Mehmed IV
| Mehmed IV محمد رابع | |
|---|---|
|
Caliph of Islam Amir al-Mu'minin Sultan of the Ottoman Empire Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques | |
.jpg) | |
| 19th Ottoman Sultan (Emperor) | |
| Reign | August 8, 1648 – November 8, 1687 |
| Predecessor | Ibrahim |
| Successor | Suleiman II |
| Regents |
See list
|
| Born |
2 January 1642 Topkapı Palace, Constantinople, Ottoman Empire |
| Died |
6 January 1693 (aged 51) Edirne, Ottoman Empire |
| Consort | Gülnûş Sultan (Legal wife) |
| Dynasty | House of Osman |
| Father | Ibrahim |
| Mother | Turhan Hatice Sultan |
| Religion | Sunni Islam |
| Tughra |
|
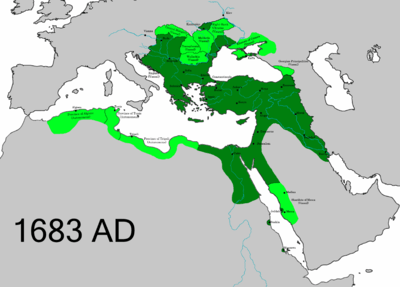
Mehmed IV (Ottoman Turkish: محمد رابع Meḥmed-i rābiʿ; Modern Turkish: IV. Mehmet; also known as Avcı Mehmed, Mehmed the Hunter; January 2, 1642 – January 6, 1693) was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1648 to 1687. He came to the throne at the age of seven after his father was overthrown in a coup. Mehmed went on to become the second longest reigning sultan in Ottoman history.[1] While the first and last years of his reign were characterized by military defeat and political instability, during his middle years he oversaw the revival of the empire's fortunes associated with the Köprülü era. Mehmed IV was known by contemporaries as a particularly pious ruler, and was referred to as gazi, or "holy warrior" for his role in the many conquests carried out during his long reign.[2] Under his reign the empire reached the height of its territorial expansion in Europe. From a young age he developed a keen interest in hunting, for which he is known in Turkish as avcı ("the Hunter").[1] In 1687 Mehmed was overthrown by soldiers disenchanted by the course of the ongoing War of the Holy League. He subsequently retired to Edirne, where he resided until his natural death in 1693.[1]
Biography
Early life

Born at Topkapı Palace, Constantinople, in 1642, he was the son of Sultan Ibrahim (r. 1640–48) by Valide Sultan Turhan Hatice, a Ruthenian (Ukrainian) concubine,[3] and the grandson of Kösem Sultan of Greek origin.[4] Soon after his birth, his father and mother quarreled, and Ibrahim was so enraged that he tore Mehmed from his mother's arms and flung the infant into a cistern. Fortunately, Mehmed was rescued by the harem servants. However, this left Mehmed with a lifelong scar on his head.[5]
Reign
Mehmed ascended to the throne in 1648 at the age of seven. His ascension took place during a very volatile time for the Ottoman Dynasty; the empire faced palace intrigues as well as uprisings in Anatolia, the defeat of the Ottoman navy by the Venetians outside the Dardanelles, and food shortages leading to riots in Constantinople. It was under these circumstances that Mehmed's mother granted Köprülü Mehmed Pasha full executive powers as Grand Vizier. Köprülü took office on September 14, 1656.[6]
Accomplishments

Sultan Mehmed IV is known as Avcı, "the Hunter", as this outdoor exercise took up much of his time.
His reign is notable for a revival of Ottoman fortunes led by the Grand Vizier Köprülü Mehmed and his son Fazıl Ahmed. They regained the Aegean islands from Venice, and Crete, during the Cretan War (1645–1669). They also fought successful campaigns against Transylvania (1660) and Poland (1670–1674). When Mehmed IV accepted the vassalage of Petro Doroshenko, Ottoman rule extended into Podolia and Right-bank Ukraine. His next vizier, Köprülü Mehmed's adopted son Merzifonlu Kara Mustafa, led campaigns against Russia, conquering Chyhyryn in 1678. He next supported the 1683 Hungarian uprising of Imre Thököly against Austrian rule, marching a vast army through Hungary and besieged Vienna. At the Battle of Vienna on the Kahlenberg Heights, the Ottomans suffered a catastrophic rout by Polish-Lithuanian forces famously led by King John III Sobieski (1674–96), and his allies, notably the Imperial army.
Great Turkish War

