Sharpless oxyamination
The Sharpless oxyamination (often known as Sharpless aminohydroxylation) is the chemical reaction of alkenes with alkyl imido osmium compounds to form vicinal amino-alcohols.[1][2][3] A comprehensive review of this reaction was authored by McLeod et al. in 2002.[4]
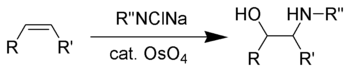
Vicinal amino-alcohols are important products in organic synthesis and recurring pharmacophores in drug discovery.[5]
References
- ↑ Sharpless, K. B.; Patrick, D. W.; Truesdale, L. K.; Biller, S. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 97, 2305. (doi:10.1021/ja00841a071)
- ↑ Herranz, E.; Biller, S. A.; Sharpless, K. B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1978, 100, 3596-3598. (doi:10.1021/ja00479a051)
- ↑ Herranz, E.; Sharpless, K. B. Org. Syn., Coll. Vol. 7, p.375 (1990); Vol. 61, p.85 (1983). (Article)
- ↑ Bodkin, J. A.; McLeod, M. D. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 2002, 2733–2746. (doi:10.1039/b111276g)
- ↑ Bäckvall, J. E.; Oshima, K.; Palermo, R. E.; Sharpless, K. B. J. Org. Chem. 1979, 44, 1953. (doi:10.1021/jo01326a013)
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 2/28/2013. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.