Pioneer program


The Pioneer program is a series of United States unmanned space missions that were designed for planetary exploration. There were a number of such missions in the program, but the most notable were Pioneer 10 and Pioneer 11, which explored the outer planets and left the solar system. Pioneer 10 and Pioneer 11 carry a golden plaque, depicting a man and a woman and information about the origin and the creators of the probes, should any extraterrestrials find them someday.
Naming
Credit for naming the first probe has been attributed to Stephen A. Saliga, who had been assigned to the Air Force Orientation Group, Wright-Patterson AFB, as chief designer of Air Force exhibits. While he was at a briefing, the spacecraft was described to him as a "lunar-orbiting vehicle with an infrared scanning device." Saliga thought the title too long and lacked theme for an exhibit design. He suggested "Pioneer" as the name of the probe since "the Army had already launched and orbited the Explorer satellite and their Public Information Office was identifying the Army as 'Pioneers in Space,'" and by adopting the name the Air Force would "make a 'quantum jump' as to who really [were] the 'Pioneers in space.'"[1]
Early Pioneer missions
The earliest missions were attempts to achieve Earth's escape velocity, simply to show it was feasible and study the Moon. This included the first launch by NASA which was formed from the old NACA. These missions were carried out by the US Air Force and Army.
Able space probes (1958–1960)
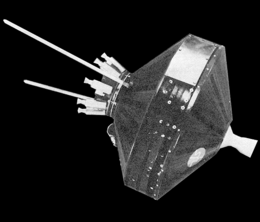



- Most missions here are listed with their most recognised name, and alternate names after in parenthesis.
- Pioneer 0 (Thor-Able 1, Pioneer) – Lunar orbiter, destroyed (Thor failure 77 seconds after launch) August 17, 1958
- Pioneer 1 (Thor-Able 2, Pioneer I) – Lunar orbiter, missed Moon (third stage partial failure) October 11, 1958
- Pioneer 2 (Thor-Able 3, Pioneer II) – Lunar orbiter, reentry (third stage failure) November 8, 1958
- Pioneer P-1 (Atlas-Able 4A, Pioneer W), probe lost September 24, 1959
- Pioneer P-3 (Atlas-Able 4, Atlas-Able 4B, Pioneer X) – Lunar probe, lost in launcher failure November 26, 1959
- Pioneer 5 (Pioneer P-2, Thor-Able 4, Pioneer V) – interplanetary space between Earth and Venus, launched March 11, 1960[2]
- Pioneer P-30 (Atlas-Able 5A, Pioneer Y) – Lunar probe, failed to achieve lunar orbit September 25, 1960
- Pioneer P-31 (Atlas-Able 5B, Pioneer Z) – Lunar probe, lost in upper stage failure December 15, 1960
Juno II lunar probes (1958–1959)
- Pioneer 3 – Lunar flyby, missed Moon due to launcher failure December 6, 1958
- Pioneer 4 – Lunar flyby, achieved Earth escape velocity, launched March 3, 1959
Later Pioneer missions (1965–1978)
Five years after the early Able space probe missions ended, NASA Ames Research Center used the Pioneer name for a new series of missions, initially aimed at the inner Solar System, before the bold flyby missions to Jupiter and Saturn. While successful, the missions returned much poorer images than the Voyager program probes would five years later. In 1978, the end of the program saw a return to the inner Solar System, with the Pioneer Venus Orbiter and Multiprobe, this time using orbital insertion rather than flyby missions.
The new missions were numbered from Pioneer 6 (alternate names in parentheses).
Pioneer 6, 7, 8, and 9
The spacecraft in Pioneer missions 6, 7, 8, and 9 comprised a new interplanetary space weather network:
- Pioneer 6 (Pioneer A) – launched December 1965
- Pioneer 7 (Pioneer B) – launched August 1966
- Pioneer 8 (Pioneer C) – launched December 1967
- Pioneer 9 (Pioneer D) – launched November 1968 (inactive since 1983)
- Pioneer E – lost in launcher failure August 1969
Pioneer 6 and Pioneer 9 are in solar orbits with 0.8 AU distance to the Sun. Their orbital periods are therefore slightly shorter than Earth's. Pioneer 7 and Pioneer 8 are in solar orbits with 1.1 AU distance to the Sun. Their orbital periods are therefore slightly longer than Earth's. Since the probes' orbital periods differ from that of the Earth, from time to time, they face a side of the Sun that cannot be seen from Earth. The probes can sense parts of the Sun several days before the Sun's rotation reveals it to ground-based Earth orbiting observatories. If a powerful solar magnetic storm is formed, they can warn Earth in advance.
Outer Solar System missions
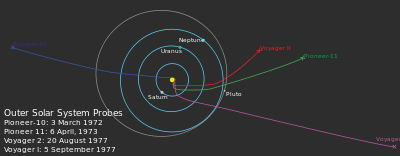

- Pioneer 10 (Pioneer F) – Jupiter, interstellar medium, launched March 1972
- Pioneer 11 (Pioneer G) – Jupiter, Saturn, interstellar medium, launched April 1973
- Pioneer H – identical to Pioneers 10 and 11. Proposed out-of-the-ecliptic mission for 1974, but were not built.[3]
Pioneer Venus project
- Pioneer Venus Orbiter (Pioneer Venus 1, Pioneer 12) – launched May 1978
- Pioneer Venus Multiprobe (Pioneer Venus 2, Pioneer 13) – launched August 1978
- Pioneer Venus Probe Bus – transport vehicle and upper atmosphere probe
- Pioneer Venus Large Probe – 300 kg parachuted probe
- Pioneer Venus North Probe – 75 kg impactor probe
- Pioneer Venus Night Probe – 75 kg impactor probe
- Pioneer Venus Day Probe – 75 kg impactor probe
See also
- Mariner program
- Pioneer anomaly
- Ranger program
- Surveyor program
- Timeline of Solar System exploration
- Voyager program
References
- ↑ "Origins of NASA Names". NASA History. www.history.nasa.gov. Retrieved 2006-10-16.
- ↑ "Aeronautics and Astronautics Chronology, 1960". NASA.
- ↑ "Pioneer H, Jupiter Swingby Out-of-the-Ecliptic Mission Study" (PDF). 20 August 1971. Retrieved 2 May 2012.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Pioneer program. |
- Pioneer (Moon) Program Page by NASA's Solar System Exploration
- Mark Wolverton's The Depths of Space online
- Thor Able – Encyclopedia Astronautica
- Space Technology Laboratories Documents Archive


