12.
- ↑ "Safercar.gov". Safercar.gov. Retrieved 2010-04-27.
- ↑ Toyota Recall Notice – SSC 80A – "2003 through 2004 Model Year Corolla and Corolla Matrix front door glass bolts safety recall notice"
- ↑ "2003 Pontiac Vibe Recalls". Motor Trend Magazine. Retrieved 2008-10-21.
- ↑ "Toyota Announces Voluntary Safety Recall on Certain Toyota Corolla and Corolla Matrix Models" (Press release). US: Toyota. 2010-08-26. Retrieved 2013-08-07.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 "Toyota Matrix Performance & Specs". Retrieved 2008-07-24.
- ↑ "Toyota cuts Matrix with Blade". AutoWeek Magazine. Retrieved 2008-06-25.
- ↑ "Toyota Releases Pricing on 2009 Corolla and Matrix – and Releases a Special-Edition FJ Cruiser". Edmunds.com. Retrieved 2008-10-28.
- ↑ "Toyota Matrix Specs". Toyota. Retrieved 2008-04-26.
- ↑ "Matrix Features". Canada: Toyota. Retrieved 2008-10-06.
- ↑ "Price Your Toyota". Canada: Toyota. Retrieved 2008-10-28.
- ↑ "Toyota Vehicles : 2011 Toyota Matrix Debuts at the Chicago Auto Show" (Press release). US: Toyota. 2011-02-08. Archived from the original on 2011-02-11. Retrieved 2010-02-26.
- ↑ "Matrix Specifications". Canada: Toyota. Retrieved 2008-10-28.
- ↑ "Toyota Vehicles : Toyota Unveils New Corolla Matrix at 2007 SEMA Show / Toyota" (Press release). US: Toyota. 2007-10-31. Retrieved 2010-04-27.
- ↑ "Toyota Vehicles : Vehicle Stability Control and Traction Control Now Standard Equipment in 2010 Toyota Corolla and Matrix / Toyota" (Press release). US: Toyota. 2009-01-23. Retrieved 2010-04-27.
- ↑ "IIHS-HLDI: Toyota Matrix". Iihs.org. November 18, 2009. Retrieved 2010-05-30.
- ↑ "IIHS-HLDI: Toyota Matrix". Iihs.org. November 18, 2009. Retrieved 2010-05-30.
- ↑ "2009 Toyota Matrix 4-DR. w/SAB". Safercar.gov. 2009. Retrieved 2013-08-07.
- ↑ "Safety/Recall" (Press release). US: Toyota. Archived from the original on 2009-11-22.
- ↑ "Toyota Announces Voluntary Recall of Certain Vehicles For The Driver's Side Power Window Master Switch" (Press release). US: Toyota. 2012-10-10. Retrieved 2012-10-10.
- ↑ Ross, Jeffrey N. (2013-08-05). "Toyota Matrix discontinued for 2014". Autoblog. Retrieved 2013-08-07.
- ↑ Cato, Jeremy (2014-07-10). "Six cars that replace the Toyota Matrix". The Globe and Mail. Canada. Retrieved 2015-01-08.
- ↑ "Scion Owners". Canada: Toyota. 2016-09-01. Retrieved 2016-10-19.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Toyota Matrix. |
| « previous — Toyota road car timeline, North American market, 1980s–present (model years) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | 1980s | 1990s | 2000s | 2010s | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Model year | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Subcompact | Tercel | Tercel | Tercel | Tercel | Tercel | Echo | Yaris Sedan | Yaris iA | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yaris Liftback | Yaris Liftback | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Starlet | Corolla FX | Prius c | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Corolla | Corolla | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compact | Corolla | Corolla | Corolla | Corolla | Corolla | Corolla | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Matrix | Matrix | Corolla iM | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Corona | Camry | Camry | Prius | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mid-size | Prius | Prius | Prius | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cressida | Cressida | Cressida | Cressida | Camry Solara | Camry Solara | Prius v | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Camry | Camry | Camry | Camry | Camry | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mirai | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Full-size | Avalon | Avalon | Avalon | Avalon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sport compact | Corolla GT-S/SR5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Celica | Celica | Celica | Celica | Celica | Celica | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Paseo | Paseo | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sports car | Celica Supra | Celica Supra | 86 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Supra | Supra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MR2 | MR2 | MR2 Spyder | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||