NGC 4567 and NGC 4568
| NGC 4567 and NGC 4568 | |
|---|---|
|
The Siamese Twins with NGC 4567 (top) and NGC 4568 (bottom) | |
| Observation data (J2000.0 epoch) | |
| Constellation | Virgo |
| Right ascension | 12h 36m 34.3s |
| Declination | +11° 14′ 17″ |
| Distance | 59.4 Mly (18.2 Mpc)[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | +10.9 |
| Absolute magnitude (V) | -13.3 |
| Characteristics | |
| Type | SA(rs)bc / SA(rs)bc |
| Apparent size (V) | 4.6' × 2.1' |
| Notable features | colliding galaxies |
| Other designations | |
| NGC 4567/8, UGC 7776, PGC 42064/9, VV 219 | |
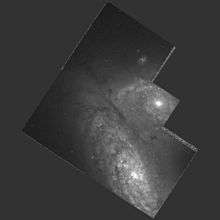
NGC 4567 and 4568 imaged by the Hubble Space Telescope
NGC 4567 and NGC 4568 (nicknamed the Siamese Twins or the Butterfly Galaxies) are a set of unbarred spiral galaxies about 60 million light-years away[1] in the constellation Virgo. They were both discovered by William Herschel in 1784. They are part of the Virgo cluster of galaxies. Only one supernova (SN 2004cc) has been observed in the Siamese Twins.
These galaxies are in the process of colliding and merging with each other, as studies of their distributions of neutral and molecular hydrogen show, with the highest star formation activity in the part where they overlap. However the system is still in an early phase of interaction.[2]
They were named "Siamese Twins" because they appear to be connected.
See also
References
- 1 2 "Distance Results for NGC 4568". NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database. Retrieved 2010-05-01.
- ↑ "Molecular Gas in the Early Stage of Interacting Galaxies: The NGC 4567/8 Pair". Retrieved 2012-05-14.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 7/26/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.
