Purpurogallin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
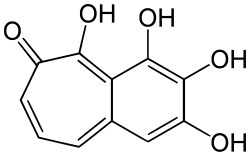
| IUPAC name
2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxybenzo[7]annulen-6-one | |
| Other names
Purpurogalline 2,3,4,6-Tetrahydroxybenzocyclohepten-5-one PPG | |
| Identifiers | |
| 569-77-7 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.478 |
| PubChem | 5281571 |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H8O5 | |
| Molar mass | 220.17 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Purpurogallin is a red, crystalline compound, and the aglycon of several glycosides from nutgalls and oak barks.[1] It can inhibit hydroxyestradiol methylation by catechol-O-methyltransferase.[2] It potently and specifically inhibits TLR1/TLR2 activation pathway.[3]
References
- ↑ Molecular structure and antioxidant specificity of purpurogallin in three types of human cardiovascular cells. Tai-Wing Wu, Ling-Hua Zeng, Jun Wu, Kwok-Pui Fung, Richard D. Weisel, Andrew Hempel and Norman Camerman, Biochemical Pharmacology, Volume 52, Issue 7, 11 October 1996, Pages 1073-1080, doi:10.1016/0006-2952(96)00447-9
- ↑ Benzotropolone inhibitors of estradiol methylation: kinetics and in silico modeling studies. Joshua D. Lambert, Dapeng Chena, Ching Y. Wang, Ni Ai, Shengmin Sang, Chi-Tang Ho, William J. Welsh and Chung S. Yang, Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, Volume 13, Issue 7, 1 April 2005, Pages 2501-2507, doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2005.01.037
- ↑ Discovery of Small-Molecule Inhibitors of the TLR1/TLR2 Complex. K. Cheng, X. Wang, S. Zhang, H. Yin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Early View, doi:10.1002/anie.201204910
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/8/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.