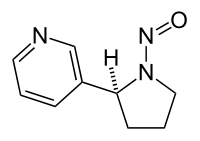
N-Nitrosonornicotine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-(1-Nitrosopyrrolidin-2-yl)pyridine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 16543-55-8 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Abbreviations | NNN |
| ChemSpider | 19957766 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.230.123 |
| KEGG | C16452 |
| PubChem | 27919 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H11N3O | |
| Molar mass | 177.21 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Oily yellow liquid |
| Melting point | 47 °C (117 °F; 320 K) |
| Boiling point | 154 °C (309 °F; 427 K) |
| Soluble | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 177 °C (351 °F; 450 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
N-Nitrosonornicotine (NNN) is a tobacco-specific nitrosamine produced during the curing and processing of tobacco. It has been classified as a Group 1 carcinogen.[1] Although no adequate studies of the relationship between exposure to NNN and human cancer have been reported, there is sufficient evidence that NNN causes cancer in experimental animals.
NNN is found in a variety of tobacco products including smokeless tobacco like chewing tobacco and snuff,[2] cigarettes, and cigars. It is present in smoke from cigars and cigarettes, in the saliva of people who chew betel quid with tobacco, and in the saliva of oral-snuff users. NNN is produced by the nitrosation of nornicotine during the curing, aging, processing, and smoking of tobacco.[3] Roughly half of the NNN originates in the unburnt tobacco, with the remainder being formed during burning.
NNN can be produced in the acidic environment of the stomach in users of oral nicotine replacement therapies, due to the combination of dietary/endogenous nitrates, and nornicotine(either present as a minor metabolite of nicotine, or as an impurity in the product). Levels found in urine are over an order of magnitude less than when tobacco is consumed, but this remains a potential source of cancer when used in the long term.[4]
References
- ↑ "Agents Classified by the IARC Monographs, Volumes 1–105" (PDF). IARC.
- ↑ Balbo, S. (April 2, 2012). "Strong Oral Carcinogen Identified in Smokeless Tobacco". American Association for Cancer Research.
- ↑ Siminszky, B.; Gavilano, L.; Bowen, S. W.; Dewey, R. E. (2005). "Conversion of nicotine to nornicotine in Nicotiana tabacum is mediated by CYP82E4, a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase" (PDF). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 102 (41): 14919–14924. doi:10.1073/pnas.0506581102. PMC 1253577
 . PMID 16192354.
. PMID 16192354. - ↑ http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/NewsEvents/UCM232146.pdf