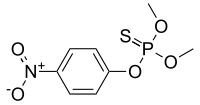
Parathion methyl
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
O,O-Dimethyl-O-p-nitrophenylphosphorothioate | |
| Other names
Azophos, Methyl parathion, O,O-Dimethyl O-4-nitrophenyl phosphorothioate, O,O-Dimethyl-p-nitrophenylthionophosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 298-00-0 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 3987 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.501 |
| EC Number | 015-035-00-7 |
| PubChem | 4130 |
| RTECS number | TG0175000 |
| UN number | 2783 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| (CH3O)2P(S)OC6H4NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 263.2 g/mol |
| Appearance | White to tan, crystalline solid or powder[1] |
| Odor | pungent, garlic-like[1] |
| Density | 1.36 g/mL (20°C)[1] |
| Melting point | 37 °C; 99 °F; 310 K[1] |
| Boiling point | 143 °C; 289 °F; 416 K[1] |
| 0.006% (25°C)[1] | |
| Vapor pressure | 0.00001 mmHg (20°C)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | reactive with strong oxidizers and water[1] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) |
67 mg/kg (rat, dermal)[2] 10-25 mg/kg (male rat, oral)[3] 24 mg/kg (female rat, oral)[3] |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
| PEL (Permissible) |
none[1] |
| REL (Recommended) |
TWA 0.2 mg/m3 [skin][1] |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) |
N.D.[1] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Parathion methyl is an organophosphate pesticide and insecticide, possessing a organothiophosphate group. It is structurally very similar to parathion-ethyl.
Applications
Parathion methyl is used as an insecticide on crops including cotton.[2]
Safety
People can be exposed to parathion methyl in the workplace by breathing it in, getting it on their skin, swallowing it, or getting it in their eyes. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has not set a legal limit (permissible exposure limit) for parathion methyl exposure in the workplace. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has set a recommended exposure limit (REL) of 0.2 mg/m3 over an 8-hour workday.[1]
Since it is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, symptoms of exposure to parathion methyl include irritated eyes and skin, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, salivation, feeling weak and tired, headache, runny nose, tightness in the chest, blurry vision, pupil constriction, irregular heartbeat, muscle twitches (fasciculation), and difficulty breathing.[1]
Parathion methyl is not classified as a carcinogen by any global agency.[2]