European Ice Age leopard
| Panthera pardus spelaea Temporal range: Late Pleistocene | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Felidae |
| Genus: | Panthera |
| Species: | P. pardus |
| Subspecies: | †P. p. spelaea |
| Trinomial name | |
| Panthera pardus spelaea Bächler, 1936 | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The European ice age leopard or Late Pleistocene ice age leopard (Panthera pardus spelaea) was a subspecies of leopard which roamed Europe in the Late Pleistocene. It resembled the modern Persian leopard. The youngest fossils date to about 24,000 years ago, but it may have survived into the Holocene in southern and eastern Europe.
Description
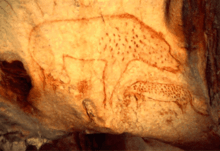
The Late Pleistocene Ice Age leopard was about the size of a modern Persian leopard (P. p. ciscaucasica). The skull was medium-long and its characteristics are closest to modern Persian leopards. The only known depiction of this leopard (from Chauvet Cave) shows a coat pattern similar to that of modern leopards. It is unclear if the spots were organised in larger rosettes like in modern Persian leopards. In contrast to modern leopards, the belly of the depicted animal is unspotted white. Fossils of small female leopards can sometimes be confused with large male lynxes. Leopards from the cold phases (glacials) of the Late Pleistocene are usually larger than those from the warm phases (interglacials). As in modern leopards, there was a strong sexual dimorphism, with males being larger than females.[1]
Evolution
The leopard first appeares in the fossil record of Europe in the Late Pliocene or Early Pleistocene. These leopards, attributed to the subspecies Panthera pardus begoueni, were replaced about 600,000 years Before Present by Panthera pardus sickenbergi, which lived until the Mid Pleistocene in Europe. Around 300,000 years ago another subspecies, Panthera pardus antiqua, replaced Panthera pardus sickenbergi. At the beginning of the Late Pleistocene, this subspecies gave rise to the Late Pleistocene ice age leopard (Panthera pardus spelaea). Another Pleistocene form from Europe, Panthera pardus vraonensis, is now regarded as a junior synonym of Panthera pardus spelaea.[1]
Distribution
Leopards were found in many parts of Europe during the Late Pleistocene. In the North, they reached the southernmost parts of Great Britain and Northern Germany (Baumann's Cave). The most complete skeleton of an Ice Age leopard is known from Vjetrenica Cave (south Bosnia and Herzegovina), where four leopard fossils have been found. These are dated to the end of the Late Pleistocene, about 29,000–37,000 BP. The latest records of the European Ice Age leopard, cave paintings in the Chauvet Cave in southern France, are dated to about 25,000–37,500 Before Present. The last leopards vanished from most parts of Europe about 24,000 years ago, just before the Last Glacial Maximum, because the youngest known fossil is 24,000 years old and was found in Croatia. In Germany the leopard survived at least into the early Weichselian.[1]
Holocene European leopards
Subfossils of leopards, imprecisely dated to the Early to Mid-Holocene, are known from Spain and Greece. The youngest subfossil records in Europe are from the Ukraine and have been dated into the first century AD. Some of these were found in the western parts of the country, close to the Carpathians; others were found in Olbia, Ukraine at the northern coast of the Black Sea. The latter might belong to captive leopards, which could have been introduced from Turkey, since Olvija was a Greek colony at this time. This scenario is certainly true for the early medieval leopard bones found in the Colosseum in Rome.[2] In Europe, leopards survived until the present day only at the southeasternmost fringes in the northern Caucasus; these are included into the Persian leopard subspecies (P. p. ciscaucasica).
Behaviour
Fossils of ice age leopards in Europe are sometimes found in caves, where they apparently sought shelter or hid their prey. They generally preferred smaller caves, most likely because larger caves were usually occupied by larger predators such as cave bears, cave lions, or humans. In European ice age caves, leopard bones are far rarer than those of lions, and all currently known fossils belong to adults, suggesting that they rarely, if ever, raised their cubs in caves. Where leopard remains are found in larger caves, they are often found in the cave's deeper recesses, as in Baumann's and Zoolithen Cave in Germany. It is not precisely known which prey species these leopards hunted, although they may have been similar to modern Persian or snow leopards, which prey on ibex, deer and wild boar. It is likely that leopards scavenged or occasionally killed cave bears during hibernation in their dens. During the cold phases, Late Pleistocene European leopards occurred mainly in mountain or alpine boreal forests or in mountains above the treeline, and were not usually found in the lowland mammoth steppes.[1]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 Cajus G. Diedrich: Late Pleistocene leopards across Europe – northernmost European German population, highest elevated records in the Swiss Alps, complete skeletons in the Bosnia Herzegowina Dinarids and comparison to the Ice Age cave art. Quaternary Science Reviews Volume 76, 15 September 2013, Pages 167–193
- ↑ R. S. Sommer & N. Benecke: Late Pleistocene and Holocene development of the felid fauna (Felidae) of Europe: a review. Journal of Zoology 269 (2006) 7–19