Teterboro Airport
| Teterboro Airport | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||
| IATA: TEB – ICAO: KTEB – FAA LID: TEB | |||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||
| Operator | Port Authority of New York and New Jersey | ||||||||||||||
| Serves | Teterboro, New Jersey | ||||||||||||||
| Location | Bergen County, New Jersey | ||||||||||||||
| Hub for | Tradewind Aviation | ||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 9 ft / 3 m | ||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 40°51′00″N 074°03′39″W / 40.85000°N 74.06083°WCoordinates: 40°51′00″N 074°03′39″W / 40.85000°N 74.06083°W | ||||||||||||||
| Website |
www | ||||||||||||||
| Maps | |||||||||||||||
 FAA airport diagram | |||||||||||||||
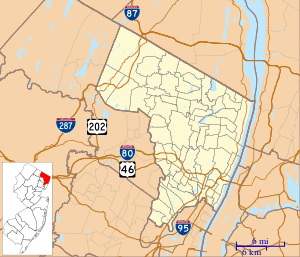 TEB  TEB  TEB Location in Bergen County, New Jersey | |||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2010) | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
Teterboro Airport (IATA: TEB[2], ICAO: KTEB, FAA LID: TEB) is a general aviation relief airport located in the boroughs of Teterboro, Moonachie, and Hasbrouck Heights in Bergen County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey.[3] It is owned and managed by the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey and operated by AFCO AvPORTS Management. The airport is in the New Jersey Meadowlands, 12 miles (19 km) from Midtown Manhattan, which makes it very popular for private and corporate aircraft. The airport has a weight limit of 100,000 pounds (45,000 kg) on aircraft, which is meant to make it nonviable as a commercial airport.
The airport takes up almost all of Teterboro and consists of 827 acres (3.35 km2): 90 acres (0.36 km2) for aircraft hangar and offices, 408 acres (1.65 km2) for aeronautical use and runways, and 329 acres (1.33 km2) undeveloped. The airport has more than 1,137 employees, of whom more than 90% are full-time.
In April 2009 the FAA reported that the airport had the third highest rate of wildlife strikes of any airport in the United States based on takeoffs and landings (43 per 100,000).[4]
Teterboro is home to many private aviation charter companies that fly nationally and globally.[5]
History
Teterboro Airport is the oldest operating airport in the New York City area. Walter C. Teter (1863–1929) acquired the property in 1917.[6] North American Aviation operated a manufacturing plant on the site during World War I. After the war, the airport served as a base of operations for Anthony Fokker, the Dutch aircraft designer. The first flight from the present airport site was made in 1919. In 1926 Colonial Air Transport at Teterboro was the first private company to deliver mail by air.[7]
During World War II, the United States Army operated the airport. The Port Authority of New York & New Jersey purchased it on April 1, 1949, from Fred L. Wehran, a private owner, and later leased it to Pan American World Airways (and its successor organization Johnson Controls) for 30 years until December 1, 2000, when the Port Authority assumed full responsibility for the operation of Teterboro.[8]
In January 1954, Arthur Godfrey buzzed the Teterboro control tower with his Douglas DC-3, resulting in the suspension of his license.[9]
In 2003, U.S. Congressman Steve Rothman helped to authorize a federal bill to retain a ban on aircraft exceeding a weight of 100,000 pounds (45 t) from taking off from Teterboro because of excessive noise levels in the surrounding residential communities.[10]
In May 2016, Ultimate Air Shuttle announced it would begin twice-weekly non-stop passenger service between the airport to Cincinnati.[11]
Facilities
Teterboro Airport covers 830 acres (340 ha) at an elevation of 9 feet (2.7 m) above mean sea level.
Buildings
Nineteen hangars on the airport have a total area of about 412,000 square feet (38,300 m2).
Two large office buildings are centrally located, one at 90 Moonachie Avenue and the other on Fred Wehran Drive, which houses the Department of Homeland Security. Both buildings have a total area of 133,418 square feet (12,394.9 m2).
Additional office and shop space totals an area of 165,611 square feet (15,385.8 m2). There is also an operations building, maintenance facility and two fuel farms.
The airport contains the Aviation Hall of Fame of New Jersey.
