Moscow International Business Center

Moscow International Business Center “Moscow City” (Russian: Московский международный деловой центр «Москва-Сити»)[1][2] is a commercial district in central Moscow, Russia. Located near the Third Ring Road in Presnensky District of Central Administrative Okrug, the Moscow City area is currently under development. The construction of the Moscow IBC is taking place on the Presnenskaya embankment of the Moscow River approximately 4 kilometers (2.5 mi) west of Red Square, and just east of the Third Ring Road. The project occupies an area of 60 hectares,[3] the territory chosen being the only area in central Moscow that can accommodate such a project. Before construction began, the area had been an old stone quarry where most of the buildings were old factories and industrial complexes that had been closed or abandoned.
In order to manage the project, a public company, CITY, was created in 1992 in order to oversee the initial creation and development of Moscow City as well as its subsequent usage. CITY is also a general contractor and both landlord and leaser. Overall responsibility for the architectural planning and design of Moscow City belongs to the architectural studio No. 6, which is a part of the large Moscow practice Mosproject-2 named after Mikhail Vasilyevich Posokhin. This group, headed by Gennadiy Lvovich Sirota, who is officially the Chief Architect of Moscow City, is in charge of overseeing the design of the complex as a whole and agreeing the details of individual projects. Each building lot has its own investor and architect. By 2014 the volume of investments in Moscow City was approximately $12 billion.[4]
The Moscow IBC is expected to become the first zone in Russia to combine business activity, living space and entertainment in one single development.[3] The Moscow government first conceived the project in 1992.[5] An estimated 250,000 – 300,000 people will be working in, living in, or visiting the complex at any given time.[3] MIBC includes 6 skyscrapers with maximum height of 300 meters or more (Shanghai has 5, Hong Kong has 6, Chicago has 6, New York has 8). Europe's tallest building, the Federation Tower, is in the Moscow IBC. The complex also includes the second-tallest, third-tallest, fifth-tallest, sixth-tallest, and seventh-tallest buildings in Europe. By 2016 twelve of twenty-three planned facilities of MIBC were already built, seven buildings are in construction and four are in the design stage.[6]
Layout
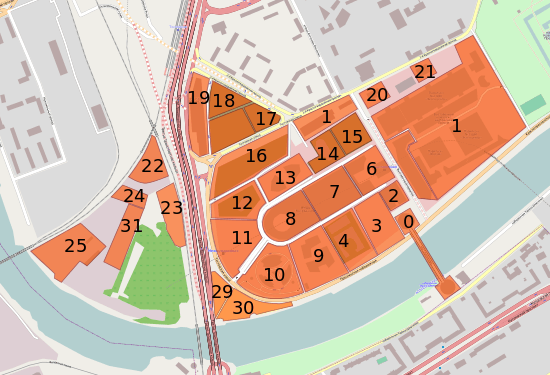