But on September 12, 1683, the Austrians and their Polish allies under King Jan Sobieski took advantage of dissent within the Turkish military command and poor disposition of his troops, winning the Battle of Vienna with a devastating flank attack led by Sobieski's Polish cavalry. The Turks retreated into Hungary, however this was only the beginning of the Great Turkish War as the armies of the Holy League began their long, but successful campaign to push back the Ottomans to the Balkans.
Later life and death
After the second Battle of Mohács (1687), the Ottoman Empire fell into deep crisis. There was a mutiny among the Ottoman troops. The commander and Grand Vizier Sarı Süleyman Pasha became frightened that he would be killed by his own troops and fled from his command, first to Belgrade and then to Istanbul. When the news of the defeat and the mutiny arrived in Istanbul in early September, Abaza Siyavuş Pasha was appointed as the commander and soon as the Grand Vizier. However, before he could take over his command, the whole Ottoman Army had disintegrated and the Ottoman household troops (Janissaries and Sipahis) started to return to their base in Istanbul under their own lower-rank officers. Sarı Suleyman Pasa was executed. Sultan Mehmed IV appointed the commander of Istanbul Straits Köprülü Fazıl Mustafa Pasha as the Grand Vizier's regent in Istanbul. He made consultations with the leaders of the army that existed and the other leading Ottoman statesmen. After these, on 8 November 1687 it was decided to depose Sultan Mehmed IV and to enthrone his brother Suleiman II as the new Sultan. Mehmed was deposed by the combined forces of Yeğen Osman and the janissaries. Mehmed was then imprisoned in Topkapı Palace. However, he was permitted to leave the Palace from time to time, as he died in Edirne Palace in 1693. He was buried in Turhan Hadice Sultan's tomb, near his mother's mosque in Constantinople. Just before he died in 1691, a plot was discovered in which the senior clerics of the empire planned to reinstate Mehmed on the throne in response to the ill health of his successor, Suleiman II.
His favourite harem girl was Emetullah Rabia Gülnûş Sultan, who was a slave girl and later his wife, was taken prisoner at Rethymnon (Turkish Resmo) in the island of Crete. Their two sons, Mustafa II and Ahmed III, became Ottoman Sultans during (1695–1703) and (1703–1730) respectively.
Marriages and Issue[7]
Consorts
- Emetullah Rabia Gülnuş Sultan, originally named Eugenia Voria and of ethnic Greek as the daughter of a Greek Orthodox priest or a member of the Venetian Verzzizi family.
- Afifa Haseki (d. 1688).
- Rabia Haseki.
- Kaniya Haseki.
- Siyavush Haseki.
- Gul-Beyaz Iqbal.
- Rukiya Bash-odalik.
- Jihan-Shah Khanum, previously a Gozde.
- Durriya Gozde.
- Navruz Gozde.
Sons
- Mustafa II (6 February 1664 – 29/30 December 1703) - son of Gülnuş Sultan.
- Ahmed III (30/31 December 1673 – 1 July 1736) - son of Gülnuş Sultan.
- Şehzade Bayazid (31 December 1678 – January 1679).
- Şehzade Ibrahim (died young).
- Şehzade Sulaiman (13 February 1681 – died young).
Daughters
- Ummi Sultan.
- Gavher Sultan.
- Khadija Sultan (1662 – 9 May 1743) - daughter of Gülnuş Sultan. Married:
- firstly 9th July 1675, Admiral H.E. Damad Mustafa Pasha.
- secondly 1690, H.H. Damad Murali Enista Hasan Pasha, Grand Vizier.
- Ummatu'llah Sultan [Ummi Kucuk] (1670 – 13 December 1720). Married:
- firstly 9 July 1675, H.H. Damad Kara Mustafa Pasha Maktul, Grand Vizier.
- secondly 13 January 1694, H.E. Damad Xerxes Kucuk Osman Pasha, 5th Vizier 1698, 4th Vizier.
- Fatma Sultan (1681 – 6 December 1700) - daughter of Gülnuş Sultan. Married:
- firstly 20 January 1696, H.E. Damad Xerxes Ibrahim Pasha Tirnakji.
- secondly 1697, Damad Topal Yusuf Pasha, Vizir 1697, and Amir-i-Haj at Damascus 1714. .
- Daughter, married after 1687 Damad Kasim Mustafa Pasha, the Pasha of Adrianople.
- Daughter (with Gul-Beyaz).
See also
Notes
- 1 2 3 Börekçi, Günhan (2009). "Mehmed IV". In Ágoston, Gábor; Bruce Masters. Encyclopedia of the Ottoman Empire. p. 370-1.
- ↑ Baer, Marc David (2008). Honored by the Glory of Islam: Conversion and Conquest in Ottoman Europe. Oxford University Press. p. 165. ISBN 978-0-19-979783-7.
- ↑ Natalia Yakovenko."Essays on History on Ukraine. From the Earliest Times until the End of the 18th Century". 1997.
- ↑ Finkel, Caroline (2005). Osman's Dream: The Story of the Ottoman Empire, 1300-1923. New York: Basic Books. p. 197. ISBN 978-0-465-02396-7.
- ↑ John Freely - Inside the Seraglio published 1999, Chapter 9: Three Mad Sultans
- ↑ Streusand, Donald E., Islamic Gunpowder Empires: Ottomans, Safavids, and Mughals (Boulder, Colo.: Westview Press, 2011), p. 57.
- ↑ The Imperial House of Osman: Genealogy [retrieved 7 March 2016].
External links
![]() Media related to Mehmed IV at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Mehmed IV at Wikimedia Commons
| Mehmed IV Born: January 2, 1642 Died: January 6, 1693[aged 51] | ||
| Regnal titles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Ibrahim |
Sultan of the Ottoman Empire August 8, 1648 – November 8, 1687 with Kösem Sultan (1648–1651) Turhan Hatice Sultan (1651–1683) |
Succeeded by Suleiman II |
| Sunni Islam titles | ||
| Preceded by Ibrahim |
Caliph of Islam Ottoman Dynasty August 8, 1648 – November 8, 1687 |
Succeeded by Suleiman II |