Solar eclipse of October 12, 1939
| Solar eclipse of October 12, 1939 | |
|---|---|
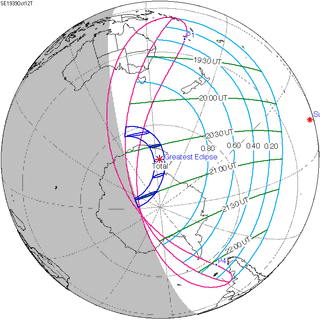 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | -0.9737 |
| Magnitude | 1.0266 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 92 sec (1 m 32 s) |
| Coordinates | 72°48′S 155°06′E / 72.8°S 155.1°E |
| Max. width of band | 418 km (260 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 20:40:23 |
| References | |
| Saros | 123 (49 of 70) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9374 |
A total solar eclipse occurred on October 12, 1939. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses 1939-1942
Each member in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saros | Map | Saros | Map | |||
| 118 | April 19, 1939 Annular |
123 | October 12, 1939 Total | |||
| 128 | April 7, 1940 Annular |
133 | October 1, 1940 Total | |||
| 138 | March 27, 1941 Annular |
143 | September 21, 1941 Total | |||
| 148 | March 16, 1942 Partial |
153 | September 10, 1942 Partial | |||
| The partial solar eclipse on August 12, 1942 occurs in the next lunar year eclipse set. | ||||||
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days).
| 21 eclipse events between July 31, 1924 and July 31, 2000 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| July 31-Aug 1 | May 19-20 | March 7 | December 24-25 | October 12 |