| Completed | Designed height | Under construction | Zero cycle | Canceled | Presumably |
| Plot number | Name | Started | Completed | Buildings in complex | Roof height | Max height | Floors | Total area, m² | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Tower 2000 and Bagration Bridge | 1996 | 2001 | 1 | 104 | 104 | 34 | 61 057 | |
| 1 | Expocentre | 1977 | 2008 | 8 | 15 | 15 | 10 | 165 000 | |
| 2-3 | Evolution Tower | 2011 | 2015 | 1 | 255 | 255 | 54 | 169 000 | Interior finishing works |
| 4 | Imperia Tower | 2006 | 2011 [7] | 2 | 239 | 239 | 59 | 287 723 | Construction of the second part of the complex |
| 6-8 | Central core | 2005 | 2016 | 1 | 50 | 50 | 6 | 450 000 | Completed part of complex[8] |
| 9 | City of Capitals | 2005 | 2009 | 3 | 302[9] | 302 | 76 | 288 680 | |
| 10 | Naberezhnaya Tower | 2003 | 2007 | 3 | 268[10] | 268 | 59 | 254 000 | |
| 11 | IQ-quarter | 2010 | 2016 | 3 | 169[11] | 169 | 42 | 228 000 | Interior finishing works |
| 12 | Eurasia Tower | 2007 | 2015 | 1 | 309 | 309 | 70 | 207 542 | Interior finishing works |
| 13 | Federation Tower | 2003 | 2016 | 2 | 374[12] | 374 | 101 | 439 154 | The tallest building in Europe[13] |
| 14 | Mercury City Tower | 2009 | 2013 | 1 | 339 | 339 | 75 | 158 528 | |
| 15 | Grand Tower[14] | 2012 | 2018 | 1 | 283 | 283 | 50 | 315 282 | Installed a construction crane |
| 16 | OKO | 2011 | 2015 | 3 | 354[15] | 354 | 85 | 429 600 | Interior finishing works |
| 17-18 | Neva Towers[16] | 2013 | 2019 | 2 | 338 | 338 | 77 | 357 000 | Constructing |
| 19 | Northern Tower | 2005 | 2007 | 1 | 108 | 132[17] | 27 | 135 000 | |
| 20 | |||||||||
| 21 | Yury Dolgoruky Tower[18] | 2016 | 2018 | 2 | 60 | 249 073 | Project | ||
| 22 | |||||||||
| 23 | |||||||||
| 24 | |||||||||
| 25 | |||||||||
| 29-30 | |||||||||
| 31 |
Buildings
Central Core
One of the most difficult structures to build in the MIBC, the Central Core, is located on plots 6, 7 and 8. The Central Core consists of two main sections – the above-ground and underground.
The underground part includes three subway stations. One is opened as a part of Filyovskaya Line branch. The second opened in 2014 will be a part of Kalininsko-Solntsevskaya Line in the future. The third station will be opened in 2016 as part of the new line. The complex will also be connected to Vnukovo and Sheremetyevo airports via a high-speed transport system. Underground, parking is provided for up to 2750 vehicles, as well as central control rooms for maintenance, security, and other operations in the centre. The underground space also houses a shopping centre, which also functions as a lobby for the underground part of the complex, with walkways and passages for travel between other buildings in the MIBC. VIP parking will be available and is located on the western side of the Central Core.
The above-ground section is divided into three functional zones: a hotel on plot 8а, a retail-entertainment complex on plots 8b and 7, and a cinema/concert hall with a capacity of 6000 people on a plot 6.
- Total area: 450,000 m2 (4,843,760 sq ft)
- Total investment: $300 million
- Construction began: 2005
- Construction completed: 2015
Tower 2000

Tower 2000, a 30-story office building with four underground floors, is located on the South bank of the Moscow River. The tower is connected to the MIBC by the Bagration pedestrian bridge, which was the first completed structure of the MIBC, finished in 1999. It is located on the opposite side of the river from the main development. There is also underground parking, restaurants, and other entertainment and attractions in the tower. The tower is 104 meters high,[19] and the total floor area of the complex is 61,057 square meters. Construction began in 1996 and was completed in late 2001.[5]
- Height: 104 m (358 ft)
- Floor count: 34
- Total area: 61,057 m²
- Construction began: 1996
- Construction completed: 2001
Evolution Tower