Control tower
The control tower was built on the east side of the airport by the FAA and went into operation on October 29, 1975. The original control tower is not operational but is still part of the original wooden Atlantic Aviation hangar on Industrial Avenue. It is on the northeast corner of the hangar.
Runways
Runway 6-24 is 6,013 feet (1,833 m) long and 150 feet (46 m) wide, with High Intensity Runway Lights (HIRL). Runway 6 approach has an Instrument Landing System (ILS) and a Medium Approach Lighting System-R (MALS-R). Runway 24 approach is equipped with both a Precision Approach Path Indicator (PAPI) and Runway End Identification Lights (REIL) systems. Runway 6-24 underwent complete overlay and grooving in 1987.
Runway 1-19 is 7,000 feet (2,100 m) long and 150 feet (46 m) wide, with HIRL. Both runways 1 and 19 are equipped with REIL systems. Runway 1 approach is equipped with a VASI system. Runway 19 approach has an ILS and a Precision Approach Path Indicator (PAPI). Runway 1-19 was overlaid and grooved in the summer of 2000, and included the installation of centerline and touchdown zone lighting. Runway 19 is the preferred runway for noise abatement procedures.
Taxiways
About 4.2 miles (6.8 km) of taxiways exist on the airport. Most are 60 feet (18 m) wide and are equipped with centerline and edge lighting systems.
Aircraft
In 2010 the airport had 153,250 aircraft operations, average 419 per day: 65.6% general aviation, 34% air taxi, 0.3% military, and <1% scheduled commercial. 121 aircraft were then based at this airport: 81% jet, 10.7% helicopter, 6.6% single-engine, and 1.7% multi-engine.[1]
Other
The Aviation Hall of Fame of New Jersey is on the airport grounds. Founded in 1972, it is the first state aviation hall of fame in the nation, honoring the men and women who brought outstanding aeronautical achievements to the state. The recently expanded museum offers visitors an opportunity to view historic air and space equipment and artifacts, photographs, fine art and an extensive model collection. The library has more than 4,000 volumes and hundreds of aviation video tapes.[12]
Public transportation
Teterboro Airport can be reached from the Port Authority Bus Terminal in Midtown Manhattan on New Jersey Transit bus routes 161 (regular service), 165 (limited weekday service) and 144 (peak periods weekdays).[3] The Teterboro station is the closest rail station along NJ Transit's Pascack Valley Line, but the Wood-Ridge station is also close to the southwest of the airport.
Incidents
In June 1966, in Hasbrouck Heights, a two-engine, Piper Aztec going to Teterboro Airport crashed, striking a tree and narrowly missing homes on Burton Avenue near Route 46. The pilot sustained injuries including a skull fracture – was taken to Hackensack Hospital by ambulance. He was carrying film for Eastman Kodak, Fair Lawn, NJ.
On September 23, 1981, a Ronson Aviation Bell 206B helicopter and a Seminole Air Charier Piper PA-34 airplane collided in flight over East Rutherford, about 2 nautical miles south of the Teterboro Airport. The airplane had a flight plan to Teterboro from Syracuse, New York. The helicopter was inbound to Teterboro from Woodbridge, NJ. The two aircraft collided at about 650 feet. The helicopter fell into the Meadowlands Sports Complex parking lot, and both persons aboard were killed. The airplane, with about 8 feet of its left wing and its right engine missing, made a gear-up landing in a marsh about seven-tenths of a mile east of the collision point. The pilot was seriously injured, and the passenger received minor injuries.[13]
On December 9, 1999, in Hasbrouck Heights a small plane crashed between two houses Thursday night killing all four people aboard, injuring three people on the ground and setting a garage on fire, authorities said.[14]
On March 9, 2002, a single engine Cessna 210 with a flight plan to Montauk, NY, crashed shortly after take-off about 2 p.m. killing the only occupant and pilot. Upon impact the plane skidded about 225 feet before it burst into flames narrowly missing cars traveling on Route 46 about 100 yards away.[15]
On September 9, 2002, a Piper Saratoga carrying a Canadian family took off from Teterboro Airport and crashed into a housing development in Hunterdon County 10 minutes later. The parents were killed, and the two children were critically injured. The incident caused millions in damage.
