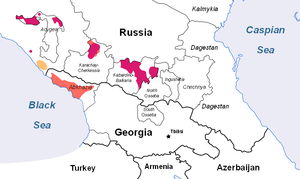
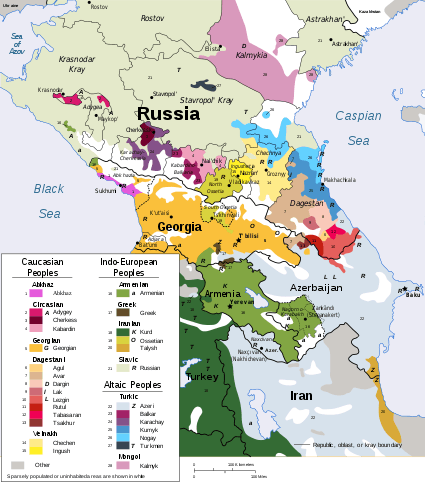
Northwest Caucasian languages
| Northwest Caucasian | |
|---|---|
|
Abkhaz–Adyghean Pontic | |
| Geographic distribution: | Caucasus |
| Linguistic classification: | One of the world's primary language families |
| Subdivisions: | |
| Glottolog: | abkh1242[1] |
|
Circassian
Abazgi
Ubykh (extinct) | |
The Northwest Caucasian languages, also called West Caucasian, Abkhazo-Adyghean, or sometimes Pontic (as opposed to Caspian for the Northeast Caucasian languages), are a group of languages spoken in the northwestern Caucasus region,[2] chiefly in three Russian republics (Adygea, Kabardino-Balkaria, Karachay–Cherkessia), the disputed territory of Abkhazia (whose sovereignty is claimed by Georgia), and Turkey, with smaller communities scattered throughout the Middle East.
Main features
Phonetics
The entire family is characterised by a paucity of phonemic vowels (two or three, depending upon the analysis) coupled with rich consonantal systems that include many forms of secondary articulation.[2] Ubykh (Ubyx), for example, had both the minimal number of vowels (two), and probably the largest inventory of consonants outside Southern Africa.
Linguistic reconstructions suggest that both the richness of the consonantal systems and the poverty of the vocalic systems may be the result of a historical process, whereby vowel features such as labialisation and palatalisation were reassigned to adjacent consonants. For example, ancestral */ki/ may have become /kʲə/ and */ku/ may have become /kʷə/, losing the old vowels */i/ and */u/ but gaining the new consonants /kʲ/ and /kʷ/. The linguist John Colarusso has further postulated that some instances of this may also be due to the levelling of an old grammatical class prefix system (so */w-ka/ may have become /kʷa/), on the basis of pairs like Ubykh /ɡʲə/ vs. Kabardian and Abkhaz /ɡʷə/ heart. This same process is claimed by some to lie behind the development of labiovelars in Proto-Indo-European which once neighboured Proto-NWC.
Grammar
Northwest Caucasian languages have rather simple noun systems, with only a handful of cases at the most, coupled with highly agglutinative verbal systems that can contain almost the entire syntactic structure of the sentence. All finite verbs are marked for agreement with three arguments: absolutive, ergative, and indirect object,[3] and there are also a wide range of applicative constructions. There is a split between "dynamic" and "stative" verbs, with dynamic verbs having an especially complex morphology. A verb's morphemes indicate the subject's and object's person, place, time, manner of action, negative, and other types of grammatical categories.
All Northwest Caucasian languages are left-branching, so that the verb comes at the end of the sentence and modifiers such as relative clauses precede a noun.
Northwest Caucasian languages do not generally permit more than one finite verb in a sentence, which precludes the existence of subordinate clauses in the Indo-European sense. Equivalent functions are performed by extensive arrays of nominal and participial non-finite verb forms, though Abkhaz appears to be developing limited subordinate clauses, perhaps under the influence of Russian.
Classification
There are five recognized languages in the Northwest Caucasian family: Abkhaz, Abaza, Kabardian or East Circassian, Adyghe or West Circassian, and Ubykh.[2][4] They are classified as follows:
- Abkhaz–Abaza (Abazgi)
- Circassian (Cherkess)
- Ubykh (extinct)
Circassian dialect continuum
Circassian (Cherkess) is a cover term for the series of dialects that include the literary languages of Adyghe and Kabardian.
