Southern Han
| Great Han / Great Yue | ||||||||||
| 大漢 / 大越 | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
 | ||||||||||
| Capital | Xingwang (Guangzhou) | |||||||||
| Languages | Middle Chinese | |||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | |||||||||
| Emperor | ||||||||||
| • | 917-941 | Emperor Gaozu | ||||||||
| • | 941-943 | Emperor Shangdi | ||||||||
| • | 943-958 | Emperor Zhongzong | ||||||||
| • | 958-971 | Emperor Houzhu | ||||||||
| Historical era | Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period | |||||||||
| • | Established | 917 | ||||||||
| • | Renamed from "Yue" to "Han" | 918 | ||||||||
| • | Ended by the Song Dynasty | 971 | ||||||||
| ||||||||||
| Today part of | | |||||||||
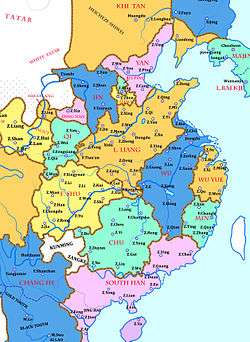
Southern Han (simplified Chinese: 南汉; traditional Chinese: 南漢; pinyin: Nán Hàn) was a kingdom that existed during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (907-960) along China’s southern coast from 917 to 971. The Kingdom greatly expanded its capital city Xingwang Fu (Chinese: 興王府; pinyin: Xìngwángfǔ), namely present-day Guangzhou. Not only did it have interaction with other Chinese kingdoms, but due to its location, it also had relations with the Viet (Chinese: 越) people to the south.
Founding of the Southern Han
Liu Yin, was named regional governor and military officer by the Tang court in 905. Though the Tang fell two years later, Liu did not declare himself the founder of a new kingdom as other southern leaders had done. He merely inherited the title of Prince of Nanping in 909.
It was not until Liu Yin’s death in 917 that his brother, Liu Yan, declared the founding of a new kingdom, which he initially called "Great Yue" (大越), but he changed the name to Great Han (大漢) next year (918). It was because his surname Liu (劉) was the imperial surname of the Han dynasty and he claimed himself a descendant of that famous dynasty. The kingdom is often referred as the Southern Han Dynasty throughout China's history.
Territorial extent
With its capital at present-day Guangzhou, the domains of the kingdom spread along the coastal regions of present-day Guangdong, Guangxi, Hanoi and the island of Hainan. It not only had borders with the kingdoms of Min, Chu and the Southern Tang, they also bordered the non-Chinese kingdoms of Dali. The Southern Tang occupied all of the northern boundary of the Southern Han after Min and Chu were conquered by the Southern Tang in 945 and 951 respectively.
Relations with Vietnam
While the Tang Dynasty was strong, the region of the present-day Vietnam remain a stable, secure part of the Southern Han's Viet domains. However, as the Tang weakened late in the 9th century, the Viet sought to regain control over their own affairs. Hanoi, which had developed as a political center during the Tang Dynasty, was the center of an early Vietnamese polity.
The Southern Han sought to bring the Viet into its orbit; however, their invasion was unsuccessful and was repelled. In 939, The Viet in the Chinese province of Annam, under the leadership of Ngo Quyen (吳權) redeclared independence.
Fall of the Southern Han
The Five Dynasties ended in 960 when the Song Dynasty was founded to replace the Later Zhou. From that point, the new Song rulers set themselves about to continue the reunification process set in motion by the Later Zhou. Through the 960s and 970s, the Song increased its influence in the south until finally it was able to force the Southern Han dynasty to submit to its rule in 971.
Rulers
| Temple Names | Posthumous Names | Personal Names | Period of Reigns | Era Names |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gao Zu (高祖 gāo zǔ) | Tian Huang Da Di (天皇大帝 tiān huáng dà dì) | Liu Yan (劉巖 liú yán)
Liu Yan (劉龑 liú yǎn) after 926 |
917-941 | Qianheng (乾亨 qián hēng) 917-925 Bailong (白龍 bái lóng) 925-928 |
| Did not exist | Shang Di (殤帝 shāng dì) | Liu Bin (劉玢 liú bīn) | 941-943 | Guangtian (光天 guāng tiān) 941-943 |
| Zhong Zong (中宗 zhōng zōng) | Wénwǔ Guāngmíng Xiào (文武光明孝皇帝)
Too tedious thus not used when referring to this sovereign |
Liu Sheng (劉晟 liú shèng) | 943-958 | Yingqian (應乾 yìng qián) 943 Qianhe (乾和 qiàn hé) 943-958 |
| Hou Zhu (後主 hòu zhǔ) | Did not exist | Liu Chang (劉鋹 liú chǎng) | 958-971 | Dabao (大寶 dà bǎo) 958-971 |
Rulers family tree
| Rulers family tree | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- Mote, F.W. (1999). Imperial China (900-1800). Harvard University Press. pp. 11, 15. ISBN 0-674-01212-7.
- Schafer, Edward H. "The History of the Empire of Southern Han: According to Chapter 65 of the Wu-tai-shih of Ou-yang Hsiu", Zinbun-kagaku-kenkyusyo (ed.), Silver Jubilee Volume of the Zinbun-kagaku-kenkyusyo. Kyoto, Kyoto University, 1954.
- Tarling, Nicholas, ed. (1999). The Cambridge History of Southeast Asia (Volume One, Part One): From early times to c. 1500. Cambridge University Press. p. 139. ISBN 0-521-66369-5.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: |