Mexico City megalopolis
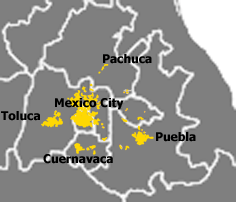
The Mexico City megalopolis, also known as the Megalopolis of Central Mexico (Spanish: Corona regional del centro de México), is a megalopolis containing Greater Mexico City and surrounding metropolitan areas.[1]
In 1996, the Programa General de Desarollo Urbano del Distrito Federal first proposed this concept to refer to the Mexico City megalopolis, or "Megalopolis of central Mexico", which was later expanded by PROAIRE, a metropolitan commission on the environment.[2]
A megalopolis, is known in Spanish as a corona regional de ciudades ("regional ring of cities"). The Megalopolis of central Mexico was defined to be integrated by the metropolitan areas of Mexico City, Puebla, Cuernavaca, Toluca and Pachuca, which may also conform complex subregional rings themselves (i.e. Greater Puebla conforming a regional ring with Atlixco, San Martín Texmelucan, Tlaxcala and Apizaco).
The megalopolis consists of 173 municipalities (91 of the state of Mexico, 29 of the state of Puebla, 37 of the state of Tlaxcala, 16 of Morelos and 16 of Hidalgo) and the 16 boroughs of the Federal District,[2] with an approximate total population of almost 27 million people.
Some sources include Greater Querétaro city, with a population of over a million, in a Mexico City megalopolis; the city is also part of the fast-growing macroregion of Bajío.[3]