Adyghe
Adyghe is one of the more widely spoken Northwest Caucasian languages. It has 500,000 speakers spread throughout Russia and the Middle East: 280,000 in Turkey; 125,000 in Russia, where it is official in the Republic of Adygea; 45,000 in Jordan, 25,000 in Syria, 20,000 in Iraq, and 4,000 in Israel. There is even a small community in the United States. Four main dialects are recognised: Temirgoy, Abadzekh, Shapsugh and Bzhedugh, as well as many minor ones such as Hakuchi spoken by the last speakers of Ubykh in Turkey. Adyghe has a large number of consonants: between 50 and 60 consonants in the various Adyghe dialects but it has only three phonemic vowels. Its consonants and consonant clusters are less complex than the Abkhaz–Abaza dialects.
Kabardian
Kabardian has just over one million speakers: 550,000 in Turkey and 450,000 in Russia, where it is an official language of the republics of Kabardino-Balkaria and Karachay–Cherkessia. Kabardian has the least number of consonants of any North-Western Caucasian language, with 48, including some rather unusual ejective fricatives and a small number of vowels. Kabardian itself has several dialects, including Terek, the literary standard, and Besleney, which is intelligible with both Terek and Adyghe. Unlike the Adyghe, Kabardian lost many of the consonants that existed in the Proto-Circassian language, for example the consonants /ʃʷʼ/ /ʐʷ/ /ʂʷ/ /ʐ/ /ʂ/ /tsʷ/ /dzʷ/ became /fʼ/ /v/ /f/ /ʑ/ /ɕ/ /f/ /v/.
Abkhaz–Abaza (Abazgi) dialect continuum
Abkhaz
Abkhaz has 100,000 speakers in Abkhazia (a de facto independent republic, but a de jure autonomous entity within Georgia), where it is the official language, and an unknown number of speakers in Turkey. It has been a literary language from the beginning of the 20th century. Abkhaz and Abaza may be said to be dialects of the same language, but each preserves phonemes which the other has lost. Abkhaz is characterised by unusual consonant clusters and one of the world's smallest vowel inventories: It has only two distinctive vowels, an open vowel /a/ and a mid vowel /ə/. Next to palatalized or labialized consonants, /a/ is realized as [e] or [o], and /ə/ as [i] or [u]. There are three major dialects: Abzhuy and Bzyp in Abkhazia and Sadz in Turkey.
Abaza
Abaza has some 45,000 speakers, 35,000 in Russia and 10,000 in Turkey. It is a literary language, but nowhere official. It shares with Abkhaz the distinction of having just two phonemic vowels. Abaza is phonologically more complex than Abkhaz, and is characterised by large consonant clusters, similar to those that can be found in Georgian. There are three major dialects, Tapant and Ashkhar. Some are partially intelligible with Abkhaz.
Ubykh
Ubykh forms a third branch, with parallels to both Adyghe and Abkhaz. The population switched to speaking Adyghe, and Ubykh became extinct on October 7, 1992, with the death of Tevfik Esenç. A dialectal division within Ubykh was suspected by Georges Dumézil, but the divergent form he described in 1965 was never investigated further. With eighty-one consonants, Ubykh had perhaps the largest inventory in the world aside from the Kx'a and Tuu families of southern Africa with their extensive system of clicks. There are pharyngealised consonants and a four-way place contrast among sibilants. It was the only Northwest Caucasian language never to have a literary form.
Relationship to other language families
A number of factors make the reconstruction of the Northwest Caucasian proto-language problematic:
- most roots in Northwest Caucasian languages are monosyllabic, and many are single consonants;
- the sound changes are often intricate, and a large number of consonants and sibilant contrasts provides further complexity;
- ablaut was extensive and still plays some part in the modern languages;
- borrowings between languages of the family were frequent;
- extensive homophony occurs in the modern languages.
For these reasons, Proto–Northwest Caucasian is widely accepted as being one of the most difficult proto-languages to deal with, and it is therefore more difficult than most to relate to other families.
Connections to Hattic
Some scholars have seen affinities between the Northwest Caucasian (Circassian) family and the extinct Hattic language. Hattic was spoken in Anatolia (Turkey), in the area around ancient Hattusa (modern Boğazköy), until about 1800 BCE, when it was replaced by the Indo-European Hittite language. The name Hetto-Iberian (or Proto-Iberian) was proposed by Georgian historian Simon Janashia for a superfamily comprising the South Caucasian languages, other Caucasian language groups, Hattic and other languages of ancient Anatolia. (The Iberian in the name refers to Caucasian Iberia, a kingdom centered in eastern Georgia which lasted from the 4th century BCE to the 5th century CE; it is not related to the Iberian Peninsula.)
