Solar eclipse of June 30, 1973
| Solar eclipse of June 30, 1973 | |
|---|---|
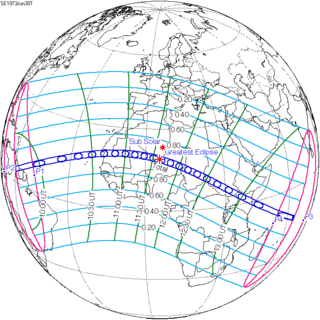 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | -0.0785 |
| Magnitude | 1.0792 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 424 sec (7 m 4 s) |
| Coordinates | 18°48′N 5°36′E / 18.8°N 5.6°E |
| Max. width of band | 256 km (159 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 11:38:41 |
| References | |
| Saros | 136 (35 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9450 |
A total solar eclipse occurred on June 30, 1973. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.
With a maximum eclipse of 7 minutes and 4 seconds, this was the last total solar eclipse that exceeds 7 minutes in this series. There will not be a longer total solar eclipse until June 25, 2150.
Observations
This eclipse was observed by a group of scientists from the Los Alamos National Laboratory using two airplanes to extend the apparent time of totality by flying along the eclipse path in the same direction as the Moon's shadow as it passed over Africa. One of the planes was a prototype of what was later to become the Concorde, which has a top speed of almost 1,300 miles per hour (2,100 km/h)(Mach 2). This enabled scientists from Los Alamos, the Paris Observatory, the Kitt Peak National Observatory, Queen Mary University of London, the University of Aberdeen and CNRS to extend totality to more than 74 minutes; nearly 10 times longer than is possible when viewing a total solar eclipse from a stationary location.[1] The data gathered resulted in three papers published in Nature[2] and a book.[3]
The eclipse was also observed by a charter flight from Mount San Antonio College in Southern California. The DC-8 with 150 passengers intercepted the eclipse at 35,000 feet (11,000 m) just off the east coast of Africa and tracked the eclipse for three minutes. The passengers rotated seats every 20 seconds so that each passenger had three 20 second opportunities at the window to observe and take pictures.
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses of 1971-1995
Template:Solar eclipse set 1971-1995
Saros 136
Solar Saros 136, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, contains 71 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on Jun 14, 1360, and reached a first annular eclipse on September 8, 1504. It was a hybrid event from November 22, 1612, through January 17, 1703, and total eclipses from January 27, 1721 through May 13, 2496. The series ends at member 71 as a partial eclipse on July 30, 2622, with the entire series lasting 1262 years. The longest eclipse occurred on June 20, 1955, with a maximum duration of totality at 7 minutes, 8 seconds.[4]
| Series members 29–43 occur between 1865 and 2117 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
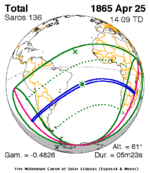 April 25, 1865 |
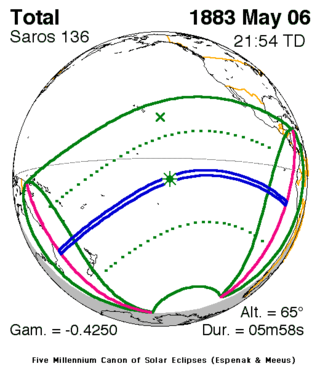 May 6, 1883 |
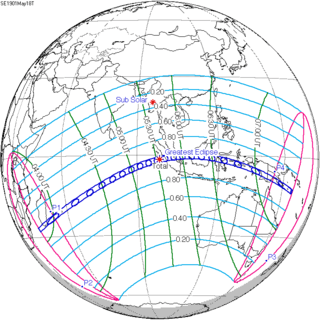 May 18, 1901 |
| 32 | 33 | 34 |
 May 29, 1919 |
 Jun 8, 1937 |
 Jun 20, 1955 |
| 35 | 36 | 37 |
 Jun 30, 1973 |
 Jul 11, 1991 |
 Jul 22, 2009 |
| 38 | 39 | 40 |
 Aug 2, 2027 |
 Aug 12, 2045 |
 Aug. 24, 2063 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 |
 Sep. 3, 2081 |
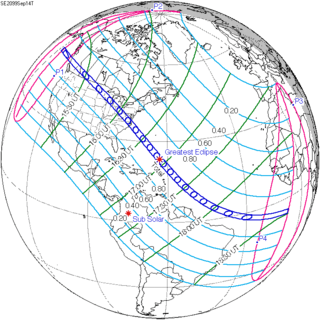 Sep. 14, 2099 |
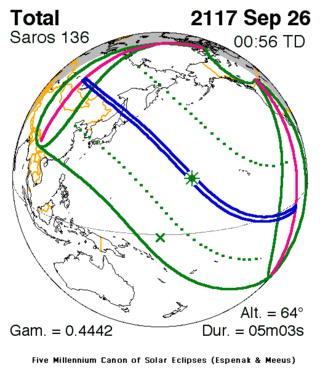 Sep. 26, 2117 |
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days).