On February 2, 2005, 7:18 a.m. a Bombardier Challenger CL-600-1A11, N370V, hurtled off a runway at Teterboro Airport (TEB), skidded across a highway and slammed into a warehouse during the morning rush, injuring 20 people, 11 of them on the plane. It was mere coincidence – a red traffic signal – thwarted a full-scale disaster. A moment later, and the intersection would have been swarming with commuter traffic. Forty-five minutes later, and classes would have been in session at a nearby high school. An hour, and the warehouse would have been filled with 200 workers. The two pilots were seriously injured, as were two occupants in a vehicle. The cabin aide, eight passengers, and one person in the building received minor injuries. Five people remained hospitalized, one of them gravely injured. A 66-year-old Paterson man who was riding in a car that was struck by the jet, was on life-support, authorities said.[16] Later that year, legislation authored by U.S. Senator Frank Lautenberg passed, which directed the FAA to install 1,000 foot arrestor beds at all U.S. airports.[17]
On September 2, 2005, at 2122 local time, a Cessna 177A, N30491, crashed in South Hackensack during an emergency landing at Teterboro airport. A Teterboro employee observed the airplane descending toward runway 24, then lost sight of the airplane as it descended below the horizon, and then observed two or three bright flashes. The pilot sustained fatal injuries and the passenger sustained serious injuries.[18]
On October 11, 2006, a small general aviation plane, a Cirrus SR20, took off from Teterboro and crashed in New York City at 2:42 pm local time. The aircraft struck the north side of an apartment building on the Upper East Side of Manhattan; it caused a fire in two apartments on the 40th and 41st floors, which was extinguished within one hour. The aircraft was owned and piloted by New York Yankees pitcher Cory Lidle, who died in the accident along with his flight instructor. As a result of this accident the FAA established restrictions for flying up the East River.
The two midair collisions have occurred over the Hudson River involving aircraft that departed from Teterboro, one in 1976,[19] and one in 2009.[20] As a result of the latest accident the FAA came up with new guidelines for pilots flying the Hudson River including mandatory reporting points and separating slower helicopter traffic from faster fixed wing traffic via assigned altitude blocks.
On January 15, 2009, US Airways Flight 1549 departing from LaGuardia Airport struck birds on take-off and lost power to both engines; Teterboro Airport was briefly considered as an emergency diversion by the pilot, Capt. Chesley B. "Sully" Sullenberger, before his successful emergency ditching of the aircraft in the Hudson River.[21][22]
On August 21, 2009 around 3:00 a.m. a Beechcraft Baron crashed while attempting to land. Both the pilot and passenger survived but sustained burns requiring the attention of Saint Barnabas Medical Center's burn unit, the only one in the state of New Jersey. The plane was believed to have originated at Reading, PA, and was carrying blood samples for Quest Diagnostics, which has a lab on property adjacent to Teterboro Airport.[23]
On October 1, 2010, at approximately 1:45 p.m., a G-4 Gulfstream overshot the runway. It was stopped by an arrester bed. Seven passengers and two pilots were on the plane. No one was injured in the crash. The cause of the accident has not yet been determined.[24]
On December 20, 2011, a single-engine TBM700 crashed on Interstate 287 near Morristown after leaving Teterboro Airport headed for Georgia. Five people, including a family of four and one other passenger were killed.
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Teterboro Airport. |
References
- 1 2 FAA Airport Master Record for TEB (Form 5010 PDF). Federal Aviation Administration. Effective November 15, 2012.
- ↑ "IATA Airport Code Search (TEB: Teterboro)". International Air Transport Association. Retrieved October 25, 2013.
- 1 2 Directions to and from the Airport, Port Authority of New York & New Jersey. Accessed July 7, 2008. "Teterboro Airport is located in the Boroughs of Teterboro, Moonachie, and Hasbrouck Heights in Bergen County, New Jersey."
- ↑ "Bird strikes by planes rising". Denver Post. April 24, 2009.
- ↑ "Meridian To Base Aircraft In Hayward, CA". AviationPros.com. January 11, 2013.
- ↑ JAY LEVIN. "The Name-Dropper: Teterboro Airport and the Bendix Diner". NorthJersey.com. Retrieved 26 April 2016.
