Mono- and diglycerides of fatty acids
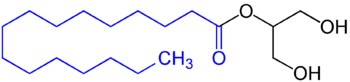

Mono- and diglycerides of fatty acids (E471) refers to a food additive composed of diglycerides and monoglycerides which is used as an emulsifier. This mixture is also sometimes referred to as partial glycerides.
Synthesis
Monoglycerides and diglycerides are both naturally present in various seed oils,[1] however their concentration is usually low and industrial production is primarily achieved by a glycerolysis reaction between triglycerides (fats/oils) and glycerol.[2] The raw materials of this may be either vegetable or animal fats and oils.
Concern for vegetarians and vegans
E471 is mainly produced from vegetable oils, although animal fats are sometimes used and cannot be completely excluded as being present in the product.[3] The fatty acids from each source are chemically identical.[4] The Vegan Society, which discourages eating animal-based foods, flags E471 as a "thing to look out for" that "can be animal OR non-animal based".[5]
See also
References
- ↑ Flickinger, Brent D.; Matsuo, Noboru (February 2003). "Nutritional characteristics of DAG oil". Lipids. 38 (2): 129–132. doi:10.1007/s11745-003-1042-8.
- ↑ Sonntag, Norman O. V. (1982). "Glycerolysis of fats and methyl esters — Status, review and critique". Journal of the American Oil Chemists Society. 59 (10): 795A–802A. doi:10.1007/BF02634442. ISSN 0003-021X.
- ↑ Clarke, Chris (2012). The Science of Ice Cream. Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 55. ISBN 9781849731270.
Mono-/diglycerides are made by partially hydrolysing vegetable fats, such as soybean oil, and palm oil. (Animal-fat-based emulsifiers are not commonly used because they are not suitable for vegetarian and certain religious diets).
- ↑ "Which E-numbers and additives are from animal origin ?". Food-Info.net. Netherlands: Wageningen University. Retrieved 4 September 2015.
Chemically the fatty acids from animal or plant origin are identical. Therefore the origin is of no importance for the function in the food. Producers thus normally choose the cheapest oils to make these fats. This is generally some vegetable oil. However, animal fats can not be excluded.
- ↑ "Vegan Catering For All" (PDF). The Vegan Society. p. 12. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 September 2015. Retrieved 4 September 2015.