The Evolution Tower is a skyscraper currently under construction on plot 2 and 3 as part of the MIBC in Moscow, Russia. Each floor will be twisted 3° in relation to the preceding one, totalling 135°. The foundation of the Evolution Tower was built by BAUER Technologii, the Russian branch of BAUER Spezialtiefbau GmbH.
Project architect Tony Kettle and Karen Forbes, Professor of Art at the University of Edinburgh, developed the design in detail, reflecting on the use of the spiral in earlier Russian architecture and proposing a dynamic composition which dramatically alters from different vantage points in the city. Its DNA related structure celebrates in a contemporary mode the inter-linking of individuals, generations and families.
Forming an important civic focus, on the key edge of the site which face towards Red Square it operates on both a personal level, and as a new expression of the city of Moscow. Its sensuous form is a critical element of the design addressing the quality of organic line, conceptual invention and a high level of technological engineering. The design recognises, indeed, celebrates the speed and energy of urban life in Moscow. It makes a statement of innovation amid the many historical landmarks.
- Architect: Tony Kettle
- Constructed by: Renaissance Construction
- Total area of a plot: 2.549 ha
- Total area: 200,000 m2 (2,152,782 sq ft)
- Height: 255 m (837 ft)
- Floor count: 54
- Construction began: 2011
- Construction completed: 2015
Imperia Tower
Imperia Tower is a 59-floor multipurpose complex located on plot 4 of the Moscow-City. The design of the tower was created by architects NBBJ. It consists of elliptical and hi-tech elements. Its location is on the first line of the MIBC, directly on the embankment.
The tower has an exit to the water and access to the city's main transportation routes. All of the tower's windows have panoramic views of the Moscow River, the Kremlin, the city center, the Sparrow Hills, Moscow University, Poklonnaya Gora and park areas in Western Moscow.
The tower space is in 3 parts:
- Apartments (premium class apartments and penthouses) – 45 000 sq.m.
- Hotel - 30 000 m2 (250 rooms)
- Business space - 76,700 sq.m. Additional space (lobbies, escalators, etc.) is more than 53 000 sq.m.
The territory of the tower also includes a part of the Moscow River embankment for a moorage, cafes, restaurants and infrastructure development.
The apartments are private residential apartments of 45 000 sq.m, on floors 40-60. Two upper floors are two-level penthouses. The separate entrance and elevators separate the apartments from the business space of the tower.
The hotel is on floors 33 to 41. With 250 rooms, it includes conference halls, restaurants, a fitness club, and a spa complex. Business space occupies the three levels from floors 2 to 31. Construction was completed in 2011.
- Investors: ZAO "Fleiner-City" (Pavel Fuks), "Valtania Holding Ltd" (Valentin Yumashev)
- Architect: NBBJ
- Leasing agent: GDO City Properties Ltd
- Total area: 287 723 m²
- Floor count: 59
- Construction began: 2006
- Construction completed: 2011
City of Capitals
The City of Capitals complex, symbolizing Moscow and St. Petersburg, is located on plot 9. The Moscow Tower was the first super-tall skyscraper in Europe.
More than half of the top floors are taken up to an entertainment complex, office suites, and large apartments. The Сity of Capitals consists of two towers – the 76-floor "Moscow Tower" and the 65-floor "St.-Petersburg Tower", reaching heights of 302 and 257 meters, respectively. Floors 17 and 18 of both towers are offices. The entire complex sits on a main lobby consisting of 6 underground floors and 4 aboveground floors of public space. The upper floors of the base structure will contain shops, a fitness centre, presentation halls, and restaurants.[20]
To create the concept for the offices in the City of Capitals, other business complexes and business centres from other parts of the world were studied.
The spatial structure of the complex, with steps of columns nine meters high, enables the organization of offices with open layouts from 500 up to 3,500 square meters. An entrance to the office section of the complex is situated near a quay, leading from underground parking to retail galleries.
- Height: 302 m (991 ft) and 257 m (843 ft)
- Total area: 288,680 m2 (3,107,326 sq ft)
- Parking capacity: 2000 cars
- Total investment: $450 million
- Construction began: 2005
- Construction completed: 2009
- Contractor:Ant Yapı
Naberezhnaya Tower

The "Naberezhnaya Tower" is a complex located on plot 10 of the Moscow-City. It includes three buildings with 17, 27 and 59 floors. In October 2004, the 17-story building was fully completed. In October 2005 the second, 27-story building was put into operation. Construction of the third skyscraper began in January 2005 and was completed in 2007. Three plazas, one for each building, are at the first level below ground and are connected by a central pier.
A first-class office complex, including one underground floor, which will be reserved for retail trade, will be located in the tower. The other underground floors will be used as parking space.
- Tower A: 85 metres, 17 floors tall, 39,718 m2 (427,521 sq ft). Completed in 2004.
- Tower B: 127 metres, 27 floors tall, 53,994 m2 (581,187 sq ft). Completed in 2005.
- Tower C: 268 meters, 59 floors tall, 160,200 m2 (1,724,378 sq ft). Completed in 2007.
- Total area of the site: 1,6 ha
- The contractor: Enka Insaat & Sanayi A.S.
- The design architect: RTKL & ENKA Architectural Office
- The structural engineers: Thornton-Tomasetti Engineers & ENKA Design Office
- Construction began: 2003
- Construction completed: 2007
IQ-quarter

