Shewanella
| Shewanella | |
|---|---|
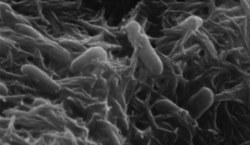 | |
| Shewanella oneidensis | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Proteobacteria |
| Class: | Gamma Proteobacteria |
| Order: | Alteromonadales |
| Family: | Shewanellaceae Ivanova et al. 2004 |
| Genus: | Shewanella MacDonell and Colwell 1985 |
| Type species | |
| Shewanella putrefaciens | |
| Species | |
|
S. abyssi | |
Shewanella is the sole genus included in the Shewanellaceae family of marine bacteria, some species within it were formerly classed as Alteromonas. Shewanella bacteria are a normal component of the surface flora of fish and are implicated in fish spoilage.[2]
Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 is a widely used laboratory model to study anaerobic respiration of metals and other anaerobic extracellular electron acceptors, and for teaching about microbial electrogenesis and microbial fuel cells.
Diet
Shewanella species respire a variety of electrons acceptors in anoxic conditions, many of which are located extracellularly. The mechanism for extracellular electron transfer involves c-type cytochromes that span the inner and outer membranes and "bacterial nanowires".[3]
See also
Shewanella haliotis Kim et al., 2007 [4]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 LPSN bacterio.net
- ↑ Adams and Moss, Food Microbiology, third edition 2008, pp 26, 138, 140,
- ↑ Powell, Corey S. (January 21, 2015). "Have We Found Alien Life?". Popular Science. Retrieved 2015-10-26.
- ↑ NEW TAXA - Proteobacteria: Duwoon Kim, Keun Sik Baik, Mi Sun Kim, Bok-Mi Jung, Tai-Sun Shin, Gyu-Hwa Chung, Moon Soo Rhee, and Chi Nam Seong Shewanella haliotis sp. nov., isolated from the gut microflora of abalone, Haliotis discus hannai Int J Syst Evol Microbiol December 2007 57:2926-2931; doi:10.1099/ijs.0.65257-0
External links
- List of bacterial genera named after personal names
- Shewanella Genome Projects (from Genomes OnLine Database)
- Comparative Analysis of Shewanella Genomes (at DOE's IMG system)