Phenylmagnesium bromide
 Complex with ethers | |
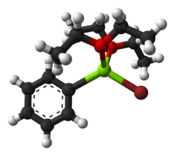 Complex with diethyl ether | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Bromido(phenyl)magnesium | |
| Other names
PMB, (bromomagnesio)benzene | |
| Identifiers | |
| 100-58-3 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 10254417 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.607 |
| PubChem | 6093422 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H5MgBr | |
| Molar mass | 181.31 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless crystals |
| Density | 1.14 g cm−3 |
| Reacts with water | |
| Solubility | Soluble in diethyl ether and THF |
| Basicity (pKb) | Strong base |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | flammable, volatile |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| R-phrases | R12 R14/15 R20/22 R35 R41 |
| S-phrases | S16 S26 S30 S33 S36/37/39 S43 S45 S60 S61 |
| Flash point | −45 °C (−49 °F; 228 K) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Phenyllithium Magnesium bromide Methylmagnesium chloride |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Phenylmagnesium bromide, with the simplified formula C
6H
5MgBr, is a magnesium-containing organometallic compound. It is commercially available as a solution in diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran (THF). Phenylmagnesium bromide is a Grignard reagent. It is often used as a synthetic equivalent for the phenyl "Ph−" synthon.
Preparation

Phenylmagnesium bromide is commercially available as solutions of diethyl ether or THF. Laboratory preparation involves treating bromobenzene with magnesium metal, usually in the form of turnings. A small amount of iodine may be used to activate the magnesium to initiate the reaction.[1]
Coordinating solvents such as ether or THF, are required to solvate (complex) the magnesium(II) center. The solvent must be aprotic since alcohols and water contain an acidic proton and thus react with phenylmagnesium bromide to give benzene. Carbonyl-containing solvents, such as acetone and ethyl acetate, are also incompatible with the reagent.
Structure
Although phenylmagnesium bromide is routinely represented as C
6H
5MgBr, the molecule is more complex. The compound invariably forms an adduct with two OR
2 ligands from the ether or THF solvent. Thus, the Mg is tetrahedral and obeys the octet rule. The Mg–O distances are 201 and 206 pm whereas the Mg–C and Mg–Br distances are 220 pm and 244 pm, respectively.[2]
Chemistry
Phenylmagnesium bromide is a strong nucleophile as well as a strong base. It can abstract even mildly acidic protons, thus the substrate must be protected where necessary. It often adds to carbonyls, such as ketones, aldehydes.[1][3] With carbon dioxide, it reacts to give benzoic acid after an acidic workup.
References
- 1 2 Robertson, D. L. (2007-01-03). "Grignard Synthesis: Synthesis of Benzoic Acid and of Triphenylmethanol". MiraCosta College. Retrieved 2008-01-25.
- ↑ Stucky, G. D.; Rundle, R. E. (1963). "The Structure of Phenylmagnesium Bromide Diethyletherate and the Nature of Grignard Reagents". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 85 (7): 1002–1003. doi:10.1021/ja00890a039.
- ↑ Bachmann, W. E.; Hetzner, H. P. (1955). "Triphenylcarbinol". Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol., 3, p. 839