Many Northwest Caucasian (Adygean) family names have prefixes like "Hath" or "Hatti", and one of the well known Adyghe tribes has the name "Hattiqwai" (Adyghe: Хьатыкъуай) (From Хьаты ("Hatti") + Кхъуэ ("male or son"); meaning "HattiSon").[5]
Connections to Indo-European
It has been conjectured[6][7] that the North-West Caucasian languages may be genetically related to the Indo-European family, at a time depth of perhaps 12,000 years before the present. This hypothesised proto-language is called Proto-Pontic, but is not widely accepted.
There does at least appear to have been extensive contact between the two proto-languages, and the resemblances may be due to this influence.
North Caucasian family
Many linguists join the Northwest and Northeast Caucasian languages into a North Caucasian family, sometimes simply called Kavkazian (in opposition to Kartvelian (South Caucasian), which is thought to be unrelated, albeit heavily influenced by their northern neighbours). This hypothesis has perhaps been best illustrated by Sergei A. Starostin and Sergei Nikolayev, who present a set of phonological correspondences and shared morphological structure. However, there is no consensus that the relationship has been demonstrated, and many consider the correspondences to be spurious for the reasons mentioned above. See the article on North Caucasian languages for details, as well as the external links below.
Higher-level connections
A few linguists have proposed even broader relationships, of which the Dene–Caucasian hypothesis is perhaps the most popular. Dene–Caucasian links the North Caucasian (including Northwest Caucasian), Basque, Burushaski, Yeniseian, Sino-Tibetan, and Na–Dene families. However, this is an even more tentative hypothesis than Nostratic, which attempts to relate Indo-European, Uralic, Kartvelian, Altaic, etc., and which is widely considered to be undemonstrated.
References
Citations
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian, eds. (2016). "Abkhaz–Adyge". Glottolog 2.7. Jena: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- 1 2 3 Hoiberg, Dale H. (2010)
- ↑ Nichols, Johanna (1986)
- ↑ Chirikba, Viacheslav (1996); p. 452
- ↑ Burney, Charles (2004); p. 106
- ↑ Colarusso, John (2003)
- ↑ Colarusso, John (1997)
Sources
- Burney, Charles (2004). Historical dictionary of the Hittites. Historical Dictionaries of Ancient Civilizations and Historical Era. Lanham, MD: Scarecrow Press. ISBN 978-0810849365.
- Chirikba, Viacheslav (1996). Common West Caucasian. The Reconstruction of its Phonological System and Parts of its Lexicon and Morphology. Leiden: Research School CNWS, School of Asian, African, and Amerindian Studies. ISBN 978-9073782716.
- Colarusso, John (1997). "Phyletic Links between Proto-Indo-European and Proto–Northwest Caucasian". The Journal of Indo-European Studies. Chicago Linguistic Society. 25 (1–2): 119–151.
- Colarusso, John (2003). "Further Etymologies between Indo-European and Northwest Caucasian". In Holisky, Dee Ann; Tuite, Kevin. Current Issues in Linguistic Theory. Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing Company. pp. 41–60. ISBN 978-1588114617. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - Hoiberg, Dale H., ed. (2010). "Abkhazo-Adyghian languages". Encyclopedia Britannica. I: A-ak Bayes (15th ed.). Chicago, IL: Encyclopedia Britannica Inc. p. 33. ISBN 978-1-59339-837-8.
- Nichols, Johanna (Mar 1986). "Head-Marking and Dependent-Marking Grammar". Language. Linguistic Society of America. 62 (1): 56–119. doi:10.1353/lan.1986.0014. JSTOR 415601.
Additional reading
- Starostin, S. A., ed. (2008) [1994]. A North Caucasian Etymological Dictionary. Caravan Books. ISBN 978-0882061177.
External links
- CIA linguistic map of the Caucasus
- Atlas of the Caucasian Languages with detailed Language Guide (by Yuri B. Koryakov)
- A Comparative Dictionary of North Caucasian Languages: Preface by Sergei Starostin & Sergein Nikolayev
- Ancient Adyghe Abkhaz–Abaza Ubykh alphabet