- ↑ "Three pilots for Colonial Air Transport, Inc. are congratulated by Managing Director Juan T. Trippe following their successful first airmail trip between Boston and New York.". Bettman Archive at Corbis. 1926. Retrieved 2009-11-27.
Pilots (l-r) Leroy Thompson, H.I. Wells, and Major T.O. Freeman are congratulated alongside one of the three airmail Fokker planes at Teterboro Airport in Teterboro, New Jersey. This was the first of such services between the U.S. Mail and private companies.
- ↑ Teterboro Airport History. Retrieved April 30, 2007.
- ↑ Henry III, William A. "The Man with the Barefoot Voice", Time (magazine), March 28, 1983, accessed April 30, 2007. "So did another burst of temper the next year, when Godfrey, an avid pilot, grew angry with the flight instructions he had been given for his DC-3 and buzzed an airport control tower in Teterboro, N. J."
- ↑ House Of Representatives Approves Rothman Measure To Keep Boeing Business Jet Out Of Teterboro, Steve Rothman press release dated September 10, 2003, accessed April 30, 2007. "In a critical step forward in his efforts to protect the quality of life of the people of Northern New Jersey, Congressman Steve Rothman (D-NJ9) last night got the U.S. House of Representatives to approve a measure he authored to stop the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) from lifting the 36-year-old, 100,000 pound weight limit at Teterboro Airport." Archived April 28, 2007, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Ultimate Air Shuttle consolidating flight operations", Ultimate Air Shuttle, May 6, 2016. Accessed October 23, 2016. "On May 31 Ultimate Air will begin nonstop flights to Teterboro, NJ, two days per week."
- ↑ Home Page, Aviation Hall of Fame and Museum of New Jersey. Accessed October 23, 2016.
- ↑ Accident Report AAR82-06, National Transportation Safety Board, May 18, 1982. Accessed October 23, 2016.
- ↑ "Hasbrouck Heights Air Disaster: December 9, 1999". hasbrouck-heights.com.
- ↑ "Teterboro Air Crash Kills Pilot: March 9, 2002". hasbrouck-heights.com.
- ↑ "Teterboro Air Crash: February 2, 2005". hasbrouck-heights.com.
- ↑ SHAWN BOBURG. "Teterboro Airport gets $1M for runway project". NorthJersey.com. Retrieved 26 April 2016.
- ↑ "Teterboro Approach Air Crash: Cessna 177 crashes while approaching Teterboro Airport September 2, 2005". hasbrouck-heights.com.
- ↑ Baird, Rob (2009-08-11). "Flashback to 1976 Hudson crash". Archived from the original on 2012-04-26. Retrieved 2009-08-11.
- ↑ Hays, Tom; Victor Epstein (2009-08-11). "Part of plane in collision raised from the Hudson". Associated Press. Retrieved 2009-08-11.
- ↑ "Memorandum: Full Transcript: Aircraft Accident, AWE1549, New York City, NY, January 15, 2009" (PDF). Federal Aviation Administration. June 19, 2009. p. 4. Retrieved February 12, 2009.
- ↑ Caruso, David B.; Marcus, Franklin (January 15, 2009). "All 155 safe after pilot ditches jet in NYC river". The Guardian. London. Associated Press. Retrieved February 12, 2009.
- ↑
- ↑ "Private jet overshoots runway at Teterboro Airport". The Associated Press. October 1, 2010.
External links
- Teterboro Airport, official website
- Teterboro Airport, Port Authority website
- Teterboro Airport (TEB) at New Jersey DOT Airport Directory
- Aviation photos of Teterboro Airport at jetphotos.net
- Passur KTEB Airport Monitor Live Flight Tracker
- Aerial image as of March 1995 from USGS The National Map
- Aviation Hall of Fame of New Jersey
- Time; January 28, 1929; Died. Walter C. Teter, 66, founder of the community & airport at Teterboro, New Jersey; after a short illness; in Manhattan.
- FAA Airport Diagram (PDF), effective December 8, 2016
- FAA Terminal Procedures for TEB, effective December 8, 2016
- Resources for this airport:
- AirNav airport information for KTEB
- ASN accident history for TEB
- FlightAware airport information and live flight tracker
- NOAA/NWS latest weather observations
- SkyVector aeronautical chart for KTEB
- FAA current TEB delay information