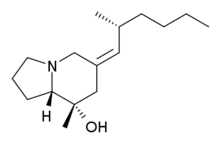
Pumiliotoxin
Pumiliotoxin A: R = –H
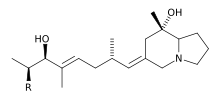
Pumiliotoxin B: R = –OH
Pumiliotoxin B: R = –OH
Pumiliotoxins (PTXs), are one of several toxins found in the skin of poison dart frogs. Closely related, though more toxic, are allopumiliotoxins, (aPTXs). Other toxins found in the skin of poison frogs include decahydroquinolines (DHQs), izidines, coccinellines, and spiropyrrolizidines. Pumiliotoxins are very poisonous in high concentrations. Pumiliotoxins are much weaker than batrachotoxins, ranging between 100 and 1000 times less poisonous. There are three different types of this toxin: A, B and C, of which toxins A and B are more toxic than C. Pumiliotoxins interfere with muscle contraction by affecting calcium channels, causing partial paralysis, difficulty moving, hyperactivity,[1] or death.
See also
References
- ↑ Daly, JW; Garraffo, HM; Spande, TF; et al. (September 2003). "Evidence for an enantioselective pumiliotoxin 7-hydroxylase in dendrobatid poison frogs of the genus Dendrobates". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100: 11092–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.1834430100. PMC 196932
 . PMID 12960405.
. PMID 12960405.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/13/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.