| 115 | 117 | 119 | 121 | 123 |
 July 31, 1924 |
 May 19, 1928 |
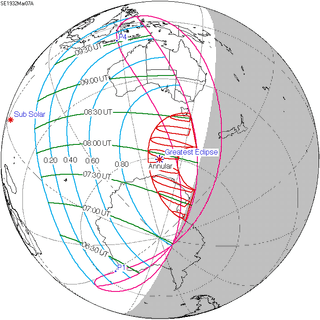 March 7, 1932 |
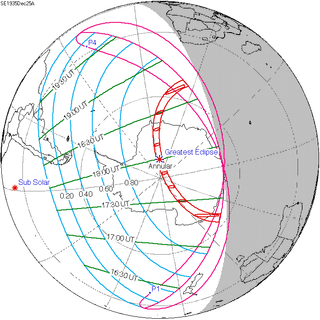 December 25, 1935 |
 October 12, 1939 |
| 125 | 127 | 129 | 131 | 133 |
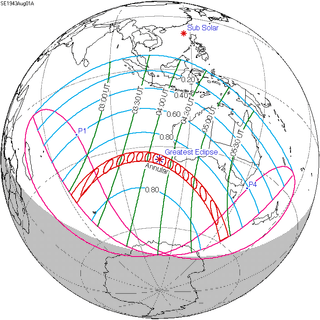 August 1, 1943 |
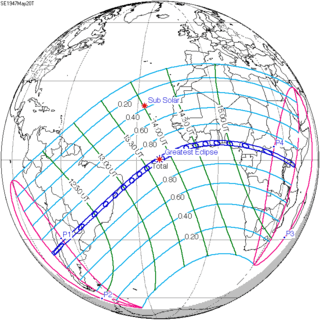 May 20, 1947 |
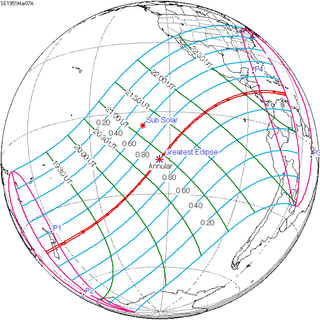 March 7, 1951 |
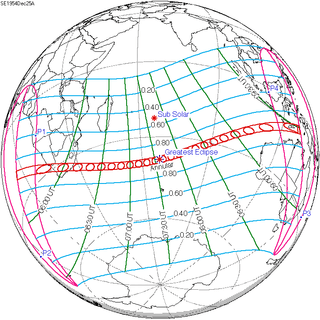 December 25, 1954 |
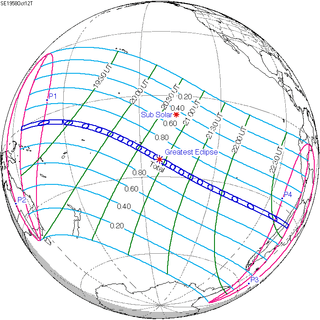 October 12, 1958 |
| 135 | 137 | 139 | 141 | 143 |
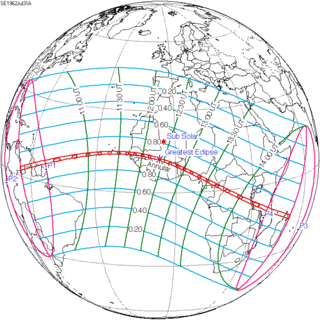 July 31, 1962 |
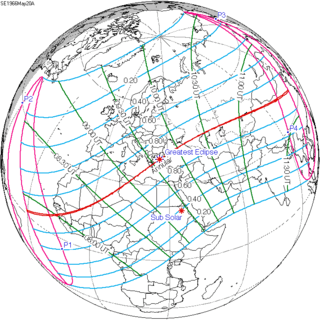 May 20, 1966 |
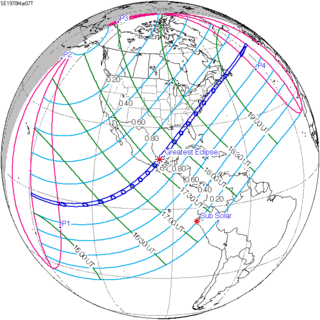 March 7, 1970 |
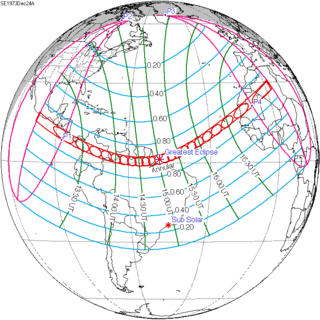 December 24, 1973 |
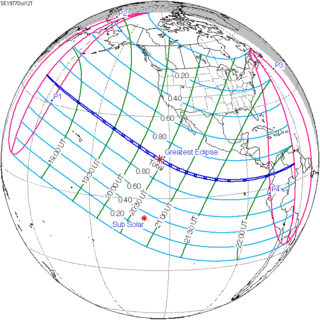 October 12, 1977 |
| 145 | 147 | 149 | 151 | 153 |
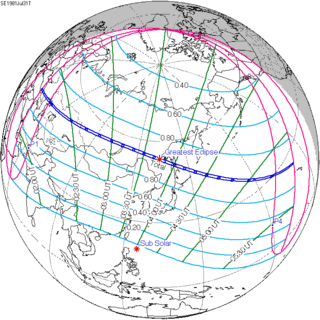 July 31, 1981 |
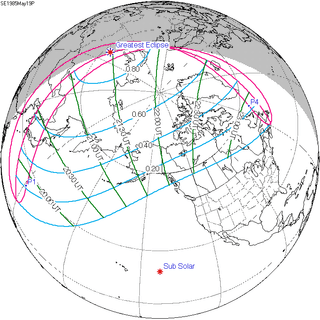 May 19, 1985 |
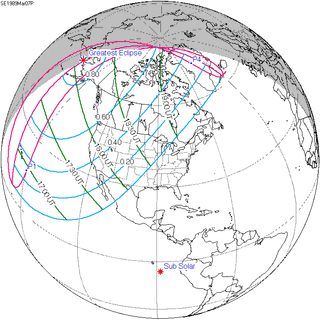 March 7, 1989 |
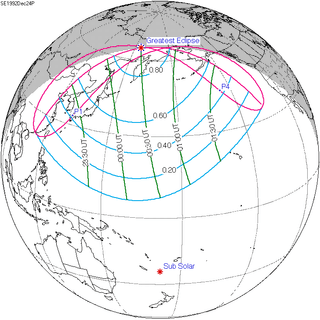 December 24, 1992 |
 October 12, 1996 |
| 155 | ||||
 July 31, 2000 | ||||
Notes
References
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 1939 October 12. |