| 22 eclipse events between September 12, 1931 and July 1, 2011. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| September 11-12 | June 30-July 1 | April 18-19 | February 4-5 | November 22-23 |
| 114 | 116 | 118 | 120 | 122 |
 September 12, 1931 |
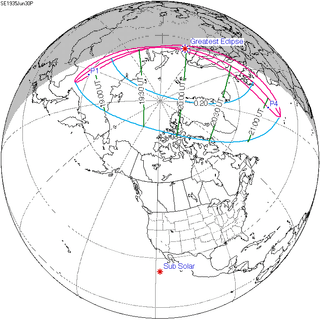 June 30, 1935 |
 April 19, 1939 |
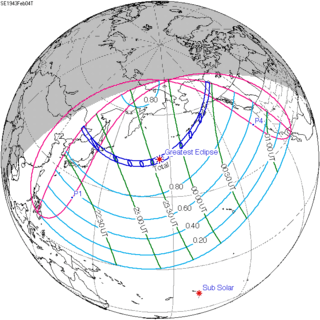 February 4, 1943 |
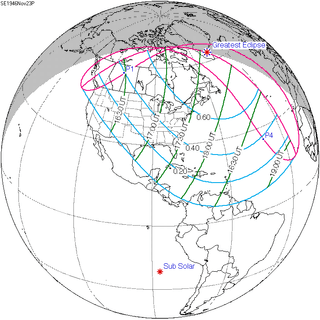 November 23, 1946 |
| 124 | 126 | 128 | 130 | 132 |
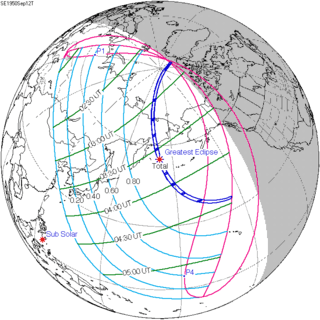 September 12, 1950 |
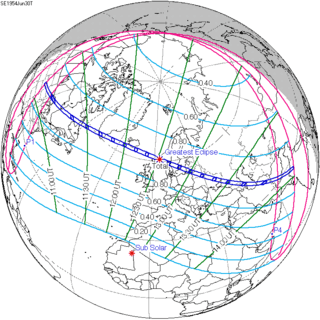 June 30, 1954 |
 April 19, 1958 |
 February 5, 1962 |
 November 23, 1965 |
| 134 | 136 | 138 | 140 | 142 |
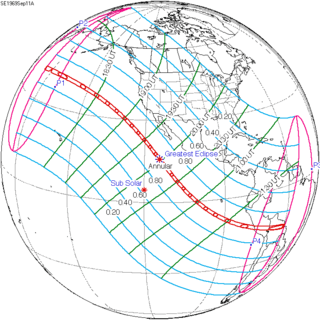 September 11, 1969 |
 June 30, 1973 |
 April 18, 1977 |
 February 4, 1981 |
 November 22, 1984 |
| 144 | 146 | 148 | 150 | 152 |
 September 11, 1988 |
 June 30, 1992 |
 April 17, 1996 |
 February 5, 2000 |
 November 23, 2003 |
| 154 | 156 | |||
 September 11, 2007 |
 July 1, 2011 | |||
Notes
- ↑ Mulkin, Barb (1981). "In Flight: The Story of Los Alamos Eclipse Missions" (PDF). Los Alamos National Laboratory. p. 42. Retrieved 2010-07-14.
- ↑ Hatherill, Chris (9 March 2016). "When Astronomers Chased a Total Eclipse in a Concorde". Vice (magazine). Retrieved 10 March 2016.
- ↑ Léna, Pierre (2015). Racing the Moon’s Shadow with Concorde 001. Springer. ISBN 978-3-319-21729-1. Retrieved 10 March 2016.
- ↑ SEsaros136 at NASA.gov
References
- Foto Solar eclipse of June 30, 1973
- Foto Solar eclipse of June 30, 1995 from Russia expedition
- http://eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov/SEplot/SEplot1951/SE1973Jun30T.GIF
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of June 30, 1995. |
