Pentagon road network
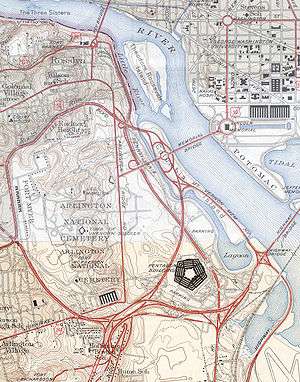
The Pentagon road network is a system of highways, mostly freeways, built by the United States federal government in the early 1940s to serve the Pentagon in northern Virginia. The roads, transferred to the Commonwealth of Virginia in 1964, are now state highways. The main part of the network is the "Mixing Bowl" at Interstate 395 (Shirley Highway) and Route 27 (Washington Boulevard), named because it had major weaving issues with traffic "mixing" between the two roads before it was rebuilt in the early 1970s.
The nickname is now more commonly used to refer to the Springfield Interchange, where I-395, I-495, and I-95 converge in nearby Springfield.
Roads
Shirley Highway (I-395)
The Henry G. Shirley Memorial Highway was built to take traffic off the Highway Bridge (now the 14th Street Bridge). The first phase, from the bridge to Arlington Ridge Road, was completed in 1942. This began at an existing cloverleaf interchange with the Mount Vernon Memorial Highway and ran southwest, parallel to the existing Jefferson Davis Highway (U.S. Route 1), to a point southeast of the Pentagon. That section included an interchange with Boundary Channel Drive, which served the Pentagon's north parking lot, and a bridge over the Rosslyn Connecting Railroad. US 1 was routed onto it, as the existing US 1 was cut in several places by ramps.
After crossing the Jefferson Davis Highway, where US 1 exited to the south, the Shirley Highway turned west, with an interchange to access the south parking lot. (Hayes Street now crosses under the highway there.) Southwest of the Pentagon, the connection to the Arlington Memorial Bridge (now Route 27) merged, and soon after was a split for the connection to Lee Boulevard (now also Route 27, Washington Boulevard). Just past that, the original construction turned southeast to end at Arlington Ridge Road.
The extension beyond to Route 7, also built by the Federal Government, opened October 23, 1943 and was dualled on October 30, 1944. The extension beyond Route 7 to U.S. Route 1 near Occoquan was built by the Virginia Department of Highways as State Route 350 from 1945 to 1952. (SR 350 was also signed along the Federally built portion southwest of US 1.)
On December 17, 1964, the road system was transferred to Virginia, and soon after the Shirley Highway became part of Interstate 95. With the cancellation of I-95 through Washington, D.C., it was renumbered Interstate 395 in 1977.
Washington Boulevard (Route 27)
What is now Route 27 was built in two sections. The western section served as a realignment of Washington Boulevard from Lee Boulevard (U.S. Route 50, now Arlington Boulevard) southeast to the Mixing Bowl. It had several grade crossings and one interchange (with Route 244, Columbia Pike).
East of the Mixing Bowl, the other part of current Route 27 headed northeast, crossing a realigned Columbia Pike, with access to the Pentagon's south parking lot to the east. Past that was another full interchange, for Pentagon service access, just before a crossing (with no ramps) of the Jefferson Davis Highway Extension and the Rosslyn Connecting Railroad. Finally, an interchange with Boundary Channel Drive (for north parking) was provided, with access only to/from the north, before the road crossed the Boundary Channel into Washington, D.C. for connections to the Mount Vernon Memorial Highway and Arlington Memorial Bridge.
Those roads were also transferred to the Virginia Department of Highways on December 17, 1964 and assigned the number Route 27.
Jefferson Davis Highway (Route 110)
The extension of the Jefferson Davis Highway ran along the east side of the Pentagon, parallel to the Rosslyn Connecting Railroad, connecting the junction of the Jefferson Davis Highway (U.S. Route 1) and Shirley Highway to Rosslyn. It had one interchange with the Pentagon, connecting to the drop-off area to the southeast. After crossing the Mixing Bowl-Arlington Memorial Bridge connection with no access, a partial interchange (access to/from the south) was provided with the main road to the bridge. The extension ended at Arlington Ridge Road just north of Lee Boulevard (U.S. Route 50). Following the September 11 attacks, Route 110 was closed to trucks and tour buses due to its proximity to the Pentagon. In September 2002, a contract was awarded to reroute Route 110 to increase the standoff distance between vehicles and the Pentagon. The project, called the Pentagon Secure Bypass,[1] was completed in 2004.
When the road was transferred to the Virginia Department of Highways on December 17, 1964, it was numbered Route 110.
Columbia Pike Extension (Route 244)
Prior to the building of the Mixing Bowl, Columbia Pike (and Route 244) ran through its site to end at the Jefferson Davis Highway (U.S. Route 1). It was truncated at that time to Arlington Ridge Road, which itself was cut by the Mixing Bowl (and later cut by Arlington National Cemetery to the north).
As part of that network, a connection was built from Arlington Ridge Road north of Columbia Pike east to the Arlington Memorial Bridge connection, continuing across that connection to the Pentagon south parking lot. It was also transferred to the Virginia Department of Highways on December 17, 1964, and numbered as an extension of Route 244.
Pentagon access
Access to the Pentagon was provided in the following places:
- South parking lot
- Shirley Highway east of the Mixing Bowl (full cloverleaf where Hayes Street now crosses, also providing access to Army Navy Drive to the south)
- Arlington Memorial Bridge connection (now Washington Boulevard) and the Columbia Pike Extension northeast of the Mixing Bowl (full cloverleaf)
- North parking lot
- Shirley Highway northeast of the Jefferson Davis Highway (partial cloverleaf with Boundary Channel Drive, providing full access)
- Arlington Memorial Bridge connection (now Washington Boulevard) south of the Boundary Channel (partial interchange—access only to/from the north—with Boundary Channel Drive)
- Service area north of the Pentagon
- Arlington Memorial Bridge connection (now Washington Boulevard) south of the Jefferson Davis Highway Extension (folded diamond)
- Drop-off area southeast of the Pentagon
- Jefferson Davis Highway Extension north of the Shirley Highway (trumpet)
The Mixing Bowl

The "Mixing Bowl" originally opened in 1942 as the junction of the Shirley Highway with the connection to the Arlington Memorial Bridge and the connection to Lee Boulevard. The western half, towards Lee Boulevard, was a full three-level Y interchange. The eastern half, towards the Memorial Bridge, was missing a ramp to enter the Shirley Highway northeastbound. Just south of the west half was another interchange, a single Y connecting to Arlington Ridge Road.
From 1970 to 1973, as part of a total reconstruction of the Shirley Highway, the interchange was totally rebuilt to eliminate all weaving of traffic, mainly by the use of collector/distributor roads. The former cloverleaf with Hayes Street became a system of ramps to the various roads. The ramp from I-395 south to Route 27 towards the Memorial Bridge was removed, and a pair of ramps at the crossing of Route 27 and Route 110 made some of the ramps at Jefferson Davis Highway redundant. Finally, a two-lane reversible HOV roadway was added in the median, becoming a four-lane two-way road from the eastern part of the interchange into Washington. Special ramps to Route 27 towards the Memorial Bridge and to the Pentagon south parking lot (via Eads Street) were provided for HOV traffic.
References
External links
- Roads to the Future—Henry G. Shirley Memorial Highway
- Roads to the Future—Mixing Bowl Interchange Complex