IQ-quarter, located on plot 11 of the Moscow-City, will be the transfer point between different subway and light railway lines, as well as other public systems. There will also be offices, hotels, a clinic, and parking.
There will be a transfer station between the metro and a high-speed transport system, which is planned to extend from Moscow-City, eventually ending at the three local airports. The multilevel terminal will connect the underground zones of Moscow-City to the metro stations and to other municipal transportation, lighted by means of light wells, with retail space, living and office areas.
The complex will contain 106 office suites, three hotels with 342 rooms, a main hospital, points of retail trade, and parking for up to 1250 vehicles.
- The heights of the buildings: Tower 1: 85 m (279 ft); Tower 2: 141 m (463 ft); Tower 3: 177 m (581 ft)
- Number of floors in the towers: Tower 1 - 22; Tower 2 - 34; Tower 3 - 43
- Territory of a building site: 1,137 ha
- Territory of a site under construction of objects: 1,025 m
- Total area: 228,000 m2 (2,454,172 sq ft)
- Construction began: 2011
- Construction completed: 2015
Eurasia (Steel Peak)

Eurasia Tower or Steel Peak, located on plot 12 of the MIBC, is an office/recreational space with a total area of 207,542 square meters. It is situated on a three-tier podium which has a fitness centre, entertainment, restaurants, and shops. Other areas are distributed as follows: 106,231 square meters is reserved for office space, and residential apartments will occupy 21,185 square meters. On the bottom floor, there is a parking space for more than 1000 cars. The external design of the building is a combination of classical and modernist styles. On the outside of the building, there is a scenic elevator which is designed to allow the visitors to view the city from a great height.
- Height: 309 m (1,014 ft)
- Number of floors: 70
- Total area: 207,542 m2 (2,233,963 sq ft)
- Parking capacity: 1000
- Architect: Swanke Hayden Connell Architects
- Developer: Mos City Group
- Total investment: $250 million
- Construction began: 2007
- Construction completed: 2015
Federation Tower
- Tower A: 95 floors – 373 m (1,224 ft)
- Tower B: 63 floors – 242 m (794 ft)
The Federation Tower is located on plot 13 of the Moscow-City. Upon completion, this will be the tallest building in Europe, at the height of 373 meters. The structure represents a design of two tri-hedral towers with heights of 373 and 242 meters above the ground, located on a common base of 10 floors. A restaurant is planned in the towers, along with office suites and residential apartments divided by technical floors. In the base of the towers a full complex of retail and household services is planned. The underground part includes parking places, technical premises, and the walkway connecting the complex with the central part of a Business Center, northern departure and a complex 12 site.
The building is actively used as a sightseeing object and a high-rise structure for extreme sports lovers (base jumpers, climbers, etc.), as well as a site for shooting films and videos (TV shows, advertising, and movie production). In 2012, the Moscow-24 TV channel shot a movie about the business complex. Another film dedicated to the skyscraper was made by the US TV Discovery Channel in 2009.
- The contractor: Renaissance Construction
- Architect: Prof. P. Schweger and S. Tchoban (Germany)
- Total investment: $1.2 billion
- Total area: 439,154 m2 (4,727,014 sq ft)
- Total area of a plot: 1,07 ha
- Height: 373 m (1,224 ft)
- Construction began: 2004
- Construction completed: 2015
Mercury City Tower

The Mercury City Tower is a multipurpose building with housing, offices and shops.[21] The tower is located on plot 14 of the MIBC. The structure's height is 339 meters [22] above ground, with five underground floors. Architect Frank Williams says that it is the first environmentally friendly building in Russia, and it is designed to collect melting snow water, as well as provide 70% of the workplaces with access to daylight.[22][23] In May 2011, the developer announced that Mercury City Tower had reached 230 m (750 ft), with over half of the external walls covered in copper coloured cladding. The construction exceeded the 301.6 m (990 ft) of City of Capitals tower, also in Moscow, on 17 January 2012. On 25 July 2012, the 75th level was under construction. The tower was initially expected to be completed in late 2012.[24] According to its development company, the building was topped out at 339 m (1,112 ft) on 1 November 2012.
- Height: 339 m (1,112 ft)
- Floor count: 75
- Total area: 158,000 m2 (1,700,698 sq ft)
- Total investment: $1 billion
- Architect: M.M. Posohin, Frank Williams (USA), G.L. Sirota
- Construction began: 2009
- Construction completed: 2013
OKO

