Protostome
| Protostomes Temporal range: Ediacaran - Recent | |
|---|---|
 | |
| A Caribbean Reef Squid, an example of a protostome | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Subkingdom: | Eumetazoa |
| (unranked): | Bilateria |
| (unranked): | Protostomia Grobben, 1908 |
| Superphyla | |
Protostomia (from Greek πρώτο - proto = first + Στόμα - stoma = mouth) are a clade of animals. Together with the deuterostomes and other phyla, they make up the Bilateria, mostly comprising animals with bilateral symmetry and three germ layers. The major distinctions between deuterostomes and protostomes are found in embryonic development.
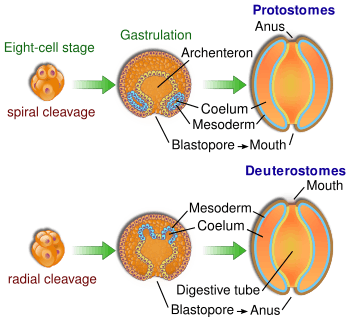
In animals at least as complex as earthworms, the embryo forms a dent on one side, the blastopore, which deepens to become the archenteron, the first phase in the growth of the gut. In deuterostomes, the original dent becomes the anus while the gut eventually tunnels through to make another opening, which forms the mouth. The protostomes were so named because it used to be thought that in their embryos the dent formed the mouth while the anus was formed later, at the opening made by the other end of the gut.
More recent research, however, shows that in protostomes the edges of the dent close up in the middle, leaving openings at the ends which become the mouth and anus.[1] However, this idea has been challenged, because the Acoelomorpha, a group which may be the sister group to the rest of the bilaterian animals, have a single mouth which leads into a blind gut (with no anus). The genes employed in the embryonic construction of this mouth are the same as those expressed around the protostome mouth.[2]
Other significant differences between protostome and deuterostome patterns of development include:
- Most protostomes are schizocoelomates, meaning a solid mass of the embryonic mesoderm splits to form a coelom. A few, such as Priapulids, have no coelom, but they may have descended from schizocoelomate ancestors. On the other hand, all known deuterostomes are enterocoelous, meaning that the coelom is formed from longitudinal pouches of the archenteron which then become separate cavities.
- Within the protostomes, some phyla undergo spiral cleavage which is determinate, meaning that the fate of the cells is determined as they are formed. This is in contrast to deuterostomes, which have radial cleavage that is indeterminate.
Current molecular data suggest that protostome animals can be divided into three major groups:
- Ecdysozoa, e.g. arthropods, nematodes
- Platyzoa, e.g. platyhelminths, rotifers
- Lophotrochozoa, e.g. molluscs, annelids
as well as minor taxa of basal or ambiguous affinity, namely the Chaetognatha.
See also
References
| Wikispecies has information related to: Protostomia |
- ↑ Arendt, D.; Technau, U.; Wittbrodt, J. (4 January 2001). "Evolution of the bilaterian larval foregut". Nature. 409 (6816): 81–85. doi:10.1038/35051075. PMID 11343117. Retrieved 2008-07-14.
- ↑ Hejnol, A.; Martindale, M.Q. (20 November 2008). "Acoel development indicates the independent evolution of the bilaterian mouth and anus". Nature. 456 (7220): 382–6. doi:10.1038/nature07309. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 18806777.