OKO - a complex of buildings - is located on plot 16 of the Moscow-City. The site is divided into 16a and 16b.
On the section 16a two high-rise buildings are being built, one of which is 49 stories and 245 meters tall (North Tower) and the other one is 85 stories with and 354 meters tall (South Tower). Each building also have an underground floor. The buildings house both residential and office space, occupying roughly the same area: for offices rid 122,493 m², residential apartments - 122,507 m².
On the section 16b a building built consisting of a three star hotel, which house 330 rooms, and a parking lot for 3740 cars. The hotel's height 79 meters with 22 floors. The parking lot have 14 floors, of which 5 are underground; the other 9 have a total height of 44 meters.
- Floor count: North Tower - 49; South Tower - 85
- Height: North Tower - 245; South Tower - 352
- Total area: 249 600 m²
- Total investment: $1-1.2 billion
- Parking capacity: 1135
- The design architect: «Skidmore, Owings & Merrill LLP»
- Construction began: 2011
- Construction completed: 2015
Northern Tower

The Northern Tower — one of the smaller buildings of the MIBC, located on plot 19. The Northern Tower was built by Strabag SE. The construction started in 2005 and finished in 2007. The height of the building is 105 m, floor area is 135 000 m². In the tower there are office suites, restaurants, cafe, a fitness centre and a parking space.
- Floor count: 27
- Total area: 135,000 m2 (1,453,128 sq ft)
- Height: 105 m (344 ft)
- Construction began: 2005
- Construction completed: 2007
Transport
Major thoroughfares through Moscow-City are the Third Ring and Kutuzovsky Prospekt.
Three metro stations were initially planned for the #4 Filyovskaya Line. The station "Delovoy Tsentr" (Business Center) opened in 2005, and was later renamed "Vystavochnaya" ("Exhibition") in 2009. The branch extended to the "Mezhdunarodnaya" ("International ") station in 2006, and all works on third station, Dorogomilovskaya (between Kiyevskaya and Delovoi Tsentr), has been canceled and the planned station has been relocated for another metro line.
In 2014, a new metro station Delovoy Tsentr adjacent to station Vystavochnaya opened which provides shuttle service to station Park Pobedy for #3 Arbatsko-Pokrovskaya Line. This particular short service is operated under the name of #8 Kalininsko-Solntsevskaya Line albeit not being directly connected to the original section in the eastern part of the capital but it is planned to extend on both ends: the east end of this section will connect to the eastern section of the line, forming a unified line; the west end will extend to the Solntsevo District which has yet been covered by the metro system.
|
See also
References
- ↑ "Official website". Eng.citynext.ru. Retrieved 25 September 2010.
- ↑ "Construction World: Integrated Body For Urban Design Policy And Development Of Moscow". Stroi.ru. Retrieved 25 September 2010.
- 1 2 3 "ОАО "СИТИ" – Москва-Сити – Московский международный деловой центр". Citynext.ru. 14 September 2010. Retrieved 25 September 2010.
- ↑ http://www.vedomosti.ru/newspaper/articles/2014/03/18/25-let-spustya
- 1 2 "Moscow International Business Centre (MIBC), Moscow". Design Build Network. Retrieved 25 September 2010.
- ↑ http://tekstilschiky.mos.ru/presscenter/news/detail/3324736.html
- ↑ Tower completed in 2011
- ↑ Сonstruction of the concert hall
- ↑ Height of Moscow Tower
- ↑ Height of C block
- ↑ Height of Tower 3
- ↑ Height of Vostok Tower
- ↑ Completed part of complex: The Zapad Tower in use, The Vostok Tower is glazed
- ↑ Grand Tower
- ↑ Height of South tower
- ↑ Neva Towers
- ↑ Antenna
- ↑ http://dolgoruky.ru/
- ↑ Emporis GmbH. "Bashnya 2000, Moscow, Russia". Emporis.com. Retrieved 25 September 2010.
- ↑ "Capital City : New standards of comfortable living". Capitalcity.ru. Retrieved 25 September 2010.
- ↑ "Mercury City Tower, Moscow". SkyscraperPage.com. Retrieved 25 September 2010.
- 1 2 Emporis GmbH. "Mercury City Tower, Moscow, Russia". Emporis.com. Retrieved 25 September 2010.
- ↑ Spliteye Multimedia LLC at http://www.spliteye.com/. "Mercury City Tower, Frank Williams And Partners Architects, LLP : Portfolio International". Archfwa.com. Retrieved 25 September 2010.
- ↑ "Russia: Moscow Mercury City Tower (332m) Photos & Renderings". Eliterics. 2011. Retrieved 13 July 2012.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: |
Coordinates: 55°44′48″N 37°32′13″E / 55.74667°N 37.53694°E






